Abstract
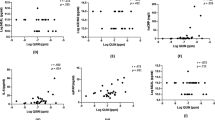
We showed previously that higher levels in CSF dopamine in HIV patients are associated with the presence of the dopamine transporter (DAT) 10/10-repeat allele which was also detected more frequently in HIV-infected individuals compared to uninfected subjects. In the current study, we investigated further whether other genetic dopamine (DA)-related polymorphisms may be related with changes in CSF DA levels and frequency of HIV infection in HIV-infected subjects. Specifically, we studied genetic polymorphisms of brain-derived neurotrophic factor, catechol-O-methyltransferase, and dopamine receptors DRD2, DRD3, and DRD4 genetic polymorphisms in uninfected and HIV-infected people in two different ethnical groups, a German cohort (Caucasian, 72 individuals with HIV infection and 22 individuals without HIV infection) and a South African cohort (Xhosan, 54 individuals with HIV infection and 19 individuals without HIV infection). We correlated the polymorphisms with CSF DA levels, HIV dementia score, CD4+ T cell counts, and HIV viral load. None of the investigated DA-related polymorphisms was associated with altered CSF DA levels, CD4+ T cell count, viral load, and HIV dementia score. The respective allele frequencies were equally distributed between HIV-infected patients and controls. Our findings do not show any influence of the studied genetic polymorphisms on CSF DA levels and HIV infection. This is in contrast to what we found previously for the DAT 3′UTR VNTR and highlights the specific role of the DAT VNTR in HIV infection and disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arendt G, Nolting T (2012) Neuro-AIDS in the cART era. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr 80:450–457
Bilder RM, Volavka J, Czobor P, Malhotra AK, Kennedy JL, Ni X, Goldman RS, Hoptman MJ, Sheitman B, Lindenmayer JP, Citrome L, McEvoy JP, Kunz M, Chakos M, Cooper TB, Lieberman JA (2002) Neurocognitive correlates of the COMT Val(158)Met polymorphism in chronic schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 52:701–707
Clifford DB (2008) HIV-associated neurocognitive disease continues in the antiretroviral era. Top HIV Med Publ Int AIDS Soc USA 16:94–98
Cloninger CR, Svrakic DM, Przybeck TR (1993) A psychobiological model of temperament and character. Arch Gen Psychiatry 50:975–990
Czub M, Czub S, Gosztonyi G, Koutsilieri E, Sopper S, Muller JG, Gerlach M, Riederer P, ter Meulen V (1999) Effects of Selegiline in a retroviral rat model for neurodegenerative disease. J Neurovirol 5:458–464
Czub S, Koutsilieri E, Sopper S, Czub M, Stahl-Hennig C, Muller JG, Pedersen V, Gsell W, Heeney JL, Gerlach M, Gosztonyi G, Riederer P, ter Meulen V (2001) Enhancement of central nervous system pathology in early simian immunodeficiency virus infection by dopaminergic drugs. Acta Neuropathol 101:85–91
Ebstein RP, Novick O, Umansky R, Priel B, Osher Y, Blaine D, Bennett ER, Nemanov L, Katz M, Belmaker RH (1996) Dopamine D4 receptor (D4DR) exon III polymorphism associated with the human personality trait of Novelty Seeking. Nat Genet 12:78–80
Egan MF, Kojima M, Callicott JH, Goldberg TE, Kolachana BS, Bertolino A, Zaitsev E, Gold B, Goldman D, Dean M, Lu B, Weinberger DR (2003) The BDNF val66met polymorphism affects activity-dependent secretion of BDNF and human memory and hippocampal function. Cell 112:257–269
Garcia JR, MacKillop J, Aller EL, Merriwether AM, Wilson DS, Lum JK (2010) Associations between dopamine D4 receptor gene variation with both infidelity and sexual promiscuity. PLoS One 5:e14162
Golden CJ (1976) Identification of brain disorders by the Stroop Color and Word Test. J Clin Psychol 32:654–658
Grandy DK, Litt M, Allen L, Bunzow JR, Marchionni M, Makam H, Reed L, Magenis RE, Civelli O (1989) The human dopamine D2 receptor gene is located on chromosome 11 at q22-q23 and identifies a TaqI RFLP. Am J Hum Genet 45:778–785
Gupta S, Bousman CA, Chana G, Cherner M, Heaton RK, Deutsch R, Ellis RJ, Grant I, Everall IP (2011) Dopamine receptor D3 genetic polymorphism (rs6280TC) is associated with rates of cognitive impairment in methamphetamine-dependent men with HIV: preliminary findings. J Neurovirol 17:239–247
Horn A, Scheller C, du Plessis S, Arendt G, Nolting T, Joska J, Sopper S, Maschke M, Obermann M, Husstedt IW, Hain J, Maponga T, Riederer P, Koutsilieri E (2013) Increases in CSF dopamine in HIV patients are due to the dopamine transporter 10/10-repeat allele which is more frequent in HIV-infected individuals. J Neural Transm 120:1411–1419
Jenuwein M, Scheller C, Neuen-Jacob E, Sopper S, Tatschner T, ter Meulen V, Riederer P, Koutsilieri E (2004) Dopamine deficits and regulation of the cAMP second messenger system in brains of simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus monkeys. J Neurovirol 10:163–170
Jonsson EG, Nothen MM, Grunhage F, Farde L, Nakashima Y, Propping P, Sedvall GC (1999) Polymorphisms in the dopamine D2 receptor gene and their relationships to striatal dopamine receptor density of healthy volunteers. Mol Psychiatry 4:290–296
Klove H (1963) Clinical Neuropsychology. The Medical clinics of North America 47:1647–1658
Kumar AM, Fernandez J, Singer EJ, Commins D, Waldrop-Valverde D, Ownby RL, Kumar M (2009) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in the central nervous system leads to decreased dopamine in different regions of postmortem human brains. J Neurovirol 1–18
Kuppers E, Beyer C (2001) Dopamine regulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression in cultured embryonic mouse striatal cells. Neuroreport 12:1175–1179
Lachman HM, Papolos DF, Saito T, Yu YM, Szumlanski CL, Weinshilboum RM (1996) Human catechol-O-methyltransferase pharmacogenetics: description of a functional polymorphism and its potential application to neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacogenetics 6:243–250
Lannfelt L, Sokoloff P, Martres M-P, Pilon C, Giros B, Jönsson E, Sedvall G, Schwartz J-C (1992) Amino acid substitution in the dopamine D3 receptor as a useful polymorphism for investigating psychiatric disorders. Psychiatr Genet 2:249–256
Levine AJ, Sinsheimer JS, Bilder R, Shapshak P, Singer EJ (2012) Functional polymorphisms in dopamine-related genes: effect on neurocognitive functioning in HIV+ adults. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 34:78–91
Lundstrom K, Turpin MP (1996) Proposed schizophrenia-related gene polymorphism: expression of the Ser9Gly mutant human dopamine D3 receptor with the Semliki Forest virus system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 225:1068–1072
Malhotra AK, Kestler LJ, Mazzanti C, Bates JA, Goldberg T, Goldman D (2002) A functional polymorphism in the COMT gene and performance on a test of prefrontal cognition. Am J Psychiatry 159:652–654
Miguez-Burbano MJ, Espinoza L, Whitehead NE, Bryant VE, Vargas M, Cook RL, Quiros C, Lewis JE, Deshratan A (2014) Brain derived neurotrophic factor and cognitive status: the delicate balance among people living with HIV, with and without alcohol abuse. Curr HIV Res 12:254–264
Nolan KA, Bilder RM, Lachman HM, Volavka J (2004) Catechol O-methyltransferase Val158Met polymorphism in schizophrenia: differential effects of Val and Met alleles on cognitive stability and flexibility. Am J Psychiatry 161:359–361
Pohjalainen T, Rinne JO, Nagren K, Lehikoinen P, Anttila K, Syvalahti EK, Hietala J (1998) The A1 allele of the human D2 dopamine receptor gene predicts low D2 receptor availability in healthy volunteers. Mol Psychiatry 3:256–260
Proschel M, Saunders A, Roses AD, Muller CR (1992) Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the human gene for the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Hum Mol Genet 1:353
Purohit V, Rapaka R, Shurtleff D (2011) Drugs of abuse, dopamine, and HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders/HIV-associated dementia. Mol Neurobiol 44:102–110
Rippeth JD, Heaton RK, Carey CL, Marcotte TD, Moore DJ, Gonzalez R, Wolfson T, Grant I, Group H (2004) Methamphetamine dependence increases risk of neuropsychological impairment in HIV infected persons. J Int Neuropsychol Soci JINS 10:1–14
Sardar A, Czudek C, Reynolds G (1996) Dopamine deficits in the brain: the neurochemical basis of parkinsonian symptoms in AIDS. NeuroReport 7:910–912
Scheller C, Sopper S, Jassoy C, ter Meulen V, Riederer P, Koutsilieri E (2000) Dopamine activates HIV in chronically infected T lymphoblasts. J Neural Transm 107:1483–1489
Scheller C, Sopper S, Jenuwein M, Neuen-Jacob E, Tatschner T, Grunblatt E, ter Meulen V, Riederer P, Koutsilieri E (2005) Early impairment in dopaminergic neurotransmission in brains of SIV-infected rhesus monkeys due to microglia activation. J Neurochem 95:377–387
Scheller C, Arendt G, Nolting T, Antke C, Sopper S, Maschke M, Obermann M, Angerer A, Husstedt IW, Meisner F, Neuen-Jacob E, Muller HW, Carey P, Ter Meulen V, Riederer P, Koutsilieri E (2010) Increased dopaminergic neurotransmission in therapy-naive asymptomatic HIV patients is not associated with adaptive changes at the dopaminergic synapses. J Neural Transm 117:699–705
Shapiro AM, Benedict RH, Schretlen D, Brandt J (1999) Construct and concurrent validity of the Hopkins Verbal Learning Test-revised. Clin Neuropsychol 13:348–358
Van Tol HH, Wu CM, Guan HC, Ohara K, Bunzow JR, Civelli O, Kennedy J, Seeman P, Niznik HB, Jovanovic V (1992) Multiple dopamine D4 receptor variants in the human population. Nature 358:149–152
Villalba K, Devieux JG, Rosenberg R, Cadet JL (2015) DRD2 and DRD4 genes related to cognitive deficits in HIV-infected adults who abuse alcohol. Behav Brain Funct BBF 11:25
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the study management of Teboho Linda as well as the technical support from Lena Ruthardt. The study was supported by Grants from “Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung” (BMBF-KI0211 Competence Network HIV/AIDS) and “Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft” (DFG-GRK 1522). Anne Horn had a fellowship for the last year of her PhD Thesis from the “Qualifikationsprogramm für Wissenschaftlerinnen der Universitaet Wuerzburg” (supported by the Bavarian Government).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horn, A., Scheller, C., du Plessis, S. et al. The dopamine-related polymorphisms BDNF, COMT, DRD2, DRD3, and DRD4 are not linked with changes in CSF dopamine levels and frequency of HIV infection. J Neural Transm 124, 501–509 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-016-1659-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-016-1659-6