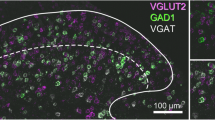
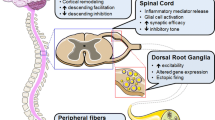
Abstract
A striking and debilitating property of the nervous system is that damage to this tissue can cause chronic intractable pain, which persists long after resolution of the initial insult. This neuropathic form of pain can arise from trauma to peripheral nerves, the spinal cord, or brain. It can also result from neuropathies associated with disease states such as diabetes, human immunodeficiency virus/AIDS, herpes, multiple sclerosis, cancer, and chemotherapy. Regardless of the origin, treatments for neuropathic pain remain inadequate. This continues to drive research into the underlying mechanisms. While the literature shows that dysfunction in numerous loci throughout the CNS can contribute to chronic pain, the spinal cord and in particular inhibitory signalling in this region have remained major research areas. This review focuses on local spinal inhibition provided by dorsal horn interneurons, and how such inhibition is disrupted during the development and maintenance of neuropathic pain.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez FJ, Taylor-Blake B, Fyffe RE, De Blas AL, Light AR (1996) Distribution of immunoreactivity for the beta 2 and beta 3 subunits of the GABAA receptor in the mammalian spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 365(3):392–412
Alvarez-Leefmans FJ, Leon-Olea M, Mendoza-Sotelo J, Alvarez FJ, Anton B, Garduno R (2001) Immunolocalization of the Na(+)–K(+)–2Cl(−) cotransporter in peripheral nervous tissue of vertebrates. Neuroscience 104(2):569–582
Anderson WB, Graham BA, Beveridge NJ, Tooney PA, Brichta AM, Callister RJ (2009) Different forms of glycine- and GABA(A)-receptor mediated inhibitory synaptic transmission in mouse superficial and deep dorsal horn neurons. Mol Pain 5:65
Antal M, Petko M, Polgar E, Heizmann CW, Storm-Mathisen J (1996) Direct evidence of an extensive GABAergic innervation of the spinal dorsal horn by fibres descending from the rostral ventromedial medulla. Neuroscience 73(2):509–518
Baba H, Ji RR, Kohno T, Moore KA, Ataka T, Wakai A, Okamoto M, Woolf CJ (2003) Removal of GABAergic inhibition facilitates polysynaptic A fiber-mediated excitatory transmission to the superficial spinal dorsal horn. Mol Cell Neurosci 24(3):818–830
Balasubramanyan S, Stemkowski PL, Stebbing MJ, Smith PA (2006) Sciatic chronic constriction injury produces cell-type-specific changes in the electrophysiological properties of rat substantia gelatinosa neurons. J Neurophysiol 96(2):579–590
Barber RP, Vaughn JE, Roberts E (1982) The cytoarchitecture of GABAergic neurons in rat spinal cord. Brain Res 238(2):305–328
Barthel F, Urban A, Schlosser L, Eulenburg V, Werdehausen R, Brandenburger T, Aragon C, Bauer I, Hermanns H (2014) Long-term application of glycine transporter inhibitors acts antineuropathic and modulates spinal N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit NR-1 expression in rats. Anesthesiology 121(1):160–169
Belelli D, Harrison NL, Maguire J, Macdonald RL, Walker MC, Cope DW (2009) Extrasynaptic GABAA receptors: form, pharmacology, and function. J Neurosci 29(41):12757–12763
Benarroch EE (2013) Cation-chloride cotransporters in the nervous system: general features and clinical correlations. Neurology 80(8):756–763
Betley JN, Wright CV, Kawaguchi Y, Erdelyi F, Szabo G, Jessell TM, Kaltschmidt JA (2009) Stringent specificity in the construction of a GABAergic pre-synaptic inhibitory circuit. Cell 139(1):161–174
Betz H, Gomeza J, Armsen W, Scholze P, Eulenburg V (2006) Glycine transporters: essential regulators of synaptic transmission. Biochem Soc Trans 34(Pt 1):55–58
Beyer C, Roberts LA, Komisaruk BR (1985) Hyperalgesia induced by altered glycinergic activity at the spinal cord. Life Sci 37(9):875–882
Bowery NG, Smart TG (2006) GABA and glycine as neurotransmitters: a brief history. Br J Pharmacol 147(Suppl 1):S109–S119
Boyle KA, Gutierrez-Mecinas M, Polgar E, Mooney N, O’Connor E, Furuta T, Watanabe M, Todd AJ (2017) A quantitative study of neurochemically defined populations of inhibitory interneurons in the superficial dorsal horn of the mouse spinal cord. Neuroscience 363:120–133
Boyle KA, Gradwell MA, Yasaka T, Dickie AC, Polgar E, Ganley RP, Orr DPH, Watanabe M, Abraira VE, Kuehn ED, Zimmerman AL, Ginty DD, Callister RJ, Graham BA, Hughes DI (2019) Defining a spinal microcircuit that gates myelinated afferent input: implications for tactile allodynia. Cell Rep 28(2):526–540 (e526)
Braz JM, Sharif-Naeini R, Vogt D, Kriegstein A, Alvarez-Buylla A, Rubenstein JL, Basbaum AI (2012) Forebrain GABAergic neuron precursors integrate into adult spinal cord and reduce injury-induced neuropathic pain. Neuron 74(4):663–675
Brock LG, Coombs JS, Eccles JC (1952) The recording of potentials from motoneurones with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol 117(4):431–460
Campbell JN, Raja SN, Meyer RA, Mackinnon SE (1988) Myelinated afferents signal the hyperalgesia associated with nerve injury. Pain 32(1):89–94
Castro-Lopes JM, Tavares I, Coimbra A (1993) GABA decreases in the spinal cord dorsal horn after peripheral neurectomy. Brain Res 620(2):287–291
Castro-Lopes JM, Malcangio M, Pan BH, Bowery NG (1995) Complex changes of GABAA and GABAB receptor binding in the spinal cord dorsal horn following peripheral inflammation or neurectomy. Brain Res 679(2):289–297
Cervero F, Laird JM (1996) Mechanisms of touch-evoked pain (allodynia): a new model. Pain 68(1):13–23
Chance FS, Abbott LF, Reyes AD (2002) Gain modulation from background synaptic input. Neuron 35(4):773–782
Chen JT, Guo D, Campanelli D, Frattini F, Mayer F, Zhou L, Kuner R, Heppenstall PA, Knipper M, Hu J (2014) Pre-synaptic GABAergic inhibition regulated by BDNF contributes to neuropathic pain induction. Nat Commun 5:5331
Chery N, de Koninck Y (1999) Junctional versus extrajunctional glycine and GABA(A) receptor-mediated IPSCs in identified lamina I neurons of the adult rat spinal cord. J Neurosci 19(17):7342–7355
Chery N, De Koninck Y (2000) GABA(B) receptors are the first target of released GABA at lamina I inhibitory synapses in the adult rat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol 84(2):1006–1011
Clements JD, Forsythe ID, Redman SJ (1987) Pre-synaptic inhibition of synaptic potentials evoked in cat spinal motoneurones by impulses in single group Ia axons. J Physiol 383:153–169
Coggeshall RE, Lekan HA, White FA, Woolf CJ (2001) A-fiber sensory input induces neuronal cell death in the dorsal horn of the adult rat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 435(3):276–282
Coombs JS, Eccles JC, Fatt P (1955a) The electrical properties of the motoneurone membrane. J Physiol 130(2):291–325
Coombs JS, Eccles JC, Fatt P (1955b) The inhibitory suppression of reflex discharges from motoneurones. J Physiol 130(2):396–413
Coombs JS, Eccles JC, Fatt P (1955c) The specific ionic conductances and the ionic movements across the motoneuronal membrane that produce the inhibitory post-synaptic potential. J Physiol 130(2):326–374
Coull JA, Boudreau D, Bachand K, Prescott SA, Nault F, Sik A, De Koninck P, De Koninck Y (2003) Trans-synaptic shift in anion gradient in spinal lamina I neurons as a mechanism of neuropathic pain. Nature 424(6951):938–942
Cronin JN, Bradbury EJ, Lidierth M (2004) Laminar distribution of GABAA- and glycine-receptor mediated tonic inhibition in the dorsal horn of the rat lumbar spinal cord: effects of picrotoxin and strychnine on expression of Fos-like immunoreactivity. Pain 112(1–2):156–163
Curtis DR, Crawford JM (1969) Central synaptic transmission-microelectrophoretic studies. Annu Rev Pharmacol 9:209–240
Daemen MA, Hoogland G, Cijntje JM, Spincemaille GH (2008) Upregulation of the GABA-transporter GAT-1 in the spinal cord contributes to pain behaviour in experimental neuropathy. Neurosci Lett 444(1):112–115
de Novellis V, Siniscalco D, Galderisi U, Fuccio C, Nolano M, Santoro L, Cascino A, Roth KA, Rossi F, Maione S (2004) Blockade of glutamate mGlu5 receptors in a rat model of neuropathic pain prevents early over-expression of pro-apoptotic genes and morphological changes in dorsal horn lamina II. Neuropharmacology 46(4):468–479
Doyon N, Vinay L, Prescott SA, De Koninck Y (2016) Chloride regulation: a dynamic equilibrium crucial for synaptic inhibition. Neuron 89(6):1157–1172
Eaton MJ, Plunkett JA, Karmally S, Martinez MA, Montanez K (1998) Changes in GAD- and GABA- immunoreactivity in the spinal dorsal horn after peripheral nerve injury and promotion of recovery by lumbar transplant of immortalized serotonergic precursors. J Chem Neuroanat 16(1):57–72
Eaton MJ, Martinez MA, Karmally S (1999) A single intrathecal injection of GABA permanently reverses neuropathic pain after nerve injury. Brain Res 835(2):334–339
Eccles JC (1960) The ferrier lecture: the nature of central inhibition. Proc Royal Soc B 153(953):445-476
Eccles JC (1964) Ionic mechanism of post-synaptic inhibition. Science 145(3637):1140–1147
Eccles JC, Eccles RM, Magni F (1961) Central inhibitory action attributable to pre-synaptic depolarization produced by muscle afferent volleys. J Physiol 159:147–166
Eccles JC, Schmidt RF, Willis WD (1962) Pre-synaptic inhibition of the spinal monosynaptic reflex pathway. J Physiol 161:282–297
Eccles JC, Schmidt R, Willis WD (1963) Pharmacological studies on pre-synaptic inhibition. J Physiol 168:500–530
Farrant M, Nusser Z (2005) Variations on an inhibitory theme: phasic and tonic activation of GABA(A) receptors. Nat Rev Neurosci 6(3):215–229
Fink AJ, Croce KR, Huang ZJ, Abbott LF, Jessell TM, Azim E (2014) Pre-synaptic inhibition of spinal sensory feedback ensures smooth movement. Nature 509(7498):43–48
Foster E, Wildner H, Tudeau L, Haueter S, Ralvenius WT, Jegen M, Johannssen H, Hosli L, Haenraets K, Ghanem A, Conzelmann KK, Bosl M, Zeilhofer HU (2015) Targeted ablation, silencing, and activation establish glycinergic dorsal horn neurons as key components of a spinal gate for pain and itch. Neuron 85(6):1289–1304
Francois A, Low SA, Sypek EI, Christensen AJ, Sotoudeh C, Beier KT, Ramakrishnan C, Ritola KD, Sharif-Naeini R, Deisseroth K, Delp SL, Malenka RC, Luo L, Hantman AW, Scherrer G (2017) A brainstem-spinal cord inhibitory circuit for mechanical pain modulation by gaba and enkephalins. Neuron 93(4):822–839 (e826)
Fukuoka T, Tokunaga A, Kondo E, Miki K, Tachibana T, Noguchi K (1998) Change in mRNAs for neuropeptides and the GABA(A) receptor in dorsal root ganglion neurons in a rat experimental neuropathic pain model. Pain 78(1):13–26
Garcia-Ramirez DL, Calvo JR, Hochman S, Quevedo JN (2014) Serotonin, dopamine and noradrenaline adjust actions of myelinated afferents via modulation of pre-synaptic inhibition in the mouse spinal cord. PLoS One 9(2):e89999
Gassner M, Leitner J, Gruber-Schoffnegger D, Forsthuber L, Sandkuhler J (2013) Properties of spinal lamina III GABAergic neurons in naive and in neuropathic mice. Eur J Pain 17(8):1168–1179
Gradwell MA, Boyle KA, Callister RJ, Hughes DI, Graham BA (2017) Heteromeric alpha/beta glycine receptors regulate excitability in parvalbumin-expressing dorsal horn neurons through phasic and tonic glycinergic inhibition. J Physiol 595(23):7185–7202
Graham BA, Hughes DI (2019) Rewards, perils and pitfalls of untangling spinal pain circuits. Curr Opin Physiol 11:35–41
Graham B, Redman S (1994) A simulation of action potentials in synaptic boutons during pre-synaptic inhibition. J Neurophysiol 71(2):538–549
Graham BA, Schofield PR, Sah P, Callister RJ (2003) Altered inhibitory synaptic transmission in superficial dorsal horn neurones in spastic and oscillator mice. J Physiol 551:905–916
Graham BA, Schofield PR, Sah P, Margrie TW, Callister RJ (2006) Distinct physiological mechanisms underlie altered glycinergic synaptic transmission in the murine mutants spastic, spasmodic, and oscillator. J Neurosci 26:4880–4890
Graham BA, Brichta AM, Callister RJ (2007) Moving from an averaged to specific view of spinal cord pain processing circuits. J Neurophysiol 98(3):1057–1063
Grudzinska J, Schemm R, Haeger S, Nicke A, Schmalzing G, Betz H, Laube B (2005) The beta subunit determines the ligand binding properties of synaptic glycine receptors. Neuron 45(5):727–739
Gulledge AT, Stuart GJ (2003) Excitatory actions of GABA in the cortex. Neuron 37(2):299–309
Harvey RJ, Depner UB, Wassle H, Ahmadi S, Heindl C, Reinold H, Smart TG, Harvey K, Schutz B, Abo-Salem OM, Zimmer A, Poisbeau P, Welzl H, Wolfer DP, Betz H, Zeilhofer HU, Muller U (2004) GlyR alpha3: an essential target for spinal PGE2-mediated inflammatory pain sensitization. Science 304(5672):884–887
Heinke B, Ruscheweyh R, Forsthuber L, Wunderbaldinger G, Sandkuhler J (2004) Physiological, neurochemical and morphological properties of a subgroup of GABAergic spinal lamina II neurones identified by expression of green fluorescent protein in mice. J Physiol 560(Pt 1):249–266
Hermanns H, Muth-Selbach U, Williams R, Krug S, Lipfert P, Werdehausen R, Braun S, Bauer I (2008) Differential effects of spinally applied glycine transporter inhibitors on nociception in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett 445(3):214–219
Hermanns H, Muth-Selbach U, Lipfert P, Braun S, Werdehausen R, Bauer I (2009) Loss of spinal glycinergic neurons is not necessary for development of neuropathic pain in transgenic mice expressing enhanced green fluorescent protein in glycinergic neurons. Neuroscience 159(3):1148–1153
Hevers W, Luddens H (1998) The diversity of GABAA receptors. Pharmacological and electrophysiological properties of GABAA channel subtypes. Mol Neurobiol 18(1):35–86
Hochman S, Shreckengost J, Kimura H, Quevedo J (2010) Pre-synaptic inhibition of primary afferents by depolarization: observations supporting nontraditional mechanisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1198:140–152
Horch KW, Lisney SJ (1981) Changes in primary afferent depolarization of sensory neurones during peripheral nerve regeneration in the cat. J Physiol 313:287–299
Hu JH, Yang N, Ma YH, Zhou XG, Jiang J, Duan SH, Mei ZT, Fei J, Guo LH (2003) Hyperalgesic effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid transporter I in mice. J Neurosci Res 73(4):565–572
Hughes DI, Mackie M, Nagy GG, Riddell JS, Maxwell DJ, Szabo G, Erdelyi F, Veress G, Szucs P, Antal M, Todd AJ (2005) P boutons in lamina IX of the rodent spinal cord express high levels of glutamic acid decarboxylase-65 and originate from cells in deep medial dorsal horn. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(25):9038–9043
Hughes DI, Sikander S, Kinnon CM, Boyle KA, Watanabe M, Callister RJ, Graham BA (2012) Morphological, neurochemical and electrophysiological features of parvalbumin-expressing cells: a likely source of axo-axonic inputs in the mouse spinal dorsal horn. J Physiol 590(16):3927–3951
Hwang JH, Yaksh TL (1997) The effect of spinal GABA receptor agonists on tactile allodynia in a surgically-induced neuropathic pain model in the rat. Pain 70(1):15–22
Ibuki T, Hama AT, Wang XT, Pappas GD, Sagen J (1997) Loss of GABA-immunoreactivity in the spinal dorsal horn of rats with peripheral nerve injury and promotion of recovery by adrenal medullary grafts. Neuroscience 76(3):845–858
Imlach WL, Bhola RF, Mohammadi SA, Christie MJ (2016) Glycinergic dysfunction in a subpopulation of dorsal horn interneurons in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Sci Rep 6:37104
Inquimbert P, Rodeau JL, Schlichter R (2007) Differential contribution of GABAergic and glycinergic components to inhibitory synaptic transmission in lamina II and laminae III–IV of the young rat spinal cord. Eur J Neurosci 26(10):2940–2949
Inquimbert P, Moll M, Latremoliere A, Tong CK, Whang J, Sheehan GF, Smith BM, Korb E, Athie MCP, Babaniyi O, Ghasemlou N, Yanagawa Y, Allis CD, Hof PR, Scholz J (2018) NMDA receptor activation underlies the loss of spinal dorsal horn neurons and the transition to persistent pain after peripheral nerve injury. Cell Rep 23(9):2678–2689
Iwagaki N, Ganley RP, Dickie AC, Polgar E, Hughes DI, Del Rio P, Revina Y, Watanabe M, Todd AJ, Riddell JS (2016) A combined electrophysiological and morphological study of neuropeptide Y-expressing inhibitory interneurons in the spinal dorsal horn of the mouse. Pain 157(3):598–612
Kahle KT, Staley KJ, Nahed BV, Gamba G, Hebert SC, Lifton RP, Mount DB (2008) Roles of the cation-chloride cotransporters in neurological disease. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 4(9):490–503
Kahle KT, Schmouth JF, Lavastre V, Latremoliere A, Zhang J, Andrews N, Omura T, Laganiere J, Rochefort D, Hince P, Castonguay G, Gaudet R, Mapplebeck JC, Sotocinal SG, Duan J, Ward C, Khanna AR, Mogil JS, Dion PA, Woolf CJ, Inquimbert P, Rouleau GA (2016) Inhibition of the kinase WNK1/HSN2 ameliorates neuropathic pain by restoring GABA inhibition. Sci Signal 9(421):ra32
Kanaka C, Ohno K, Okabe A, Kuriyama K, Itoh T, Fukuda A, Sato K (2001) The differential expression patterns of messenger RNAs encoding K-Cl cotransporters (KCC1,2) and Na-K-2Cl cotransporter (NKCC1) in the rat nervous system. Neuroscience 104(4):933–946
Keller AF, Coull JA, Chery N, Poisbeau P, De Koninck Y (2001) Region-specific developmental specialization of GABA-glycine cosynapses in laminas I–II of the rat spinal dorsal horn. J Neurosci 21(20):7871–7880
Keller AF, Beggs S, Salter MW, De Koninck Y (2007) Transformation of the output of spinal lamina I neurons after nerve injury and microglia stimulation underlying neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 3:27
Kelly JS, Gottesfeld Z, Schon F (1973) Reduction in GADI activity from the dorsal lateral region of the deafferented rat spinal cord. Brain Res 62(2):581–586
Kim YH, Back SK, Davies AJ, Jeong H, Jo HJ, Chung G, Na HS, Bae YC, Kim SJ, Kim JS, Jung SJ, Oh SB (2012) TRPV1 in GABAergic interneurons mediates neuropathic mechanical allodynia and disinhibition of the nociceptive circuitry in the spinal cord. Neuron 74(4):640–647
Kingery WS, Fields RD, Kocsis JD (1988) Diminished dorsal root GABA sensitivity following chronic peripheral nerve injury. Exp Neurol 100(3):478–490
Knabl J, Witschi R, Hosl K, Reinold H, Zeilhofer UB, Ahmadi S, Brockhaus J, Sergejeva M, Hess A, Brune K, Fritschy JM, Rudolph U, Mohler H, Zeilhofer HU (2008) Reversal of pathological pain through specific spinal GABAA receptor subtypes. Nature 451(7176):330–334
Koga K, Kanehisa K, Kohro Y, Shiratori-Hayashi M, Tozaki-Saitoh H, Inoue K, Furue H, Tsuda M (2017) Chemogenetic silencing of GABAergic dorsal horn interneurons induces morphine-resistant spontaneous nocifensive behaviours. Sci Rep 7(1):4739
Kohno T, Moore KA, Baba H, Woolf CJ (2003) Peripheral nerve injury alters excitatory synaptic transmission in lamina II of the rat dorsal horn. J Physiol 548(Pt 1):131–138
Kontinen VK, Stanfa LC, Basu A, Dickenson AH (2001) Electrophysiologic evidence for increased endogenous gabaergic but not glycinergic inhibitory tone in the rat spinal nerve ligation model of neuropathy. Anesthesiology 94(2):333–339
Labrakakis C, Lorenzo LE, Bories C, Ribeiro-da-Silva A, De Koninck Y (2009) Inhibitory coupling between inhibitory interneurons in the spinal cord dorsal horn. Mol Pain 5:24
Laird JM, Bennett GJ (1992) Dorsal root potentials and afferent input to the spinal cord in rats with an experimental peripheral neuropathy. Brain Res 584(1–2):181–190
Lee JW, Siegel SM, Oaklander AL (2009) Effects of distal nerve injuries on dorsal-horn neurons and glia: relationships between lesion size and mechanical hyperalgesia. Neuroscience 158(2):904–914
Leitner J, Westerholz S, Heinke B, Forsthuber L, Wunderbaldinger G, Jager T, Gruber-Schoffnegger D, Braun K, Sandkuhler J (2013) Impaired excitatory drive to spinal GABAergic neurons of neuropathic mice. PLoS One 8(8):e73370
Lever I, Cunningham J, Grist J, Yip PK, Malcangio M (2003) Release of BDNF and GABA in the dorsal horn of neuropathic rats. Eur J Neurosci 18(5):1169–1174
Li L, Chen SR, Chen H, Wen L, Hittelman WN, Xie JD, Pan HL (2016) Chloride homeostasis critically regulates synaptic NMDA receptor activity in neuropathic pain. Cell Rep 15(7):1376–1383
Lian Y, Wang Y, Ma K, Zhao L, Zhang Z, Shang Y, Si J, Li L (2012) Expression of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor alpha2 subunit in the dorsal root ganglion of rats with sciatic nerve injury. Neural Regen Res 7(32):2492–2499
Liu F, Yuan H (2014) Role of glia in neuropathic pain. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 19:798–807
Loomis CW, Khandwala H, Osmond G, Hefferan MP (2001) Coadministration of intrathecal strychnine and bicuculline effects synergistic allodynia in the rat: an isobolographic analysis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 296(3):756–761
Lorenzo LE, Magnussen C, Bailey AL, St Louis M, De Koninck Y, Ribeiro-da-Silva A (2014) Spatial and temporal pattern of changes in the number of GAD65-immunoreactive inhibitory terminals in the rat superficial dorsal horn following peripheral nerve injury. Mol Pain 10:57
Lu Y, Dong H, Gao Y, Gong Y, Ren Y, Gu N, Zhou S, Xia N, Sun YY, Ji RR, Xiong L (2013) A feed-forward spinal cord glycinergic neural circuit gates mechanical allodynia. J Clin Investig 123(9):4050–4062
Lynch JW (2004) Molecular structure and function of the glycine receptor chloride channel. Physiol Rev 84(4):1051–1095
Lynch JW, Callister RJ (2006) Glycine receptors: a new therapeutic target in pain pathways.”. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 7:48–53
Machelska H, Celik MÖ (2016) Recent advances in understanding neuropathic pain: glia, sex differences, and epigenetics. F1000Res 5:2743. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.9621.1
Mackie M, Hughes DI, Maxwell DJ, Tillakaratne NJ, Todd AJ (2003) Distribution and colocalisation of glutamate decarboxylase isoforms in the rat spinal cord. Neuroscience 119(2):461–472
Magoul R, Onteniente B, Geffard M, Calas A (1987) Anatomical distribution and ultrastructural organization of the GABAergic system in the rat spinal cord. An immunocytochemical study using anti-GABA antibodies. Neuroscience 20(3):1001–1009
Maione S, Siniscalco D, Galderisi U, de Novellis V, Uliano R, Di Bernardo G, Berrino L, Cascino A, Rossi F (2002) Apoptotic genes expression in the lumbar dorsal horn in a model neuropathic pain in rat. Neuroreport 13(1):101–106
Malan TP, Mata HP, Porreca F (2002) Spinal GABA(A) and GABA(B) receptor pharmacology in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Anesthesiology 96(5):1161–1167
Mao S, Garzon-Muvdi T, Di Fulvio M, Chen Y, Delpire E, Alvarez FJ, Alvarez-Leefmans FJ (2012) Molecular and functional expression of cation-chloride cotransporters in dorsal root ganglion neurons during postnatal maturation. J Neurophysiol 108(3):834–852
Mayhew JA, Callister RJ, Walker FR, Smith D, Graham BA (2019) Ageing alters signaling properties in the mouse spinal dorsal horn. Molecular Pain 15:1-13
McEwen BS (1999) Stress and hippocampal plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci 22:105–122
Melzack R, Wall PD (1965) Pain mechanisms: a new theory. Science 150(3699):971–979
Miletic G, Draganic P, Pankratz MT, Miletic V (2003) Muscimol prevents long-lasting potentiation of dorsal horn field potentials in rats with chronic constriction injury exhibiting decreased levels of the GABA transporter GAT-1. Pain 105(1–2):347–353
Miraucourt LS, Dallel R, Voisin DL (2007) Glycine inhibitory dysfunction turns touch into pain through PKCgamma interneurons. PLoS One 2(11):e1116
Mitchell SJ, Silver RA (2003) Shunting inhibition modulates neuronal gain during synaptic excitation. Neuron 38(3):433–445
Modol L, Cobianchi S, Navarro X (2014) Prevention of NKCC1 phosphorylation avoids downregulation of KCC2 in central sensory pathways and reduces neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury. Pain 155(8):1577–1590
Moore KA, Kohno T, Karchewski LA, Scholz J, Baba H, Woolf CJ (2002) Partial peripheral nerve injury promotes a selective loss of GABAergic inhibition in the superficial dorsal horn of the spinal cord. J Neurosci 22(15):6724–6731
Morita K, Motoyama N, Kitayama T, Morioka N, Kifune K, Dohi T (2008) Spinal antiallodynia action of glycine transporter inhibitors in neuropathic pain models in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326(2):633–645
Mukhida K, Mendez I, McLeod M, Kobayashi N, Haughn C, Milne B, Baghbaderani B, Sen A, Behie LA, Hong M (2007) Spinal GABAergic transplants attenuate mechanical allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Stem Cells 25(11):2874–2885
Muller F, Heinke B, Sandkuhler J (2003) Reduction of glycine receptor-mediated miniature inhibitory post-synaptic currents in rat spinal lamina I neurons after peripheral inflammation. Neuroscience 122(3):799–805
Muller E, Le-Corronc H, Legendre P (2008) Extrasynaptic and post-synaptic receptors in glycinergic and GABAergic neurotransmission: a division of labor? Front Mol Neurosci 1:3
Naik AK, Pathirathna S, Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2008) GABAA receptor modulation in dorsal root ganglia in vivo affects chronic pain after nerve injury. Neuroscience 154(4):1539–1553
Nowak A, Mathieson HR, Chapman RJ, Janzso G, Yanagawa Y, Obata K, Szabo G, King AE (2011) Kv3.1b and Kv3.3 channel subunit expression in murine spinal dorsal horn GABAergic interneurones. J Chem Neuroanat 42(1):30–38
Obata K, Yamanaka H, Fukuoka T, Yi D, Tokunaga A, Hashimoto N, Yoshikawa H, Noguchi K (2003) Contribution of injured and uninjured dorsal root ganglion neurons to pain behavior and the changes in gene expression following chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve in rats. Pain 101(1–2):65–77
Patel S, Naeem S, Kesingland A, Froestl W, Capogna M, Urban L, Fox A (2001) The effects of GABA(B) agonists and gabapentin on mechanical hyperalgesia in models of neuropathic and inflammatory pain in the rat. Pain 90(3):217–226
Petitjean H, Pawlowski SA, Fraine SL, Sharif B, Hamad D, Fatima T, Berg J, Brown CM, Jan LY, Ribeiro-da-Silva A, Braz JM, Basbaum AI, Sharif-Naeini R (2015) Dorsal horn parvalbumin neurons are gate-keepers of touch-evoked pain after nerve injury. Cell Rep 13(6):1246–1257
Pieraut S, Laurent-Matha V, Sar C, Hubert T, Mechaly I, Hilaire C, Mersel M, Delpire E, Valmier J, Scamps F (2007) NKCC1 phosphorylation stimulates neurite growth of injured adult sensory neurons. J Neurosci 27(25):6751–6759
Polgar E, Todd AJ (2008) Tactile allodynia can occur in the spared nerve injury model in the rat without selective loss of GABA or GABA(A) receptors from synapses in laminae I–II of the ipsilateral spinal dorsal horn. Neuroscience 156(1):193–202
Polgar E, Hughes DI, Riddell JS, Maxwell DJ, Puskar Z, Todd AJ (2003) Selective loss of spinal GABAergic or glycinergic neurons is not necessary for development of thermal hyperalgesia in the chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain. Pain 104(1–2):229–239
Polgar E, Gray S, Riddell JS, Todd AJ (2004) Lack of evidence for significant neuronal loss in laminae I–III of the spinal dorsal horn of the rat in the chronic constriction injury model. Pain 111(1–2):144–150
Polgar E, Hughes DI, Arham AZ, Todd AJ (2005) Loss of neurons from laminas I–III of the spinal dorsal horn is not required for development of tactile allodynia in the spared nerve injury model of neuropathic pain. J Neurosci 25(28):6658–6666
Polgar E, Durrieux C, Hughes DI, Todd AJ (2013) A quantitative study of inhibitory interneurons in laminae I–III of the mouse spinal dorsal horn. PLoS One 8(10):e78309
Prescott SA, De Koninck Y (2003) Gain control of firing rate by shunting inhibition: roles of synaptic noise and dendritic saturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(4):2076–2081
Prescott SA, Sejnowski TJ, De Koninck Y (2006) Reduction of anion reversal potential subverts the inhibitory control of firing rate in spinal lamina I neurons: towards a biophysical basis for neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 2:32
Price TJ, Cervero F, de Koninck Y (2005) Role of cation-chloride-cotransporters (CCC) in pain and hyperalgesia. Curr Top Med Chem 5(6):547–555
Price TJ, Hargreaves KM, Cervero F (2006) Protein expression and mRNA cellular distribution of the NKCC1 cotransporter in the dorsal root and trigeminal ganglia of the rat. Brain Res 1112(1):146–158
Rivera C, Voipio J, Payne JA, Ruusuvuori E, Lahtinen H, Lamsa K, Pirvola U, Saarma M, Kaila K (1999) The K+/Cl− co-transporter KCC2 renders GABA hyperpolarizing during neuronal maturation. Nature 397(6716):251–255
Rocha-Gonzalez HI, Mao S, Alvarez-Leefmans FJ (2008) Na + , K+, 2Cl− cotransport and intracellular chloride regulation in rat primary sensory neurons: thermodynamic and kinetic aspects. J Neurophysiol 100(1):169–184
Rode F, Jensen DG, Blackburn-Munro G, Bjerrum OJ (2005) Centrally-mediated antinociceptive actions of GABA(A) receptor agonists in the rat spared nerve injury model of neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 516(2):131–138
Ross SE, Mardinly AR, McCord AE, Zurawski J, Cohen S, Jung C, Hu L, Mok SI, Shah A, Savner EM, Tolias C, Corfas R, Chen S, Inquimbert P, Xu Y, McInnes RR, Rice FL, Corfas G, Ma Q, Woolf CJ, Greenberg ME (2010) Loss of inhibitory interneurons in the dorsal spinal cord and elevated itch in Bhlhb5 mutant mice. Neuron 65(6):886–898
Rudomin P (2009) In search of lost pre-synaptic inhibition. Exp Brain Res 196(1):139–151
Rudomin P, Schmidt RF (1999) Pre-synaptic inhibition in the vertebrate spinal cord revisited. Exp Brain Res 129(1):1–37
Ruscheweyh R, Sandkuhler J (2005) Long-range oscillatory Ca2+ waves in rat spinal dorsal horn. Eur J Neurosci 22(8):1967–1976
Russier M, Kopysova IL, Ankri N, Ferrand N, Debanne D (2002) GABA and glycine co-release optimizes functional inhibition in rat brainstem motoneurons in vitro. J Physiol 541(Pt 1):123–137
Sandkuhler J (2009) Models and mechanisms of hyperalgesia and allodynia. Physiol Rev 89(2):707–758
Satoh O, Omote K (1996) Roles of monoaminergic, glycinergic and GABAergic inhibitory systems in the spinal cord in rats with peripheral mononeuropathy. Brain Res 728(1):27–36
Schoffnegger D, Heinke B, Sommer C, Sandkuhler J (2006) Physiological properties of spinal lamina II GABAergic neurons in mice following peripheral nerve injury. J Physiol 577(Pt 3):869–878
Schoffnegger D, Ruscheweyh R, Sandkuhler J (2008) Spread of excitation across modality borders in spinal dorsal horn of neuropathic rats. Pain 135(3):300–310
Scholz J, Broom DC, Youn DH, Mills CD, Kohno T, Suter MR, Moore KA, Decosterd I, Coggeshall RE, Woolf CJ (2005) Blocking caspase activity prevents transsynaptic neuronal apoptosis and the loss of inhibition in lamina II of the dorsal horn after peripheral nerve injury. J Neurosci 25(32):7317–7323
Segev I (1990) Computer study of pre-synaptic inhibition controlling the spread of action potentials into axonal terminals. J Neurophysiol 63(5):987–998
Semyanov A, Walker MC, Kullmann DM, Silver RA (2004) Tonically active GABA A receptors: modulating gain and maintaining the tone. Trends Neurosci 27(5):262–269
Sherman SE, Loomis CW (1995) Strychnine-dependent allodynia in the urethane-anesthetized rat is segmentally distributed and prevented by intrathecal glycine and betaine. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 73(12):1698–1705
Sherrington C (1932) Inhibition as a coordinative factor. Nobel lecture. In: Nobel lectures, physiology or medicine 1922–1941, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1965
Shih A, Miletic V, Miletic G, Smith LJ (2008) Midazolam administration reverses thermal hyperalgesia and prevents gamma-aminobutyric acid transporter loss in a rodent model of neuropathic pain. Anesth Analg 106(4):1296–1302 (table of contents)
Sieghart W (1995) Structure and pharmacology of gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor subtypes. Pharmacol Rev 47(2):181–234
Simpson RK Jr, Huang W (1998) Glycine receptor reduction within segmental gray matter in a rat model in neuropathic pain. Neurol Res 20(2):161–168
Sivilotti L, Woolf CJ (1994) The contribution of GABAA and glycine receptors to central sensitization: disinhibition and touch-evoked allodynia in the spinal cord. J Neurophysiol 72(1):169–179
Somers DL, Clemente FR (2002) Dorsal horn synaptosomal content of aspartate, glutamate, glycine and GABA are differentially altered following chronic constriction injury to the rat sciatic nerve. Neurosci Lett 323(3):171–174
Spike RC, Watt C, Zafra F, Todd AJ (1997) An ultrastructural study of the glycine transporter GLYT2 and its association with glycine in the superficial laminae of the rat spinal dorsal horn. Neuroscience 77(2):543–551
Staley KJ, Mody I (1992) Shunting of excitatory input to dentate gyrus granule cells by a depolarizing GABAA receptor-mediated post-synaptic conductance. J Neurophysiol 68(1):197–212
Stiller CO, Cui JG, O’Connor WT, Brodin E, Meyerson BA, Linderoth B (1996) Release of gamma-aminobutyric acid in the dorsal horn and suppression of tactile allodynia by spinal cord stimulation in mononeuropathic rats. Neurosurgery 39(2):367–374 (discussion 374–365)
Stuart GJ, Redman SJ (1992) The role of GABAA and GABAB receptors in pre-synaptic inhibition of Ia EPSPs in cat spinal motoneurones. J Physiol 447:675–692
Tadros MA, Farrell KE, Schofield PR, Brichta AM, Graham BA, Fuglevand AJ, Callister RJ (2014) Intrinsic and synaptic homeostatic plasticity in motoneurons from mice with glycine receptor mutations. J Neurophysiol 111:1487–1498
Takahashi A, Mashimo T, Uchida I (2006) GABAergic tonic inhibition of substantia gelatinosa neurons in mouse spinal cord. Neuroreport 17(12):1331–1335
Takazawa T, MacDermott AB (2010) Glycinergic and GABAergic tonic inhibition fine tune inhibitory control in regionally distinct subpopulations of dorsal horn neurons. J Physiol 588(Pt 14):2571–2587
Takkala P, Zhu Y, Prescott SA (2016) Combined changes in chloride regulation and neuronal excitability enable primary afferent depolarization to elicit spiking without compromising its inhibitory effects. PLoS Comput Biol 12(11):e1005215
Thanawala MS, Regehr WG (2013) Pre-synaptic calcium influx controls neurotransmitter release in part by regulating the effective size of the readily releasable pool. J Neurosci 33(11):4625–4633
Todd AJ, Sullivan AC (1990) Light microscope study of the coexistence of GABA-like and glycine-like immunoreactivities in the spinal cord of the rat. J Comp Neurol 296(3):496–505
Torsney C, MacDermott AB (2006) Disinhibition opens the gate to pathological pain signaling in superficial neurokinin 1 receptor-expressing neurons in rat spinal cord. J Neurosci 26(6):1833–1843
Vaysse L, Sol JC, Lazorthes Y, Courtade-Saidi M, Eaton MJ, Jozan S (2011) GABAergic pathway in a rat model of chronic neuropathic pain: modulation after intrathecal transplantation of a human neuronal cell line. Neurosci Res 69(2):111–120
Verdier D, Lund JP, Kolta A (2003) GABAergic control of action potential propagation along axonal branches of mammalian sensory neurons. J Neurosci 23(6):2002–2007
Wall PD (1982) The effect of peripheral nerve lesions and of neonatal capsaicin in the rat on primary afferent depolarization. J Physiol 329:21–35
Wall PD, Devor M (1981) The effect of peripheral nerve injury on dorsal root potentials and on transmission of afferent signals into the spinal cord. Brain Res 209(1):95–111
Wei B, Kumada T, Furukawa T, Inoue K, Watanabe M, Sato K, Fukuda A (2013) Pre- and post-synaptic switches of GABA actions associated with Cl- homeostatic changes are induced in the spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve in a rat model of trigeminal neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 228:334–348
Wei Z, Fei Y, Su W, Chen G (2019) Emerging role of schwann cells in neuropathic pain: receptors, glial mediators and myelination. Front Cell Neurosci 13:116
Werdehausen R, Mittnacht S, Bee LA, Minett MS, Armbruster A, Bauer I, Wood JN, Hermanns H, Eulenburg V (2015) The lidocaine metabolite N-ethylglycine has antinociceptive effects in experimental inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain 156(9):1647–1659
Whiteside GT, Munglani R (2001) Cell death in the superficial dorsal horn in a model of neuropathic pain. J Neurosci Res 64(2):168–173
Willis WD Jr (1999) Dorsal root potentials and dorsal root reflexes: a double-edged sword. Exp Brain Res 124(4):395–421
Woolf CJ, Wall PD (1982) Chronic peripheral nerve section diminishes the primary afferent A-fibre mediated inhibition of rat dorsal horn neurones. Brain Res 242(1):77–85
Xu YF, Cai YQ, Cai GQ, Jiang J, Sheng ZJ, Wang ZG, Fei J (2008) Hypoalgesia in mice lacking GABA transporter subtype 1. J Neurosci Res 86(2):465–470
Yaksh TL (1989) Behavioral and autonomic correlates of the tactile evoked allodynia produced by spinal glycine inhibition: effects of modulatory receptor systems and excitatory amino acid antagonists. Pain 37(1):111–123
Yamamoto T, Yaksh TL (1993) Effects of intrathecal strychnine and bicuculline on nerve compression-induced thermal hyperalgesia and selective antagonism by MK-801. Pain 54(1):79–84
Yang Z, Taran E, Webb TI, Lynch JW (2012) Stoichiometry and subunit arrangement of alpha1beta glycine receptors as determined by atomic force microscopy. Biochemistry 51(26):5229–5231
Yasaka T, Kato G, Furue H, Rashid MH, Sonohata M, Tamae A, Murata Y, Masuko S, Yoshimura M (2007) Cell-type-specific excitatory and inhibitory circuits involving primary afferents in the substantia gelatinosa of the rat spinal dorsal horn in vitro. J Physiol 581(Pt 2):603–618
Yowtak J, Wang J, Kim HY, Lu Y, Chung K, Chung JM (2013) Effect of antioxidant treatment on spinal GABA neurons in a neuropathic pain model in the mouse. Pain 154(11):2469–2476
Zeilhofer HU (2005) The glycinergic control of spinal pain processing. Cell Mol Life Sci 62(18):2027–2035
Zhou HY, Chen SR, Byun HS, Chen H, Li L, Han HD, Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK, Pan HL (2012) N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptor- and calpain-mediated proteolytic cleavage of K+–Cl− cotransporter-2 impairs spinal chloride homeostasis in neuropathic pain. J Biol Chem 287(40):33853–33864
Funding
This work was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) of Australia (Grant 631000 and 1043933, 1144638 to B.A.G), and the Hunter Medical Research Institute (Grant to B.A.G).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gradwell, M.A., Callister, R.J. & Graham, B.A. Reviewing the case for compromised spinal inhibition in neuropathic pain. J Neural Transm 127, 481–503 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-019-02090-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-019-02090-0