Summary.
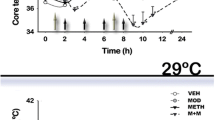
The present study aimed to investigate the protective effects of melatonin, ethanol and temperature changes on methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity in both sexes of mice. Mice exhibited a similar degree of striatal dopamine depletion when methamphetamine was administered during the light and dark cycles. Moreover, 10 mg/kg, but not 5 mg/kg, of methamphetamine, significantly increased body temperature even though dopamine depletions were observed following both doses. Melatonin (80 mg/kg) dissolved in 30% (v/v) ethanol and 30% ethanol alone exerted a moderate to full protection against methamphetamine-induced dopamine depletions in both sexes of mice, whereas the same dose of melatonin in 3% ethanol exerted no protective effect. Furthermore, ethanol attenuated methamphetamine-induced dopamine depletions in a dose-dependent manner with the exception of high efficacy of ethanol at low doses. Finally, the protective effects of ethanol were not blocked by bicuculline. Together, we conclude that ethanol may protect mice against methamphetamine-induced dopamine depletion probably via non-GABAA receptor activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received February 20, 2001; accepted April 8, 2001
Acknowledgements The authors thank Dr. Liao P-C. and Dr. Chuang J-I. for technical assistance. This study was supported partially by a Project grant (NSC89-2413-006-017) funded by National Science Council in Taiwan and a Research grant (89CYCY05) from NCKUCM.
Authors' address: Dr. L. Yu, Institute of Behavioral Medicine, National Cheng Kung University College of Medicine, 1 University Rd., Tainan 70101, Taiwan, e-mail: lungyu@mail.ncku.edu.tw
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L., Cherng, CF. & Chen, C. Melatonin in concentrated ethanol and ethanol alone attenuate methamphetamine-induced dopamine depletions in C57BL/6J mice. J Neural Transm 109, 1477–1490 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020200096
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020200096