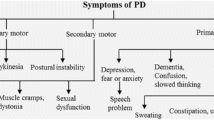
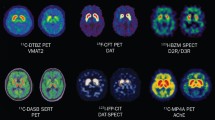
Abstract
Neurodegeneration of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system and concurrent dopamine (DA) deficiency in the basal ganglia represent core features of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Despite the central role of DA in the pathogenesis of PD, dopaminergic systems outside of the midbrain have not been systematically investigated for Lewy body pathology or neurodegeneration. Dopaminergic neurons show a surprisingly rich neurobiological diversity, suggesting that there is not one general type of dopaminergic neuron, but rather a spectrum of different dopaminergic phenotypes. This heterogeneity on the cellular level could account for the observed differences in susceptibility of the dopaminergic systems to the PD disease process. In this review, we will summarize the long history from the first description of PD to the rationally derived DA replacement therapy, describe the basal neuroanatomical and neuropathological features of the different dopaminergic systems in health and PD, explore how neuroimaging techniques broadened our view of the dysfunctional dopaminergic systems in PD and discuss how dopaminergic replacement therapy ameliorates the classical motor symptoms but simultaneously induces a new set of hyperdopaminergic symptoms.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 123I-IBZM:
-
123I-iodobenzamide
- 18F-FDG:
-
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose
- AADC:
-
Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase
- DA:
-
Dopamine
- DAT:
-
Dopamine transporter
- ICD:
-
Impulse control disorder
- LB:
-
Lewy body
- LID:
-
l-dopa-induced dyskinesia
- LN:
-
Lewy neurite
- MCI:
-
Mild cognitive impairment
- MSA:
-
Multiple system atrophy
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- PDD:
-
Parkinson’s disease dementia
- PSP:
-
Progressive supranuclear palsy
- RBD:
-
REM sleep behavior disorder
- RRF:
-
Retrorubral field
- SN:
-
Substantia nigra
- STR:
-
Striatum
- TH:
-
Tyrosine hydroxylase
- UPDRS:
-
Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale
- VMAT2:
-
Vesicular monoamine transporter 2
- VTA:
-
Ventral tegmental area
References
Aarsland D, Brønnick K, Larsen JP, Tysnes OB, Alves G (2009a) Cognitive impairment in incident, untreated Parkinson disease: the Norwegian ParkWest study. Neurology 72(13):1121–1126
Aarsland D, Marsh L, Schrag A (2009b) Neuropsychiatric symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 24(15):2175–2186
Ahlskog JE, Muenter MD (2001) Frequency of levodopa-related dyskinesias and motor fluctuations as estimated from the cumulative literature. Mov Disord 16(3):448–458
Alberico SL, Cassell MD, Narayanan NS (2015) The vulnerable ventral tegmental area in Parkinson’s disease. Basal Ganglia 5(2–3):51–55
Apaydin H, Ahlskog JE, Parisi JE, Boeve BF, Dickson DW (2002) Parkinson disease neuropathology: later-developing dementia and loss of the levodopa response. Arch Neurol 59(1):102–112
Arai R, Karasawa N, Geffard M, Nagatsu T, Nagatsu I (1994) Immunohistochemical evidence that central serotonin neurons produce dopamine from exogenous l-dopa in the rat, with reference to the involvement of aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase. Brain Res 667(2):295–299
Arai R, Karasawa N, Geffard M, Nagatsu I (1995) l-dopa is converted to dopamine in serotonergic fibers of the striatum of the rat: a double-labeling immunofluorescence study. Neurosci Lett 195(3):195–198
Archibald NK, Clarke MP, Mosimann UP, Burn DJ (2009) The retina in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 132(Pt 5):1128–1145
Barone P, Poewe W, Albrecht S, Debieuvre C, Massey D, Rascol O, Tolosa E, Weintraub D (2010) Pramipexole for the treatment of depressive symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 9(6):573–580
Barraud Q, Obeid I, Aubert I, Barrière G, Contamin H, McGuire S, Ravenscroft P, Porras G, Tison F, Bezard E, Ghorayeb I (2010) Neuroanatomical study of the A11 diencephalospinal pathway in the non-human primate. PloS One 5(10):e13306
Bastide MF, Meissner WG, Picconi B, Fasano S, Fernagut P-O, Feyder M, Francardo V, Alcacer C, Ding Y, Brambilla R, Fisone G, Jon Stoessl A, Bourdenx M, Engeln M, Navailles S, Deurwaerdère P de, Ko WKD, Simola N, Morelli M, Groc L, Rodriguez M-C, Gurevich EV, Quik M, Morari M, Mellone M, Gardoni F, Tronci E, Guehl D, Tison F, Crossman AR, Kang UJ, Steece-Collier K, Fox S, Carta M, Angela Cenci M, Bézard E (2015) Pathophysiology of l-dopa-induced motor and non-motor complications in Parkinson’s disease. Progr Neurobiol 132:96–168
Bauckneht M, Chincarini A, Carli F de, Terzaghi M, Morbelli S, Nobili F, Arnaldi D (2018) Presynaptic dopaminergic neuroimaging in REM sleep behavior disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev 41:266–274
Bayersdorfer F, Voigt A, Schneuwly S, Botella JA (2010) Dopamine-dependent neurodegeneration in Drosophila models of familial and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 40(1):113–119
Beach TG, Adler CH, Sue LI, Peirce JB, Bachalakuri J, Dalsing-Hernandez JE, Lue LF, Caviness JN, Connor DJ, Sabbagh MN, Walker DG (2008) Reduced striatal tyrosine hydroxylase in incidental Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol 115(4):445–451
Ben-Jonathan N, Hnasko R (2001) Dopamine as a prolactin (PRL) inhibitor. Endocr Rev 22(6):724–763
Bergstrom BP, Garris PA (2003) “Passive stabilization” of striatal extracellular dopamine across the lesion spectrum encompassing the presymptomatic phase of Parkinson’s disease: a voltammetric study in the 6-OHDA-lesioned rat. J Neurochem 87(5):1224–1236
Biousse V, Skibell BC, Watts RL, Loupe DN, Drews-Botsch C, Newman NJ (2004) Ophthalmologic features of Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 62(2):177–180
Birkmayer W, Hornykiewicz O (1961) The l-3,4-dioxyphenylalanine (DOPA)-effect in Parkinson-akinesia. Wiener Klin Wochenschr 73:787–788
Björklund A, Dunnett SB (2007) Dopamine neuron systems in the brain: an update. Trends Neurosci 30(5):194–202
Björklund A, Hökfelt T (1984) Distributional of tyrosine hydroxylaseimmunoreactive neurons in the rat brain. In: Handbook of chemical neuroanatomy. (classical transmitters in the CNS, part I), vol 2, pp 277–379
Błaszczyk JW, Orawiec R, Duda-Kłodowska D, Opala G (2007) Assessment of postural instability in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Exp Brain Res 183(1):107–114
Bodkin JA, Amsterdam JD (2002) Transdermal selegiline in major depression: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study in outpatients. Am J Psychiatry 159(11):1869–1875
Bogerts B, Häntsch J, Herzer M (1983) A morphometric study of the dopamine-containing cell groups in the mesencephalon of normals, Parkinson patients, and schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 18(9):951–969
Bohnen NI, Müller MLTM, Zarzhevsky N, Koeppe RA, Bogan CW, Kilbourn MR, Frey KA, Albin RL (2011) Leucoaraiosis, nigrostriatal denervation and motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 134(Pt 8):2358–2365
Boller F, Mizutani T, Roessmann U, Gambetti P (1980) Parkinson disease, dementia, and Alzheimer disease: clinicopathological correlations. Ann Neurol 7(4):329–335
Bosboom JLW, Stoffers D, Wolters EC (2004) Cognitive dysfunction and dementia in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 111(10–11):1303–1315
Bowen FP, Kamienny RS, Burns MM, Yahr M (1975) Parkinsonism: effects of levodopa treatment on concept formation. Neurology 25(8):701–704
Boyce S, Rupniak NM, Steventon MJ, Iversen SD (1990) Nigrostriatal damage is required for induction of dyskinesias by l-dopa in squirrel monkeys. Clin Neuropharmacol 13(5):448–458
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, De Vos Rob AI, Steur ENJ, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24(2):197–211
Braak H, Ghebremedhin E, Rub U, Bratzke H, Del Tredici K (2004) Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res 318(1):121–134
Brichta L, Greengard P (2014) Molecular determinants of selective dopaminergic vulnerability in Parkinson’s disease: an update. Front Neuroanat 8:152
Broussolle E, Dentresangle C, Landais P, Garcia-Larrea L, Pollak P, Croisile B, Hibert O, Bonnefoi F, Galy G, Froment JC, Comar D (1999) The relation of putamen and caudate nucleus 18F-Dopa uptake to motor and cognitive performances in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 166(2):141–151
Brown RSE, Herbison AE, Grattan DR (2015) Effects of prolactin and lactation on A15 dopamine neurones in the rostral preoptic area of female mice. J Neuroendocrinol 27(9):708–717
Butcher L, Engel J, Fuxe K (1970) l-dopa induced changes in central monoamine neurons after peripheral decarboxylase inhibition. J Pharm Pharmacol 22(4):313–316
Caballol N, Martí MJ, Tolosa E (2007) Cognitive dysfunction and dementia in Parkinson disease. Mov Disord 22(Suppl 17):S358–S366
Carlsson A (1959) The occurrence, distribution and physiological role of catecholamines in the nervous system. Pharmacol Rev 11(2:part 2):490–493
Carlsson A, Lindqvist M, Magnusson T (1957) 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine and 5-hydroxytryptophan as reserpine antagonists. Nature 180(4596):1200
Carta M, Bezard E (2011) Contribution of pre-synaptic mechanisms to l-dopa-induced dyskinesia. Neuroscience 198:245–251
Carta M, Carlsson T, Kirik D, Björklund A (2007) Dopamine released from 5-HT terminals is the cause of l-dopa-induced dyskinesia in parkinsonian rats. Brain 130(Pt 7):1819–1833
Caudle WM, Richardson JR, Wang MZ, Taylor TN, Guillot TS, McCormack AL, Colebrooke RE, Di Monte DA, Emson PC, Miller GW (2007) Reduced vesicular storage of dopamine causes progressive nigrostriatal neurodegeneration. J Neurosci 27(30):8138–8148
Cave JW, Fujiwara N, Weibman AR, Baker H (2016) Cytoarchitectural changes in the olfactory bulb of Parkinson’s disease patients. NPJ Parkinson’s Dis 2:16011
Chan CS, Guzman JN, Ilijic E, Mercer JN, Rick C, Tkatch T, Meredith GE, Surmeier DJ (2007) ‘Rejuvenation’ protects neurons in mouse models of Parkinson’s disease. Nature 447:1081
Chan CS, Gertler TS, Surmeier DJ (2010) A molecular basis for the increased vulnerability of substantia nigra dopamine neurons in aging and Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 25(Suppl 1):S63–S70
Chaudhuri KR, Schapira AHV (2009) Non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: dopaminergic pathophysiology and treatment. Lancet Neurol 8(5):464–474
Chen Y-K, Lu J-Y, Chan DML, Mok VCT, Yeung MA, Wong KS, Ungvari GS, Tang WK (2010) Anxiety disorders in Chinese patients with Parkinson’s disease. Int J Psychiatry Med 40(1):97–107
Cheng H-C, Ulane CM, Burke RE (2010) Clinical progression in Parkinson disease and the neurobiology of axons. Ann Neurol 67(6):715–725
Chung CY, Seo H, Sonntag KC, Brooks A, Lin L, Isacson O (2005) Cell type-specific gene expression of midbrain dopaminergic neurons reveals molecules involved in their vulnerability and protection. Hum Mol Genet 14(13):1709–1725
Cilia R, Siri C, Marotta G, Isaias IU, Gaspari D de, Canesi M, Pezzoli G, Antonini A (2008) Functional abnormalities underlying pathological gambling in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 65(12):1604–1611
Clarkson J, Herbison AE (2011) Dual phenotype kisspeptin-dopamine neurones of the rostral periventricular area of the third ventricle project to gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neurones. J Neuroendocrinol 23(4):293–301
Clemens S, Hochman S (2004) Conversion of the modulatory actions of dopamine on spinal reflexes from depression to facilitation in D3 receptor knock-out mice. J Neurosci 24(50):11337–11345
Collette F, van der Linden M, Laureys S, Delfiore G, Degueldre C, Luxen A, Salmon E (2005) Exploring the unity and diversity of the neural substrates of executive functioning. Hum Brain Mapp 25(4):409–423
Compta Y, Parkkinen L, O’Sullivan SS, Vandrovcova J, Holton JL, Collins C, Lashley T, Kallis C, Williams DR, Silva R de, Lees AJ, Revesz T (2011) Lewy- and Alzheimer-type pathologies in Parkinson’s disease dementia: which is more important? Brain 134(Pt 5):1493–1505
Cools R, Barker RA, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW (2001) Enhanced or impaired cognitive function in Parkinson’s disease as a function of dopaminergic medication and task demands. Cerebral Cortex 11(12):1136–1143 (New York, 1991)
Cools R, Clark L, Robbins TW (2004) Differential responses in human striatum and prefrontal cortex to changes in object and rule relevance. J Neurosci 24(5):1129–1135
Cotzias GC, Papavasiliou PS, Gellene R (1969) Modification of Parkinsonism—chronic treatment with l-dopa. N Engl J Med 280(7):337–345
Dahlstroem A, Fuxe K (1964) Evidence for the existence of monoamine-containing neurons in the central nervous system. I. Demonstration of monoamines in the cell bodies of brain stem neurons. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 232:1–55
Damier P, Hirsch EC, Agid Y, Graybiel AM (1999) The substantia nigra of the human brain. II. Patterns of loss of dopamine-containing neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 122(Pt 8):1437–1448
DelleDonne A, Klos KJ, Fujishiro H, Ahmed Z, Parisi JE, Josephs KA, Frigerio R, Burnett M, Wszolek ZK, Uitti RJ, Ahlskog JE, Dickson DW (2008) Incidental Lewy body disease and preclinical Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 65(8):1074–1080
Di Monte DA, McCormack A, Petzinger G, Janson AM, Quik M, Langston WJ (2000) Relationship among nigrostriatal denervation, parkinsonism, and dyskinesias in the MPTP primate model. Mov Disord 15(3):459–466
Dickson DW, Fujishiro H, DelleDonne A, Menke J, Ahmed Z, Klos KJ, Josephs KA, Frigerio R, Burnett M, Parisi JE, Ahlskog JE (2008) Evidence that incidental Lewy body disease is pre-symptomatic Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 115(4):437–444
Dickson DW, Braak H, Duda JE, Duyckaerts C, Gasser T, Halliday GM, Hardy J, Leverenz JB, Del Tredici K, Wszolek ZK, Litvan I (2009) Neuropathological assessment of Parkinson’s disease: refining the diagnostic criteria. Lancet Neurol 8(12):1150–1157
Dissanayaka NNW, Sellbach A, Matheson S, O’Sullivan JD, Silburn PA, Byrne GJ, Marsh R, Mellick GD (2010) Anxiety disorders in Parkinson’s disease: prevalence and risk factors. Mov Disord 25(7):838–845
Doty RL, Deems DA, Stellar S (1988) Olfactory dysfunction in parkinsonism: a general deficit unrelated to neurologic signs, disease stage, or disease duration. Neurology 38(8):1237–1244
Double KL, Reyes S, Werry EL, Halliday GM (2010) Selective cell death in neurodegeneration: why are some neurons spared in vulnerable regions? Progr Neurobiol 92(3):316–329
Downes JJ, Roberts AC, Sahakian BJ, Evenden JL, Morris RG, Robbins TW (1989) Impaired extra-dimensional shift performance in medicated and unmedicated Parkinson’s disease: evidence for a specific attentional dysfunction. Neuropsychologia 27(11–12):1329–1343
Ebersbach G, Moreau C, Gandor F, Defebvre L, Devos D (2013) Clinical syndromes: Parkinsonian gait. Mov Disord 28(11):1552–1559
Ehringer H, Hornykiewicz O (1960) Distribution of noradrenaline and dopamine (3-hydroxytyramine) in the human brain and their behavior in diseases of the extrapyramidal system. Klin Wochenschr 38:1236–1239
Evans AH, Pavese N, Lawrence AD, Tai YF, Appel S, Doder M, Brooks DJ, Lees AJ, Piccini P (2006) Compulsive drug use linked to sensitized ventral striatal dopamine transmission. Ann Neurol 59(5):852–858
Fahn S, Libsch LR, Cutler RW (1971) Monoamines in the human neostriatum: topographic distribution in normals and in Parkinson’s disease and their role in akinesia, rigidity, chorea, and tremor. J Neurol Sci 14(4):427–455
Fearnley JM, Lees AJ (1991) Ageing and Parkinson’s disease: substantia nigra regional selectivity. Brain 114(Pt 5):2283–2301
Fleetwood-Walker SM, Hope PJ, Mitchell R (1988) Antinociceptive actions of descending dopaminergic tracts on cat and rat dorsal horn somatosensory neurones. J Physiol 399(1):335–348
Flückiger E, Müller EE, Thorner MO, Halász B, Fuxe K, Agnati LF, Kalia M, Goldstein M, Andersson K, Härfstrand A, Clark B (1985) The dopaminergic system, vol 1. Springer, Berlin
Gandhi S, Vaarmann A, Yao Z, Duchen MR, Wood NW, Abramov AY (2012) Dopamine induced neurodegeneration in a PINK1 model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 7(5):e37564
Garris PA, Walker QD, Wightman RM (1997) Dopamine release and uptake rates both decrease in the partially denervated striatum in proportion to the loss of dopamine terminals. Brain Res 753(2):225–234
Gelb DJ, Oliver E, Gilman S (1999) Diagnostic criteria for Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 56(1):33–39
Gerlach M, Double K, Arzberger T, Leblhuber F, Tatschner T, Riederer P (2003) Dopamine receptor agonists in current clinical use: comparative dopamine receptor binding profiles defined in the human striatum. J Neural Transm 110(10):1119–1127
German DC, Manaye K, Smith WK, Woodward DJ, Saper CB (1989) Midbrain dopaminergic cell loss in Parkinson’s disease: computer visualization. Ann Neurol 26(4):507–514
Gibb WRG, Lees AJ (1989) The significance of the lewy body in the diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 15(1):27–44
Gibb WR, Lees AJ (1991) Anatomy, pigmentation, ventral and dorsal subpopulations of the substantia nigra, and differential cell death in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 54(5):388–396
Goldstein DS, Holmes C, Bentho O, Sato T, Moak J, Sharabi Y, Imrich R, Conant S, Eldadah BA (2008) Biomarkers to detect central dopamine deficiency and distinguish Parkinson disease from multiple system atrophy. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 14(8):600–607
Gotham AM, Brown RG, Marsden CD (1988) ‘Frontal’ cognitive function in patients with Parkinson’s disease ‘on’and ‘off’ levodopa. Brain 111(2):299–321
Greffard S, Verny M, Bonnet A-M, Beinis J-Y, Gallinari C, Meaume S, Piette F, Hauw J-J, Duyckaerts C (2006) Motor score of the Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale as a good predictor of Lewy body-associated neuronal loss in the substantia nigra. Arch Neurol 63(4):584–588
Gurevich E (1999) Distribution of dopamine D3 receptor expressing neurons in the human forebrain comparison with D2 receptor expressing neurons. Neuropsychopharmacology 20(1):60–80
Haehner A, Hummel T, Reichmann H (2011) Olfactory loss in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis 2011:1–6
Hagenah J, Klein C, Sieberer M, Vieregge P (1999) Exogenous levodopa is not toxic to elderly subjects with non-parkinsonian movement disorders: further clinical evidence. J Neural Transm 106(3–4):301–307
Halász N, Johansson O, Hökfelt T, Ljungdahl Å, Goldstein M (1981) Immunohistochemical identification of two types of dopamine neuron in the rat olfactory bulb as seen by serial sectioning. J Neurocytol 10(2):251–259
Halliday GM, McRitchie DA, Cartwright H, Pamphlett R, Hely MA, Morris JGL (1996) Midbrain neuropathology in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease and diffuse Lewy body disease. J Clin Neurosci 3(1):52–60
Halliday GM, Leverenz JB, Schneider JS, Adler CH (2014) The neurobiological basis of cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 29(5):634–650
Harnois C, Di Paolo T (1990) Decreased dopamine in the retinas of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 31(11):2473–2475
Hauser RA, Rascol O, Korczyn AD, Jon Stoessl A, Watts RL, Poewe W, Deyn PP de, Lang AE (2007) Ten-year follow-up of Parkinson’s disease patients randomized to initial therapy with ropinirole or levodopa. Mov Disord 22(16):2409–2417
Heller J, Brcina N, Dogan I, Holtbernd F, Romanzetti S, Schulz JB, Schiefer J, Reetz K (2017) Brain imaging findings in idiopathic REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD)—a systematic review on potential biomarkers for neurodegeneration. Sleep Med Rev 34:23–33
Hellwig S, Amtage F, Kreft A, Buchert R, Winz OH, Vach W, Spehl TS, Rijntjes M, Hellwig B, Weiller C, Winkler C, Weber WA, Tüscher O, Meyer PT (2012) 18FFDG-PET is superior to 123IIBZM-SPECT for the differential diagnosis of parkinsonism. Neurology 79(13):1314–1322
Hilker R, Schweitzer K, Coburger S, Ghaemi M, Weisenbach S, Jacobs AH, Rudolf J, Herholz K, Heiss W-D (2005) Nonlinear progression of Parkinson disease as determined by serial positron emission tomographic imaging of striatal fluorodopa F 18 activity. Arch Neurol 62(3):378–382
Hirsch E, Graybiel AM, Agid YA (1988) Melanized dopaminergic neurons are differentially susceptible to degeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Nature 334:345
Hirsch EC, Faucheux B, Damier P, Mouatt-Prigent A, Agid Y (1997) Neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 50:79–88
Ho AK, Iansek R, Marigliani C, Bradshaw JL, Gates S (1999) Speech impairment in a large sample of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Behav Neurol 11(3):131–137
Hobson P, Meara J (2015) Mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease and its progression onto dementia: a 16-year outcome evaluation of the Denbighshire cohort. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 30(10):1048–1055
Holthoff-Detto VA, Kessler J, Herholz K, Bonner H, Pietrzyk U, Wurker M, Ghaemi M, Wienhard K, Wagner R, Heiss W-D (1997) Functional effects of striatal dysfunction in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 54(2):145–150
Hoogland J, Boel JA, Bie RMA de, Geskus RB, Schmand BA, Dalrymple-Alford JC, Marras C, Adler CH, Goldman JG, Tröster AI, Burn DJ, Litvan I, Geurtsen GJ (2017) Mild cognitive impairment as a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease dementia. Mov Disord 32(7):1056–1065
Hornykiewicz O (1963) The tropical localization and content of noradrenalin and dopamine (3-hydroxytyramine) in the substantia nigra of normal persons and patients with Parkinson’s disease. Wiener Klin Wochenschr 75:309–312
Hsiao I-T, Weng Y-H, Hsieh C-J, Lin W-Y, Wey S-P, Kung M-P, Yen T-C, Lu C-S, Lin K-J (2014) Correlation of Parkinson disease severity and 18F-DTBZ positron emission tomography. JAMA Neurol 71(6):758–766
Huisman E, Uylings HBM, Hoogland PV (2004) A 100% increase of dopaminergic cells in the olfactory bulb may explain hyposmia in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 19(6):687–692
Huisman E, Uylings HBM, Hoogland PV (2008) Gender-related changes in increase of dopaminergic neurons in the olfactory bulb of Parkinson’s disease patients. Mov Disord 23(10):1407–1413
Hurtig HI, Trojanowski JQ, Galvin J, Ewbank D, Schmidt ML, Lee VM-Y, Clark CM, Glosser G, Stern MB, Gollomp SM, Arnold SE (2000) Alpha-synuclein cortical Lewy bodies correlate with dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 54(10):1916–1921
Iranzo A, Lomeña F, Stockner H, Valldeoriola F, Vilaseca I, Salamero M, Molinuevo JL, Serradell M, Duch J, Pavía J, Gallego J, Seppi K, Högl B, Tolosa E, Poewe W, Santamaria J (2010) Decreased striatal dopamine transporter uptake and substantia nigra hyperechogenicity as risk markers of synucleinopathy in patients with idiopathic rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder: a prospective study. Lancet Neurol 9(11):1070–1077
Iranzo A, Tolosa E, Gelpi E, Molinuevo JL, Valldeoriola F, Serradell M, Sanchez-Valle R, Vilaseca I, Lomeña F, Vilas D, LLadó A, Gaig C, Santamaria J (2013) Neurodegenerative disease status and post-mortem pathology in idiopathic rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder. An observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol 12(5):443–453
Irwin DJ, White MT, Toledo JB, Xie SX, Robinson JL, van Deerlin V, Lee VM-Y, Leverenz JB, Montine TJ, Duda JE, Hurtig HI, Trojanowski JQ (2012) Neuropathologic substrates of Parkinson disease dementia. Ann Neurol 72(4):587–598
Ito K, Nagano-Saito A, Kato T, Arahata Y, Nakamura A, Kawasumi Y, Hatano K, Abe Y, Yamada T, Kachi T, Brooks DJ (2002) Striatal and extrastriatal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease with dementia: a 6-18Ffluoro-l-dopa PET study. Brain 125(Pt 6):1358–1365
Jackson CR, Ruan G-X, Aseem F, Abey J, Gamble K, Stanwood G, Palmiter RD, Iuvone PM, McMahon DG (2012) Retinal dopamine mediates multiple dimensions of light-adapted vision. J Neurosci 32(27):9359–9368
Jankovic J (2008) Parkinson’s disease: clinical features and diagnosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79(4):368–376
Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y (1980) Is the mesocortical dopaminergic system involved in Parkinson disease? Neurology 30(12):1326
Javoy-Agid F, Ruberg M, Taquet H, Bokobza B, Agid Y, Gaspar P, Berger B, N’Guyen-Legros J, Alvarez C, Gray F (1984) Biochemical neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease. Adv Neurol 40:189–198
Jenner P (2008) Preventing and controlling dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease—a view of current knowledge and future opportunities. Mov Disord 23(Suppl 3):S585–S598
Jong GJ de, Meerwaldt JD, Schmitz PI (1987) Factors that influence the occurrence of response variations in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 22(1):4–7
Joutsa J, Johansson J, Seppanen M, Noponen T, Kaasinen V (2015) Dorsal-to-ventral shift in midbrain dopaminergic projections and increased thalamic/raphe serotonergic function in early Parkinson disease. J Nucl Med 56(7):1036–1041
Juh R, Kim J, Moon D, Choe B, Suh T (2004) Different metabolic patterns analysis of parkinsonism on the 18F-FDG PET. Eur J Radiol 51(3):223–233
Kägi G, Bhatia KP, Tolosa E (2010) The role of DAT-SPECT in movement disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81(1):5–12
Kalia LV, Lang AE (2015) Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 386(9996):896–912
Karson CN (1983) Spontaneous eye-blink rates and dopaminergic systems. Brain 106(3):643–653
Kempster PA, Gibb WR, Stern GM, Lees AJ (1989) Asymmetry of substantia nigra neuronal loss in Parkinson’s disease and its relevance to the mechanism of levodopa related motor fluctuations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52(1):72–76
Kish SJ, Shannak K, Hornykiewicz O (1988) Uneven pattern of dopamine loss in the striatum of patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Pathophysiologic and clinical implications. N Engl J Med 318(14):876–880
Koller WC, Glatt S, Vetere-Overfield B, Hassanein R (1989) Falls and Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neuropharmacol 12(2):98–105
Kordower JH, Olanow CW, Dodiya HB, Chu Y, Beach TG, Adler CH, Halliday GM, Bartus RT (2013) Disease duration and the integrity of the nigrostriatal system in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 136(Pt 8):2419–2431
Korshunov KS, Blakemore LJ, Trombley PQ (2017) Dopamine: a modulator of circadian rhythms in the central nervous system. Front Cell Neurosci 11:91
Kulisevsky J (2000) Role of dopamine in learning and memory: implications for the treatment of cognitive dysfunction in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Drugs Aging 16(5):365–379
Kulisevsky J, Avila A, Barbanoj M, Antonijoan R, Berthier ML, Gironell A (1996) Acute effects of levodopa on neuropsychological performance in stable and fluctuating Parkinson’s disease patients at different levodopa plasma levels. Brain 119(Pt 6):2121–2132
Kulisevsky J, Pagonabarraga J, Pascual-Sedano B, García-Sánchez C, Gironell A (2008) Prevalence and correlates of neuropsychiatric symptoms in Parkinson’s disease without dementia. Mov Disord 23(13):1889–1896
La Fuente-Fernández R de, Sossi V, Huang Z, Furtado S, Lu J-Q, Calne DB, Ruth TJ, Stoessl AJ (2004) Levodopa-induced changes in synaptic dopamine levels increase with progression of Parkinson’s disease: implications for dyskinesias. Brain 127(Pt 12):2747–2754
Lange KW, Robbins TW, Marsden CD, James M, Owen AM, Paul GM (1992) L-dopa withdrawal in Parkinson’s disease selectively impairs cognitive performance in tests sensitive to frontal lobe dysfunction. Psychopharmacology 107(2–3):394–404
Langston JW, Forno LS (1978) The hypothalamus in Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol 3(2):129–133
Lee H-J, Baek SM, Ho D-H, Suk J-E, Cho E-D, Lee S-J (2011) Dopamine promotes formation and secretion of non-fibrillar alpha-synuclein oligomers. Exp Mol Med 43(4):216–222
Lemke MR, Brecht HM, Koester J, Kraus PH, Reichmann H (2005) Anhedonia, depression, and motor functioning in Parkinson’s disease during treatment with pramipexole. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 17(2):214–220
Lewek MD, Poole R, Johnson J, Halawa O, Huang X (2010) Arm swing magnitude and asymmetry during gait in the early stages of Parkinson’s disease. Gait Posture 31(2):256–260
Lewis SJ, Pavese N, Rivero-Bosch M, Eggert K, Oertel W, Mathias CJ, Brooks DJ, Gerhard A (2012) Brain monoamine systems in multiple system atrophy: a positron emission tomography study. Neurobiol Dis 46(1):130–136
Lindvall O, Björklund A, Skagerberg G (1983) Dopamine-containing neurons in the spinal cord: anatomy and some functional aspects. Ann Neurol 14(3):255–260
Lohr KM, Bernstein AI, Stout KA, Dunn AR, Lazo CR, Alter SP, Wang M, Li Y, Fan X, Hess EJ, Yi H, Vecchio LM, Goldstein DS, Guillot TS, Salahpour A, Miller GW (2014) Increased vesicular monoamine transporter enhances dopamine release and opposes Parkinson disease-related neurodegeneration in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(27):9977–9982
Lopez IC, Ruiz PJG, Del Pozo SVF, Bernardos VS (2010) Motor complications in Parkinson’s disease: ten year follow-up study. Mov Disord 25(16):2735–2739
Lotharius J (2002) Impaired dopamine storage resulting from alpha-synuclein mutations may contribute to the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 11(20):2395–2407
Luquin MR, Scipioni O, Vaamonde J, Gershanik O, Obeso JA (1992) Levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease: clinical and pharmacological classification. Mov Disord 7(2):117–124
Mamikonyan E, Siderowf AD, Duda JE, Potenza MN, Horn S, Stern MB, Weintraub D (2008) Long-term follow-up of impulse control disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 23(1):75–80
Martinez-Martin P, Schapira AHV, Stocchi F, Sethi K, Odin P, MacPhee G, Brown RG, Naidu Y, Clayton L, Abe K, Tsuboi Y, MacMahon D, Barone P, Rabey M, Bonuccelli U, Forbes A, Breen K, Tluk S, Olanow CW, Thomas S, Rye D, Hand A, Williams AJ, Ondo W, Chaudhuri KR (2007) Prevalence of nonmotor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease in an international setting; study using nonmotor symptoms questionnaire in 545 patients. Mov Disord 22(11):1623–1629
Mattila PM, Rinne JO, Helenius H, Dickson DW, Röyttä M (2000) Alpha-synuclein-immunoreactive cortical Lewy bodies are associated with cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 100(3):285–290
Mattila PM, Röyttä M, Lönnberg P, Marjamäki P, Helenius H, Rinne JO (2001) Choline acetyltransferase activity and striatal dopamine receptors in Parkinson’s disease in relation to cognitive impairment. Acta Neuropathol 102(2):160–166
Matzuk MM, Saper CB (1985) Preservation of hypothalamic dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 18(5):552–555
McRitchie DA, Hardman CD, Halliday GM (1996) Cytoarchitectural distribution of calcium binding proteins in midbrain dopaminergic regions of rats and humans. J Comp Neurol 364(1):121–150
McRitchie DA, Cartwright HR, Halliday GM (1997) Specific A10 dopaminergic nuclei in the midbrain degenerate in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 144(1):202–213
Meles SK, Vadasz D, Renken RJ, Sittig-Wiegand E, Mayer G, Depboylu C, Reetz K, Overeem S, Pijpers A, Reesink FE, van Laar T, Heinen L, Teune LK, Hoffken H, Luster M, Kesper K, Adriaanse SM, Booij J, Leenders KL, Oertel WH (2017) FDG PET, dopamine transporter SPECT, and olfaction: combining biomarkers in REM sleep behavior disorder. Mov Disord 32(10):1482–1486
Michalowska M, Fiszer U, Krygowska-Wajs A, Owczarek K (2005) Falls in Parkinson’s disease. Causes and impact on patients’ quality of life. Funct Neurol 20(4):163–168
Monchi O, Petrides M, Petre V, Worsley K, Dagher A (2001) Wisconsin card sorting revisited: distinct neural circuits participating in different stages of the task identified by event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosci 21(19):7733–7741
Monchi O, Petrides M, Strafella AP, Worsley KJ, Doyon J (2006) Functional role of the basal ganglia in the planning and execution of actions. Ann Neurol 59(2):257–264
Montague PR, Hyman SE, Cohen JD (2004) Computational roles for dopamine in behavioural control. Nature 431:760
Moore RY, Whone AL, Brooks DJ (2008) Extrastriatal monoamine neuron function in Parkinson’s disease: an 18F-dopa PET study. Neurobiol Dis 29(3):381–390
Morris ME, Iansek R, Matyas TA, Summers JJ (1994) The pathogenesis of gait hypokinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 117(5):1169–1181
Morrish PK, Sawle GV, Brooks DJ (1995) Clinical and 18F dopa PET findings in early Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 59(6):597–600
Mosharov EV, Borgkvist A, Sulzer D (2015) Presynaptic effects of levodopa and their possible role in dyskinesia. Mov Disord 30(1):45–53
Mundiñano I-C, Caballero M-C, Ordóñez C, Hernandez M, DiCaudo C, Marcilla I, Erro M-E, Tuñon M-T, Luquin M-R (2011) Increased dopaminergic cells and protein aggregates in the olfactory bulb of patients with neurodegenerative disorders. Acta Neuropathol 122(1):61–74
Muslimovic D, Post B, Speelman JD, Schmand B (2005) Cognitive profile of patients with newly diagnosed Parkinson disease. Neurology 65(8):1239–1245
Nandhagopal R, Kuramoto L, Schulzer M, Mak E, Cragg J, Lee CS, McKenzie J, McCormick S, Samii A, Troiano A, Ruth TJ, Sossi V, La Fuente-Fernandez R de, Calne DB, Stoessl AJ (2009) Longitudinal progression of sporadic Parkinson’s disease: a multi-tracer positron emission tomography study. Brain 132(Pt 11):2970–2979
Natale ER de, Wilson H, Pagano G, Politis M (2018) Imaging transplantation in movement disorders. Int Rev Neurobiol 143:213–263
Nedergaard S, Flatman JA, Engberg I (1993) Nifedipine- and omega-conotoxin-sensitive Ca2+ conductances in guinea-pig substantia nigra pars compacta neurones. J Physiol 466:727–747
Nègre-Pagès L, Grandjean H, Lapeyre-Mestre M, Montastruc JL, Fourrier A, Lépine JP, Rascol O (2010) Anxious and depressive symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: the French cross-sectionnal DoPaMiP study. Mov Disord 25(2):157–166
Nguyen-Legros J (1988) Functional neuroarchitecture of the retina: hypothesis on the dysfunction of retinal dopaminergic circuitry in Parkinson’s disease. Surg Radiol Anat 10(2):137–144
Nuti A, Ceravolo R, Piccinni A, Dell’Agnello G, Bellini G, Gambaccini G, Rossi C, Logi C, Dell’Osso L, Bonuccelli U (2004) Psychiatric comorbidity in a population of Parkinson’s disease patients. Eur J Neurol 11(5):315–320
O’Sullivan SS, Wu K, Politis M, Lawrence AD, Evans AH, Bose SK, Djamshidian A, Lees AJ, Piccini P (2011) Cue-induced striatal dopamine release in Parkinson’s disease-associated impulsive-compulsive behaviours. Brain 134(Pt 4):969–978
Obeso JA, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Lanciego JL, Rodriguez Diaz M (2004) How does Parkinson’s disease begin? The role of compensatory mechanisms. Trends Neurosci 27(3):125–127 (author reply 127–8)
Oertel WH (2017) Recent advances in treating Parkinson’s disease. F1000Research 6:260
Ortuño-Lizarán I, Beach TG, Serrano GE, Walker DG, Adler CH, Cuenca N (2018) Phosphorylated α-synuclein in the retina is a biomarker of Parkinson’s disease pathology severity. Mov Disord 33(8):1315–1324
Ota M, Nakata Y, Ito K, Kamiya K, Ogawa M, Murata M, Obu S, Kunugi H, Sato N (2013) Differential diagnosis tool for parkinsonian syndrome using multiple structural brain measures. Comput Math Methods Med 2013:1–10
Otsuka M, Ichiya Y, Kuwabara Y, Hosokawa S, Sasaki M, Yoshida T, Fukumura T, Masuda K, Kato M (1996) Differences in the reduced 18F-Dopa uptakes of the caudate and the putamen in Parkinson’s disease: correlations with the three main symptoms. J Neurol Sci 136(1–2):169–173
Owen AM, Roberts AC, Hodges JR, Summers BA, Polkey CE, Robbins TW (1993) Contrasting mechanisms of impaired attentional set-shifting in patients with frontal lobe damage or Parkinson’s disease. Brain 116(Pt 5):1159–1175
Owen AM, Sahakian BJ, Hodges JR, Summers BA, Polkey CE, Robbins TW (1995) Dopamine-dependent frontostriatal planning deficits in early Parkinson’s disease. Neuropsychology 9(1):126–140
Pacelli C, Giguère N, Bourque M-J, Lévesque M, Slack RS, Trudeau L-É (2015) Elevated mitochondrial bioenergetics and axonal arborization size are key contributors to the vulnerability of dopamine neurons. Curr Biol 25(18):2349–2360
Pahwa R, Stacy MA, Factor SA, Lyons KE, Stocchi F, Hersh BP, Elmer LW, Truong DD, Earl NL (2007) Ropinirole 24-hour prolonged release: randomized, controlled study in advanced Parkinson disease. Neurology 68(14):1108–1115
Palkovits M, Záborszky L, Feminger A, Mezey É, Fekete MIK, Herman JP, Kanyicska B, Szabó D (1980) Noradrenergic innervation of the rat hypothalamus: experimental biochemical and electron microscopic studies. Brain Res 191(1):161–171
Pallone JA (2007) Introduction to Parkinson’s disease. Dis Month 53(4):195–199
Pandey S, Srivanitchapoom P (2017) Levodopa-induced dyskinesia: clinical features, pathophysiology, and medical management. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 20(3):190–198
Parent A, Fortin M, Côté PY, Cicchetti F (1996) Calcium-binding proteins in primate basal ganglia. Neurosci Res 25(4):309–334
Parkinson J (1817) An essay on the shaking palsy. Whittingham and Rowland for Sherwood, London
Paulus W, Jellinger K (1991) The neuropathologic basis of different clinical subgroups of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 50(6):743–755
Pavese N, Evans AH, Tai YF, Hotton G, Brooks DJ, Lees AJ, Piccini P (2006) Clinical correlates of levodopa-induced dopamine release in Parkinson disease: a PET study. Neurology 67(9):1612–1617
Pavese N, Moore RY, Scherfler C, Khan NL, Hotton G, Quinn NP, Bhatia KP, Wood NW, Brooks DJ, Lees AJ, Piccini P (2010) In vivo assessment of brain monoamine systems in parkin gene carriers: a PET study. Exp Neurol 222(1):120–124
Pavese N, Rivero-Bosch M, Lewis SJ, Whone AL, Brooks DJ (2011) Progression of monoaminergic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: a longitudinal 18F-dopa PET study. NeuroImage 56(3):1463–1468
Paviour DC, Price SL, Stevens JM, Lees AJ, Fox NC (2005) Quantitative MRI measurement of superior cerebellar peduncle in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 64(4):675–679
Pedersen KF, Alves G, Aarsland D, Larsen JP (2009) Occurrence and risk factors for apathy in Parkinson disease: a 4-year prospective longitudinal study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80(11):1279–1282
Pedersen KF, Larsen JP, Tysnes O-B, Alves G (2017) Natural course of mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease: a 5-year population-based study. Neurology 88(8):767–774
Perez XA, Parameswaran N, Huang LZ, O’Leary KT, Quik M (2008) Pre-synaptic dopaminergic compensation after moderate nigrostriatal damage in non-human primates. J Neurochem 105(5):1861–1872
Perry EK, McKeith I, Thompson P, Marshall E, Kerwin J, Jabeen S, Edwardson JA, Ince P, Blessed G, Irving D, Perry RH (1991) Topography, extent, and clinical relevance of neurochemical deficits in dementia of Lewy body type, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 640(1):197–202
Piccini P, Burn DJ, Ceravolo R, Maraganore D, Brooks DJ (1999) The role of inheritance in sporadic Parkinson’s disease: evidence from a longitudinal study of dopaminergic function in twins. Ann Neurol 45(5):577–582
Pifl C, Rajput A, Reither H, Blesa J, Cavada C, Obeso JA, Rajput AH, Hornykiewicz O (2014) Is Parkinson’s disease a vesicular dopamine storage disorder? Evidence from a study in isolated synaptic vesicles of human and nonhuman primate striatum. J Neurosci 34(24):8210–8218
Pillon B, Dubois B, Bonnet AM, Esteguy M, Guimaraes J, Vigouret JM, Lhermitte F, Agid Y (1989) Cognitive slowing in Parkinson’s disease fails to respond to levodopa treatment: the 15-objects test. Neurology 39(6):762–768
Politis M (2014) Neuroimaging in Parkinson disease: from research setting to clinical practice. Nat Rev Neurol 10(12):708–722
Politis M, Piccini P, Pavese N, Koh S-B, Brooks DJ (2008) Evidence of dopamine dysfunction in the hypothalamus of patients with Parkinson’s disease: an in vivo 11C-raclopride PET study. Exp Neurol 214(1):112–116
Post MR, Lieberman OJ, Mosharov EV (2018) Can interactions between α-synuclein, dopamine and calcium explain selective neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease? Front Neurosci 12:161
Postuma RB, Lang AE, Gagnon JF, Pelletier A, Montplaisir JY (2012) How does parkinsonism start? Prodromal parkinsonism motor changes in idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder. Brain 135(Pt 6):1860–1870
Postuma RB, Berg D, Stern M, Poewe W, Olanow CW, Oertel W, Obeso J, Marek K, Litvan I, Lang AE, Halliday G, Goetz CG, Gasser T, Dubois B, Chan P, Bloem BR, Adler CH, Deuschl G (2015) MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 30(12):1591–1601
Price KS, Farley IJ, Hornykiewicz O (1978) Neurochemistry of Parkinson’s disease: relation between striatal and limbic dopamine. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 19:293–300
Price S, Paviour D, Scahill R, Stevens J, Rossor M, Lees A, Fox N (2004) Voxel-based morphometry detects patterns of atrophy that help differentiate progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson’s disease. NeuroImage 23(2):663–669
Puopolo M, Raviola E, Bean BP (2007) Roles of subthreshold calcium current and sodium current in spontaneous firing of mouse midbrain dopamine neurons. J Neurosci 27(3):645–656
Rabinovici GD, Stephens ML, Possin KL (2015) Executive dysfunction. Continuum: lifelong learning in neurology. Behav Neurol Neuropsychiatry 21(3):646–659
Rajput AH, Stern W, Laverty WH (1984) Chronic low-dose levodopa therapy in Parkinson’s disease: an argument for delaying levodopa therapy. Neurology 34(8):991–996
Reichmann H, Brecht HM, Kraus PH, Lemke MR (2002) Pramipexol bei der Parkinson-Krankheit. Ergebnisse einer Anwendungsbeobachtung (Pramipexole in Parkinson disease. Results of a treatment observation). Der Nervenarzt 73(8):745–750
Reichmann H, Brecht MH, Köster J, Kraus PH, Lemke MR (2003) Pramipexole in routine clinical practice: a prospective observational trial in Parkinson’s disease. CNS Drugs 17(13):965–973
Reijnders JSAM, Ehrt U, Weber WEJ, Aarsland D, Leentjens AFG (2008) A systematic review of prevalence studies of depression in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 23(2):183–189 (quiz 313)
Remy P, Doder M, Lees A, Turjanski N, Brooks D (2005) Depression in Parkinson’s disease: loss of dopamine and noradrenaline innervation in the limbic system. Brain 128(Pt 6):1314–1322
Ribelayga C, Cao Y, Mangel SC (2008) The circadian clock in the retina controls rod-cone coupling. Neuron 59(5):790–801
Rinne JO, Rummukainen J, Paljärvi L, Rinne UK (1989) Dementia in Parkinson’s disease is related to neuronal loss in the medial substantia nigra. Ann Neurol 26(1):47–50
Rinne JO, Portin R, Ruottinen H, Nurmi E, Bergman J, Haaparanta M, Solin O (2000) Cognitive impairment and the brain dopaminergic system in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 57(4):470
Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Jahanshahi M, Krack P, Litvan I, Macias R, Bezard E, Obeso JA (2009) Initial clinical manifestations of Parkinson’s disease: features and pathophysiological mechanisms. Lancet Neurol 8(12):1128–1139
Rowe J, Stephan KE, Friston K, Frackowiak R, Lees A, Passingham R (2002) Attention to action in Parkinson’s disease: impaired effective connectivity among frontal cortical regions. Brain 125(Pt 2):276–289
Rylander D, Parent M, O’Sullivan SS, Dovero S, Lees AJ, Bezard E, Descarries L, Cenci MA (2010) Maladaptive plasticity of serotonin axon terminals in levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Ann Neurol 68(5):619–628
Scatton B, Javoy-Agid F, Rouquier L, Dubois B, Agid Y (1983) Reduction of cortical dopamine, noradrenaline, serotonin and their metabolites in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 275(2):321–328
Schenck CH, Boeve BF, Mahowald MW (2013) Delayed emergence of a parkinsonian disorder or dementia in 81% of older men initially diagnosed with idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder: a 16-year update on a previously reported series. Sleep Med 14(8):744–748
Scherfler C, Schwarz J, Antonini A, Grosset D, Valldeoriola F, Marek K, Oertel W, Tolosa E, Lees AJ, Poewe W (2007) Role of DAT-SPECT in the diagnostic work up of parkinsonism. Mov Disord 22(9):1229–1238
Schneider JS (1989) Levodopa-induced dyskinesias in parkinsonian monkeys: relationship to extent of nigrostriatal damage. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 34(1):193–196
Schrag A (2000) What contributes to quality of life in patients with Parkinson’s disease? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 69(3):308–312
Segura-Aguilar J, Paris I, Muñoz P, Ferrari E, Zecca L, Zucca FA (2014) Protective and toxic roles of dopamine in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 129(6):898–915
Seibyl JP, Marek KL, Quinlan D, Sheff K, Zoghbi S, Zea-Ponce Y, Baldwin RM, Fussell B, Smith EO, Charney DS, van Dyck C (1995) Decreased single-photon emission computed tomographic 123Ibeta-CIT striatal uptake correlates with symptom severity in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 38(4):589–598
Seidel K, Mahlke J, Siswanto S, Krüger R, Heinsen H, Auburger G, Bouzrou M, Grinberg LT, Wicht H, Korf H-W, den Dunnen W, Rüb U (2015) The brainstem pathologies of Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain Pathol (Zurich Switzerland) 25(2):121–135
Sengoku R, Saito Y, Ikemura M, Hatsuta H, Sakiyama Y, Kanemaru K, Arai T, Sawabe M, Tanaka N, Mochizuki H, Inoue K, Murayama S (2008) Incidence and extent of Lewy body-related alpha-synucleinopathy in aging human olfactory bulb. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67(11):1072–1083
Siderowf A, Lang AE (2012) Premotor Parkinson’s disease. Concepts and definitions. Mov Disord 27(5):608–616
Smeets WJAJ, González A (2000) Catecholamine systems in the brain of vertebrates: new perspectives through a comparative approach. Brain Res Rev 33(2–3):308–379
Smith EE (1999) Storage and executive processes in the frontal lobes. Science 283(5408):1657–1661
Sokoloff P, Giros B, Martres M-P, Bouthenet M-L, Schwartz J-C (1990) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature 347:146
Steeves TDL, Miyasaki J, Zurowski M, Lang AE, Pellecchia G, van Eimeren T, Rusjan P, Houle S, Strafella AP (2009) Increased striatal dopamine release in Parkinsonian patients with pathological gambling: a 11C raclopride PET study. Brain 132(Pt 5):1376–1385
Stiasny-Kolster K, Doerr Y, Moller JC, Hoffken H, Behr TM, Oertel WH, Mayer G (2005) Combination of ‘idiopathic’ REM sleep behaviour disorder and olfactory dysfunction as possible indicator for alpha-synucleinopathy demonstrated by dopamine transporter FP-CIT-SPECT. Brain 128(Pt 1):126–137
Surmeier DJ (2018) Determinants of dopaminergic neuron loss in Parkinson’s disease. FEBS J 285:3657–3668
Surmeier DJ, Guzman JN, Sanchez-Padilla J, Goldberg JA (2011) The origins of oxidant stress in Parkinson’s disease and therapeutic strategies. Antioxid Redox Signal 14(7):1289–1301
Surmeier DJ, Obeso JA, Halliday GM (2017) Selective neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 18(2):101–113
Swainson R, Rogers RD, Sahakian BJ, Summers BA, Polkey CE, Robbins TW (2000) Probabilistic learning and reversal deficits in patients with Parkinson’s disease or frontal or temporal lobe lesions: possible adverse effects of dopaminergic medication. Neuropsychologia 38(5):596–612
Taylor AE, Saint-Cyr JA, Lang AE (1986) Frontal lobe dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. The cortical focus of neostriatal outflow. Brain 109(Pt 5):845–883
Taylor TN, Caudle WM, Shepherd KR, Noorian A, Jackson CR, Iuvone PM, Weinshenker D, Greene JG, Miller GW (2009) Nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease revealed in an animal model with reduced monoamine storage capacity. J Neurosci 29(25):8103–8113
Tedroff J, Pedersen M, Aquilonius S-M, Hartvig P, Jacobsson G, Langstrom B (1996) Levodopa-induced changes in synaptic dopamine in patients with Parkinson’s disease as measured by [11C]raclopride displacement and PET. Neurology 46(5):1430
Thobois S, Lhommée E, Klinger H, Ardouin C, Schmitt E, Bichon A, Kistner A, Castrioto A, Xie J, Fraix V, Pelissier P, Chabardes S, Mertens P, Quesada J-L, Bosson J-L, Pollak P, Broussolle E, Krack P (2013) Parkinsonian apathy responds to dopaminergic stimulation of D2/D3 receptors with piribedil. Brain 136(Pt 5):1568–1577
Tillerson JL, Caudle WM, Parent JM, Gong C, Schallert T, Miller GW (2006) Olfactory discrimination deficits in mice lacking the dopamine transporter or the D2 dopamine receptor. Behav Brain Res 172(1):97–105
Tison F, Mons N, Geffard M, Henry P (1991) The metabolism of exogenous l-dopa in the brain: an immunohistochemical study of its conversion to dopamine in non-catecholaminergic cells of the rat brain. J Neural Transm 3(1):27–39
Trétiakoff C (1919) Contribution a l’etude de l’anatomie pathologique du locus niger de Soemmering avec quelques deductions relatives a la pathogenie des troubles du tonus musculaire et de la maladie de Parkinson
Turiault M, Parnaudeau S, Milet A, Parlato R, Rouzeau J-D, Lazar M, Tronche F (2007) Analysis of dopamine transporter gene expression pattern—generation of DAT-iCre transgenic mice. FEBS J 274(14):3568–3577
Ubeda-Bañon I, Saiz-Sanchez D, La Rosa-Prieto C de, Argandoña-Palacios L, Garcia-Muñozguren S, Martinez-Marcos A (2010) alpha-Synucleinopathy in the human olfactory system in Parkinson’s disease: involvement of calcium-binding protein- and substance P-positive cells. Acta Neuropathol 119(6):723–735
Uhl GR (1998) Hypothesis: the role of dopaminergic transporters in selective vulnerability of cells in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 43(5):555–560
Uhl GR, Hedreen JC, Price DL (1985) Parkinson’s disease: loss of neurons from the ventral tegmental area contralateral to therapeutic surgical lesions. Neurology 35(8):1215–1218
Vaillancourt DE, Schonfeld D, Kwak Y, Bohnen NI, Seidler R (2013) Dopamine overdose hypothesis: evidence and clinical implications. Mov Disord 28(14):1920–1929
van de Kar LD, Lorens SA (1979) Differential serotonergic innervation of individual hypothalamic nuclei and other forebrain regions by the dorsal and median midbrain raphe nuclei. Brain Res 162(1):45–54
Vernier P, Moret F, Callier S, Snapyan M, Wersinger C, Sidhu A (2004) The degeneration of dopamine neurons in Parkinson’s disease: insights from embryology and evolution of the mesostriatocortical system. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1035:231–249
Vingerhoets FJ, Schulzer M, Calne DB, Snow BJ (1997) Which clinical sign of Parkinson’s disease best reflects the nigrostriatal lesion? Ann Neurol 41(1):58–64
Vlaar AMM, van Kroonenburgh MJPG, Kessels AGH, Weber WEJ (2007) Meta-analysis of the literature on diagnostic accuracy of SPECT in parkinsonian syndromes. BMC Neurol 7:27
Vogt Weisenhorn DM, Giesert F, Wurst W (2016) Diversity matters—heterogeneity of dopaminergic neurons in the ventral mesencephalon and its relation to Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 139(Suppl 1):8–26
Voon V, Mehta AR, Hallett M (2011) Impulse control disorders in Parkinson’s disease: recent advances. Curr Opin Neurol 24(4):324–330
Voon V, Napier TC, Frank MJ, Sgambato-Faure V, Grace AA, Rodriguez-Oroz M, Obeso J, Bezard E, Fernagut P-O (2017) Impulse control disorders and levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease: an update. Lancet Neurol 16(3):238–250
Vriend C, Pattij T, van der Werf YD, Voorn P, Booij J, Rutten S, Berendse HW, van den Heuvel OA (2014) Depression and impulse control disorders in Parkinson’s disease: two sides of the same coin? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 38:60–71
Wager TD, Smith EE (2003) Neuroimaging studies of working memory: a meta-analysis. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 3(4):255–274
Wager TD, Jonides J, Reading S (2004) Neuroimaging studies of shifting attention: a meta-analysis. NeuroImage 22(4):1679–1693
Waters CM, Peck R, Rossor M, Reynolds GP, Hunt SP (1988) Immunocytochemical studies on the basal ganglia and substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s chorea. Neuroscience 25(2):419–438
Watson C, Paxinos G, Puelles L (eds) (2012) The mouse nervous system, 1st edn. Elsevier/Academic Press, London
Weingarten CP, Sundman MH, Hickey P, Chen N-k (2015) Neuroimaging of Parkinson’s disease: expanding views. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 59:16–52
Weintraub D (2008) Dopamine and impulse control disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 64(Suppl 2):S93–S100
Weintraub D, Newberg AB, Cary MS, Siderowf AD, Moberg PJ, Kleiner-Fisman G, Duda JE, Stern MB, Mozley D, Katz IR (2005) Striatal dopamine transporter imaging correlates with anxiety and depression symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. J Nucl Med 46(2):227–232
Weintraub D, Comella CL, Horn S (2008) Parkinson’s disease—Part 1: Pathophysiology, symptoms, burden, diagnosis, and assessment. Am J Manag Care 14(2 Suppl):S40–S48
Weintraub D, Koester J, Potenza MN, Siderowf AD, Stacy M, Voon V, Whetteckey J, Wunderlich GR, Lang AE (2010) Impulse control disorders in Parkinson disease: a cross-sectional study of 3090 patients. Arch Neurol 67(5):589–595
Williams DR, Watt HC, Lees AJ (2006) Predictors of falls and fractures in bradykinetic rigid syndromes: a retrospective study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77(4):468–473
Wilson DA, Sullivan RM (1995) The D2 antagonist spiperone mimics the effects of olfactory deprivation on mitral/tufted cell odor response patterns. J Neurosci 15(8):5574–5581
Yamada T, McGeer PL, Baimbridge KG, McGeer EG (1990) Relative sparing in Parkinson’s disease of substantia nigra dopamine neurons containing calbindin-D28K. Brain Res 526(2):303–307
Yamanishi T, Tachibana H, Oguru M, Matsui K, Toda K, Okuda B, Oka N (2013) Anxiety and depression in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Intern Med (Tokyo Japan) 52(5):539–545
Yetnikoff L, Lavezzi HN, Reichard RA, Zahm DS (2014) An update on the connections of the ventral mesencephalic dopaminergic complex. Neuroscience 282:23–48
Zarow C, Lyness SA, Mortimer JA, Chui HC (2003) Neuronal loss is greater in the locus coeruleus than nucleus basalis and substantia nigra in Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. Arch Neurol 60(3):337–341
Zeiss CJ (2005) Neuroanatomical phenotyping in the mouse: the dopaminergic system. Vet Pathol 42(6):753–773
Zigmond MJ, Abercrombie ED, Berger TW, Grace AA, Stricker EM (1990) Compensations after lesions of central dopaminergic neurons: some clinical and basic implications. Trends Neurosci 13(7):290–296
Zweig RM, Cardillo JE, Cohen M, Giere S, Hedreen JC (1993) The locus ceruleus and dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 43(5):986
Acknowledgements
WHO is supported by the Charitable Hertie Foundation, Frankfurt/Main, Germany. WHO received personal fees for educational talks and/or consultancy, outside of the submitted work, from Abbvie, Adamas, Bristol-Myer-Squibb, Desitin, Mundipharma, Neuropore, Novartis, Roche and UCB Pharma, and grants from the Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst, the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, the International Parkinson-Fonds The Netherlands, the ParkinsonFonds Deutschland, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, USA, the National Research Fond Luxembourg, from Roche International, Switzerland and Novartis Pharma, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geibl, F.F., Henrich, M.T. & Oertel, W.H. Mesencephalic and extramesencephalic dopaminergic systems in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 126, 377–396 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-019-01970-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-019-01970-9