Summary.
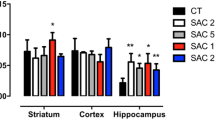
Sodium azide (20 mg/kg sc), given for a maximum of 3 days to rats, significantly decreased the α-tocopherol concentrations in the cortex on day 2 and in the striatum on day 3. In these brain regions the oxidized glutathione values showed 30 to 36% (statistically not significant) elevation on day 3. Reduced glutathione levels were not altered. The observations suggest an important role for α-tocopherol in the defense against azide induced free radicals probably including NO and lipid peroxide radicals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received February 8, 2000; accepted October 17, 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vécsei, L., Tajti, J., Klivényi, P. et al. Sodium azide treatment decreases striatal and cortical concentrations of α-tocopherol in rats. J Neural Transm 108, 273–278 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020170072
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020170072