Abstract
Background
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the globus pallidus internus (GPi) has become an accepted treatment for severe cervical dystonia (CD). Assessment of therapeutic efficacy of DBS mostly focused on head position at rest but hardly on limitations of head and neck mobility, which represent a functionally important impairment in CD.
Objective
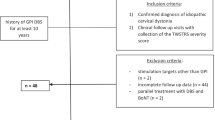
We aimed to determine prospectively head and neck range of motion (ROM) preoperatively and during chronic bilateral GPi DBS in a series of 11 patients with idiopathic CD or segmental dystonia with prominent CD using a computerized motion analysis.
Methods
Maximum horizontal rotation of the head in the transverse plane and lateral inclination in the frontal plane were measured preoperatively and at a median of 7 months of chronic GPi DBS, using an ultrasound-based three-dimensional measuring system combined with surface electromyography of cervical muscles.
Results
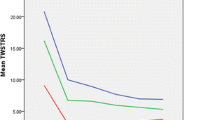
Horizontal rotation of the head increased from 78.8° ± 31.5° (mean ± SD) preoperatively to 100.7° ± 24.7° with GPi DBS (p < 0.01), thereby improvement of head rotation to the anti-dystonic side (+ 14,2° ± 12,2°) was greater than to the pro-dystonic side (+ 7,8° ± 9,2°; p < 0.05). Movement-related agonistic-antagonistic EMG modulation during head rotation was enhanced with GPi DBS in both sternocleidomastoid (modulation index (MI) 35.8% ± 26.7% preoperatively vs. 67.3% ± 16.9% with GPi DBS, p < 0.01), and splenius capitis muscles (MI 1.9% ± 24.5% preoperatively vs. 44.8% ± 11.6% with GPi DBS, p < 0.01).
Conclusion
Chronic bilateral GPi DBS significantly improves head ROM in CD, likely due to enhanced agonist–antagonist EMG activity with reduced co-contraction. Computerized motion analysis provides an objective measurement to assess the improvement of head and neck mobility in CD.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material (data transparency)
All original data are available from the authors upon request.
Code availability (software application or custom code)
Not applicable.
References
Alam M, Schwabe K, Lütjens G, Capelle HH, Manu M, von Wrangel C, Müller-Vahl K, Schrader C, Scheinichen D, Blahak C, Heissler HE, Krauss JK (2015) Comparative characterization of single cell activity in the globus pallidus internus of patients with dystonia or Tourette syndrome. J Neural Transm 122:687–699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1277-0
Albanese A, Bhatia K, Bressman SB, Delong MR, Fahn S, Fung VS, Hallett M, Jankovic J, Jinnah HA, Klein C, Lang AE, Mink JW, Teller JK (2013) Phenomenology and classification of dystonia: a consensus update. Mov Disord 28:863–873. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25475
Beck S, Richardson SP, Shamim EA, Dang N, Schubert M, Hallett M (2008) Short intracortical and surround inhibition are selectively reduced during movement initiation in focal hand dystonia. J Neurosci 28:10363–10369. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3564-08.2008
Blahak C, Wöhrle JC, Capelle HH, Bäzner H, Grips E, Weigel R, Kekelia K, Krauss JK (2008) Health-related quality of life in segmental dystonia is improved by bilateral pallidal stimulation. J Neurol 255:178–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-008-0614-3
Boccagni C, Carpaneto J, Micera S, Bagnato S, Galardi G (2008) Motion analysis in cervical dystonia. Neurol Sci 29:375–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-008-1033-z
Camfield L, Ben-Shlomo Y, Warner T, ESDE Collaborative Group (2002) Impact of cervical dystonia on quality of life. Mov Disord 17:838–841. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.10127
Carbon M, Su S, Dhawan V, Raymond D, Bressman S, Eidelberg D (2004) Regional metabolism in primary torsion dystonia: effects of penetrance and genotype. Neurology 62:1384–1390. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.WNL.0000120541.97467.FE
Chen J, Solinger AB, Poncet JF, Lantz CA (1999) Meta-analysis of normative cervical motion. Spine 15:1571–1578. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-199908010-00011
Consky ES, Lang AE (1994) Clinical assessments of patients with cervical dystonia. In: Jankovic J, Hallett M (eds) Therapy with botulinum toxin. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 211–237
Currá A, Berardelli A, Agostino R, Giovannelli M, Koch G, Manfredi M (2000) Movement cueing and motor execution in patients with dystonia: a kinematic study. Mov Disord 15:103–112. https://doi.org/10.1002/1531-8257(200001)15:1%3c103::aid-mds1016%3e3.0.co;2-3
Delagi EF, Perotto A, Iazetti J, Morrison D (1975) Anatomic guide for the electromyographer. Charles C. Thomas, Springfield
Erro R, Rocchi L, Antelmi E, Liguori R, Tinazzi M, Berardelli A, Rothwell J, Bhatia KP (2018) High frequency somatosensory stimulation in dystonia: evidence for defective inhibitory plasticity. Mov Disord 33:1902–1909. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27470
Fahn S, Bressman SB, Marsden CD (1998) Classification of dystonia. Adv Neurol 78:1–10
Gregori B, Agostino R, Bologna M, Dinapoli L, Colosimo C, Accornero N, Berardelli A (2008) Fast voluntary neck movements in patients with cervical dystonia: a kinematic study before and after therapy with botulinum toxin type A. Clin Neurophysiol 119:273–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2007.10.007
Grips E, Blahak C, Capelle HH, Bäzner H, Weigel R, Sedlaczek O, Krauss JK, Wöhrle JC (2007) Patterns of reoccurrence of segmental dystonia after discontinuation of deep brain stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:318–320. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2006.089409
Hallett M (2011) Neurophysiology of dystonia: the role of inhibition. Neurobiol Dis 42:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2010.08.025
Hermens HJ, Freriks B, Disselhorst-Klug C, Rau G (2000) Development of recommendations for SEMG sensors and sensor placement procedures. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 10:361–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1050-6411(00)00027-4
Huh R, Chung M (2019) Range of voluntary neck motility predicts outcome of pallidal DBS for cervical dystonia. Acta Neurochir 161:2491–2498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-04076-z
Kaji R, Ikeda A, Ikeda T, Kubori T, Mezaki T, Kohara N, Kanda M, Nagamine T, Honda M, Rothwell JC, Shibasaki H, Kimura J (1995) Physiological study of cervical dystonia. Task-specific abnormality incontingent negative variation. Brain 118:511–522. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/118.2.511
Kassavetis P, Sadnicka A, Saifee TA, Pareés I, Kojovic M, Bhatia KP, Rothwell JC, Edwards MJ (2018) Reappraising the role of motor surround inhibition in dystonia. J Neurol Sci 390:178–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2018.04.015
Kiss ZHT, Doig-Beyaert K, Eliasziw M, Tsui J, Haffenden A, Suchowersky O (2007) The Canadian Multicentre study of deep brain stimulation for cervical dystonia. Brain 130:2879–2886. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awm229
Krauss JK, Pohle T, Weber S, Ozdoba C, Burgunder JM (1999) Bilateral stimulation of globus pallidus internus for treatment of cervical dystonia. Lancet 354:837–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(99)80022-1
Krauss JK, Yianni J, Loher TJ, Aziz TZ (2004) Deep brain stimulation for dystonia. J Clin Neurophysiol 21:18–30. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004691-200401000-00004
Kroneberg D, Plettig P, Schneider GH, Kühn AA (2018) Motor cortical plasticity relates to symptom severity and clinical benefit from deep brain stimulation in cervical dystonia. Neuromodulation 21:735–740. https://doi.org/10.1111/ner.12690
Kuhlman KA (1993) Cervical range of motion in the elderly. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 74:1071–1079. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9993(93)90064-H
Kupsch A, Benecke R, Müller J, Trottenberg T, Schneider GH, Poewe W, Eisner W, Wolters A, Müller JU, Deuschl G, Pinsker MO, Skogseid IM, Roeste GK, Vollmer-Haase J, Brentrup A, Krause M, Tronnier V, Schnitzler A, Voges J, Nikkhah G, Vesper J, Naumann M, Volkmann J (2006) Pallidal deep-brain stimulation in primary generalized or segmental dystonia. N Engl J Med 355:1978–1990. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa063618
Loher TJ, Bärlocher CB, Krauss JK (2006) Dystonic movement disorders and spinal degenerative disease. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 84:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1159/000092681
Malmstroem EM, Karlberg M, Melander A, Magnusson M (2003) Zebris versus myrin: a comparative study between a three-dimensional ultrasound movement analysis and an inclinometer/compass method. Spine 28:E433-440. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.BRS.0000090840.45802.D4
Martikainen KK, Luukkaala TH, Marttila RJ (2010) Working capacity and cervical dystonia. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 16:215–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2009.07.006
Moro E, LeReun C, Krauss JK, Albanese A, Lin JP, Walleser Autiero S, Brionne TC, Vidailhet M (2017) Efficacy of pallidal stimulation in isolated dystonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Neurol 24:552–560. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13255
Ni Z, Kim SJ, Phielipp N, Ghosh S, Udupa K, Gunraj CA, Saha U, Hodaie M, Kalia SK, Lozano AM, Lee DJ, Moro E, Fasano A, Hallett M, Lang AE, Chen R (2018) Pallidal deep brain stimulation modulates cortical excitability and plasticity. Ann Neurol 83:352–362. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25156
Poewe W, Burbaud P, Castelnovo G, Jost WH, Ceballos-Baumann AO, Banach M, Potulska-Chromik A, Ferreira JJ, Bihari K, Ehler E, Bares M, Dzyak LA, Belova AN, Pham E, Liu WJ, Picaut P (2016) Efficacy and safety of abobotulinumtoxin A liquid formulation in cervical dystonia: A randomized-controlled trial. Mov Disord 31:1649–1657. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26760
Prodoehl J, MacKinnon CD, Comella CL, Corcos DM (2006) Rate of force production and relaxation is impaired in patients with focal hand dystonia. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 12:363–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2006.01.008
Quartarone A, Hallett M (2013) Emerging concepts in the physiological basis of dystonia. Mov Disord 28:958–967. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25532
Rothwell JC, Obeso JA, Day BL, Marsden CD (1983) Pathophysiology of dystonias. Adv Neurol 39:851–863
Ruge D, Cif L, Limousin P, Gonzalez V, Vasques X, Hariz MI, Coubes P, Rothwell JC (2011a) Shaping reversibility? Long-term deep brain stimulation in dystonia: the relationship between effects on electrophysiologyandclinical symptoms. Brain 134:2106–2115. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr122
Ruge D, Tisch S, Hariz MI, Zrinzo L, Bhatia KP, Quinn NP, Jahanshahi M, Limousin P, Rothwell JC (2011b) Deep brain stimulation effects in dystonia: time course of electrophysiological changes in early treatment. Mov Disord 26:1913–1921. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23731
Schrader C, Capelle HH, Kinfe TM, Blahak C, Bäzner H, Lütjens G, Dressler D, Krauss JK (2011) GPi-DBS may induce a hypokinetic gait disorder with freezing of gait in patients with dystonia. Neurology 77:483–488. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e318227b19e
Sedov A, Usova S, Semenova U, Gamaleya A, Tomskiy A, Crawford JD, Corneil B, Jinnah HA, Shaikh AG (2019) The role of pallidum in the neural integrator model of cervical dystonia. Neurobiol Dis 125:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2019.01.011
Sedov A, Usova S, Semenova U, Gamaleya A, Tomskiy A, Beylergil SB, Jinnah HA, Shaikh AG (2020) Pallidal activity in cervical dystonia with and without head tremor. Cerebellum 19:409–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-020-01119-5
Shaikh AG, Wong A, Zee DS, Jinnah HA (2015) Why are voluntary head movements in cervical dystonia slow? Parkinsonism Relat Disord 21:561–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.03.005
Skogseid IM, Malt UF, Røislien J, Kerty E (2007) Determinants and status of quality of life after long-term botulinum toxin therapy for cervical dystonia. Eur J Neurol 14:1129–1137. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2007.01922.x
Skogseid IM, Ramm-Pettersen J, Volkmann J, Kerty E, Dietrichs E, Røste GK (2012) Good long-term efficacy of pallidal stimulation in cervical dystonia: a prospective, observer-blinded study. Eur J Neurol 19:610–615. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03591.x
Tisch S, Limousin P, Rothwell JC, Asselman P, Zrinzo L, Jahanshahi M, Bhatia KP, Hariz MI (2006) Changes in forearm reciprocal inhibition following pallidal stimulation for dystonia. Neurology 66:1091–1093. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000204649.36458.8f
Tsuboi T, Wong JK, Almeida L, Hess CW, Wagle Shukla A, Foote KD, Okun MS, Ramirez-Zamora A (2020a) A pooled meta-analysis of GPi and STN deep brain stimulation outcomes for cervical dystonia. J Neurol 267:1278–1290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-020-09703-9
Tsuboi T, Wong JK, Okun MS, Ramirez-Zamora A (2020b) Quality of life outcomes after deep brain stimulation in dystonia: a systematic review. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 70:82–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2019.11.016
Volkmann J, Mueller J, Deuschl G, Kühn AA, Krauss JK, Poewe W, Timmermann L, Falk D, Kupsch A, Kivi A, Schneider GH, Schnitzler A, Südmeyer M, Voges J, Wolters A, Wittstock M, Müller JU, Hering S, Eisner W, Vesper J, Prokop T, Pinsker M, Schrader C, Kloss M, Kiening K, Boetzel K, Mehrkens J, Skogseid IM, Ramm-Pettersen J, Kemmler G, Bhatia KP, Vitek JL, Benecke R, DBS Study Group for Dystonia (2014) Pallidal neurostimulation in patients with medication-refractory cervical dystonia: a randomised, sham-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 13:875–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70143-7
Walsh RA, Sidiropoulos C, Lozano AM, Hodaie M, Poon YY, Fallis M, Moro E (2013) Bilateral pallidal stimulation in cervical dystonia: blinded evidence of benefit beyond 5 years. Brain 136:761–769. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awt009
Williams MA, McCarthy CJ, Chorti A, Cooke MW, Gates S (2010) A systematic review of reliability and validity studies of methods for measuring active and passive cervical range of motion. J Manip Physiol Ther 33:138–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmpt.2009.12.009
Wissel J, Kanovsky P, Ruzicka E, Bares M, Hortova H, Streitova H, Jech R, Roth J, Brenneis C, Müller J, Schnider P, Auff E, Richardson A, Poewe W (2001) Efficacy and safety of a standardised 500 unit dose of Dysport (clostridium botulinum toxin type A haemaglutinin complex) in a heterogeneous cervical dystonia population: results of a prospective, multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group study. J Neurol 248:1073–1078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004150170028
Woehrle JC, Blahak C, Kekelia K, Capelle HH, Baezner H, Grips E, Weigel R, Krauss JK (2009) Chronic deep brain stimulation for segmental dystonia. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 87:379–384. https://doi.org/10.1159/000249819
Yianni J, Bain PG, Gregory RP, Nandi D, Joint C, Scott RB, Stein JF, Aziz TZ (2003) Post-operative progress of dystonia patients following globus pallidus internus deep brain stimulation. Eur J Neurol 10:239–247. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1468-1331.2003.00592.x
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CB: conception and design of the work; data acquisition; analysis and interpretation of data; draft of manuscript. MEW: data acquisition; revision of manuscript. AS: data acquisition; revision of manuscript. HB: conception and design of the work; revision of manuscript. JKK: conception and design of the work; draft and revision of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
J. K. Krauss is a consultant to Medtronic and Boston Scientific, he received honoraria for speaking from AbbVie. C. Blahak received travel grants from Ipsen, A. Saryyeva received travel grants from Medtronic. The other authors report no financial disclosures.
Ethiacl approval
Ethics approval/consent to participate/consent for publication.
Informed consent
All patients gave their written informed consent to surgery, the study and the publication of results. The study was approves by the local ethic committee (Faculty of Medicine Mannheim, University of Heidelberg).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blahak, C., Wolf, M.E., Saryyeva, A. et al. Improvement of head and neck range of motion induced by chronic pallidal deep brain stimulation for cervical dystonia. J Neural Transm 128, 1205–1213 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-021-02365-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-021-02365-5