Abstract
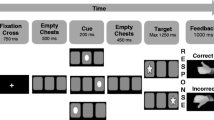
Studies have demonstrated inefficient use of antecedent-focused emotion regulation strategies in children with ADHD attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). In the current study we tested for the first time if ADHD is also associated with difficulties in response-focused strategies by measuring the ability to override action tendencies induced by emotional information. Performance data on a computer-based approach-avoidance paradigm of 28 children with ADHD and 38 typically developing children between 8 and 15 years of age were analyzed, by comparing a congruent condition in which they were instructed to approach positive and avoid negative pictures and an incongruent condition where they had to override these automatic reactions and approach negative and avoid positive pictures. Children also rated the valence and salience of the pictures. Children with ADHD and typically developing children rated the emotional valence of the pictures appropriately and similarly, while positive pictures were rated as more arousing by children with ADHD. Solid congruency effects were found indicating that the task measured response-focused emotion regulation; however groups did not differ in this respect. Our findings do not support a deficit in emotion regulation in ADHD in terms of the ability to override natural tendencies to approach positive and avoid negative pictures.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abikoff HB, Jensen PS, Arnold LLE, Hoza B, Hechtman L, Pollack S, Wigal T (2002) Observed classroom behavior of children with ADHD: relationship to gender and comorbidity. J Abnorm Child Psych 30(4):349–359. doi:10.1023/a:1015713807297
American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edition, text revision (DSM-IV-TR). American Psychiatric Association, Washington DC
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edn. American Psychiatric Publishing, Arlington
Anastopoulos AD, Smith TF, Garrett ME, Morrissey-Kane E, Schatz NK, Sommer JL, Ashley-Koch A (2011) Self-regulation of emotion, functional impairment, and comorbidity among children with AD/HD. J Attent Disord 15(7):583–592. doi:10.1177/1087054710370567
Angold A, Costello EJ, Erkanli A (1999) Comorbidity. J Child Psychol Psych 40(1):57–87. doi:10.1017/s0021963098003448
Bamford S, Ward R (2008) Predispositions to approach and avoid are contextually sensitive and goal dependent. Emotion 8(2):174–183. doi:10.1037/1528-3542.8.2.174
Bamford S, Broyd SJ, Benikos N, Ward R, Wiersema JR, Sonuga-Barke E (2015) The late positive potential: a neural marker of the regulation of emotion-based approach-avoidance actions? Biol Psychol 105:115–123. doi:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2015.01.009
Bradley MM, Lang PJ (1994) Measuring emotion—the self-assessment mannequin and the semantic differential. J Behav Ther Exp Psy 25(1):49–59. doi:10.1016/0005-7916(94)90063-9
Brown EC, Tas C, Kuzu D, Esen-Danaci A, Roelofs K, Bruene M (2014) Social approach and avoidance behaviour for negative emotions is modulated by endogenous oxytocin and paranoia in schizophrenia. Psychiat Res 219(3):436–442. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2014.06.038
Center for the Study of Emotion and Attention [CSEA-NIMH] (1999) The international affective picture system: digitized photographs. The Center for Research in Psychophysiology, University of Florida, Gainesville
Chen M, Bargh JA (1999) Consequences of automatic evaluation: immediate behavioral predispositions to approach or avoid the stimulus. Pers Soc Psychol B 25(2):215–224. doi:10.1177/0146167299025002007
Chhabildas N, Pennington BF, Willcutt EG (2001) A comparison of the neuropsychological profiles of the DSM-IV subtypes of ADHD. J Abnorm Child Psych 29(6):529–540. doi:10.1023/a:1012281226028
De Houwer J, Crombez G, Baeyens F, Hermans D (2001) On the generality of the affective Simon effect. Cognit Emot 15(2):189–206. doi:10.1080/0269993004200051
Deckers A, Roelofs J, Muris P, Rinck M (2014) Desire for social interaction in children with autism spectrum disorders. Res Autism Spect Dis 8(4):449–453. doi:10.1016/j.rasd.2013.12.019
Ent MR, Baumeister RF, Tice DM (2015) Trait self-control and the avoidance of temptation. Pers Indiv Differ 74:12–15. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2014.09.031
Ferdinand RF, van der Ende J (2002) Nederlandse vertaling van de DISC IV; Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children. Afdeling kinder- en jeugdpsychiatrie van het Sophia Ziekenhuis, Rotterdam
Gomez R, Corr PJ (2010) Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder symptoms: associations with Gray’s and Tellegen’s models of personality. Pers Indiv Differ 49(8):902–906. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2010.06.033
Gray JA, McNaughton N (2000) The neuropsychology of anxiety: an enquiry into the functions of the septo-hippocampal system. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Grégoire J (2000) L’évaluation clinique de l’intelligence de l’enfant: Théorie et pratique du WISC-III. Mardaga, Liège
Grietens H, Hoppenbrouwers K, Desoete A, Wiersema JR, Van Leeuwen K (2010) JOnG! Theoretische achtergronden, onderzoeksopzet en verloop van het eerst meetmoment. Steunpunt Welzijn, Volksgezondheid en Gezin, Leuven
Gross JJ (2015) Emotion regulation: current status and future prospects. Psychol Inq 26(1):1–26. doi:10.1080/1047840x.2014.940781
Heym N, Kantini E, Checkley HLR, Cassaday HJ (2015) Gray’s revised reinforcement sensitivity theory in relation to attention-deficit/hyperactivity and Tourette-like behaviors in the general population. Pers Indiv Differ 78:24–28. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2015.01.012
Hundt NE, Kimbrel NA, Mitchell JT, Nelson-Gray RO (2008) High BAS, but not low BIS, predicts externalizing symptoms in adults. Pers Indiv Differ 44(3):565–575. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2007.09.018
Jensen PS, Hinshaw SP, Kraemer HC, Lenora N, Newcorn JH, Abikoff HB, Vitiello B (2001) ADHD comorbidity findings from the MTA study: comparing comorbid subgroups. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 40(2):147–158. doi:10.1097/00004583-200102000-00009
Klein AM, Becker ES, Rinck M (2011) Approach and avoidance tendencies in spider fearful children: the approach-avoidance task. J Child Fam Stud 20(2):224–231. doi:10.1007/s10826-010-9402-7
Köchel A, Leutgeb V, Schienle A (2014) Disrupted response inhibition toward facial anger cues in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): an event-related potential study. J Child Neurol 29(4):459–468. doi:10.1177/0883073813476139
Kort W, Schittekatte M, Dekker PH, Verhaeghe P, Compaan M, Bosmans M, Vermeir G (2005) Wechsler intelligence scale for children Derde Editie NL: Handleiding. Harcourt Test Publishers, Amsterdam
Kowatch RA, Youngstrom EA, Danielyan A, Findling RL (2005) Review and meta-analysis of the phenomenology and clinical characteristics of mania in children and adolescents. Bipolar Disord 7(6):483–496. doi:10.1111/j.1399-5618.2005.00261.x
Kujawa A, Klein DN, Hajcak G (2012) Electrocortical reactivity to emotional images and faces in middle childhood to early adolescence. Dev Cogn Neurosci 2(4):458–467. doi:10.1016/j.dcn.2012.03.005
Lang PJ (1980) Behavioral treatment and bio-behavioral assessment: computer applications. In: Sidowski JB, Johnson JH, Williams TA (eds) Technology in mental health care delivery systems. Ablex, Norwood, pp 119–137
Lang PJ, Bradley MM, Cuthbert BN (2008) International affective picture system (IAPS): affective ratings of pictures and instruction manual. Technical Report A-8. University of Florida, Gainesville
López-Martín S, Albert J, Fernández-Jaén A, Carretié L (2013) Emotional distraction in boys with ADHD: neural and behavioral correlates. Brain Cognition 83(1):10–20. doi:10.1016/j.bandc.2013.06.004
Maedgen JW, Carlson CL (2000) Social functioning and emotional regulation in the attention deficit hyperactivity disorder subtypes. J Clin Child Psychol 29(1):30–42. doi:10.1207/S15374424jccp2901_4
Martel MM (2009) Research review: a new perspective on attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Emotion dysregulation and trait models. J Child Psychol Psych 50(9):1042–1051. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2009.02105.x
Martel MM, Gremillion ML, Roberts B (2012) Temperament and common disruptive behavior problems in preschool. Pers Indiv Differ 53(7):874–879. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2012.07.011
McManis MH, Bradley MM, Berg WK, Cuthbert BN, Lang PJ (2001) Emotional reactions in children: verbal, physiological, and behavioral responses to affective pictures. Psychophysiology 38(2):222–231. doi:10.1017/s0048577201991140
Meinzer MC, Pettit JW, Viswesvaran C (2014) The co-occurrence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and unipolar depression in children and adolescents: a meta-analytic review. Clin Psychol Rev 34(8):595–607. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2014.10.002
Melnick SM, Hinshaw SP (2000) Emotion regulation and parenting in AD/HD and comparison boys: linkages with social behaviors and peer preference. J Abnorm Child Psych 28(1):73–86. doi:10.1023/a:1005174102794
Mitchell JT, Nelson-Gray RO (2006) Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in adults: relationship to Gray’s behavioral approach system. Pers Indiv Differ 40(4):749–760. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2005.08.011
Oosterlaan J, Baeyens D, Scheres A, Antrop I, Roeyers H, Sergeant JA (2008) Handleiding Vragenlijst voor Gedragsproblemen bij Kinderen (VvGK). Harcourt, Amsterdam
Passarotti AM, Sweeney JA, Pavuluri MN (2010) Emotion processing influences working memory circuits in pediatric bipolar disorder and attention—deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 49(10):1064–1080. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2010.07.009
Pelham WE, Gnagy EM, Greenslade KE, Milich R (1992) Teacher ratings of DSM-III-R symptoms for the disruptive behavior disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 31(2):210–218. doi:10.1097/00004583-199203000-00006
Phaf RH, Mohr SE, Rotteveel M, Wicherts JM (2014) Approach, avoidance, and affect: a meta-analysis of approach-avoidance tendencies in manual reaction time tasks. Front Psychol 5:16. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00378
Posner J, Maia TV, Fair D, Peterson BS, Sonuga-Barke EJ, Nagel BJ (2011) The attenuation of dysfunctional emotional processing with stimulant medication: an fMRI study of adolescents with ADHD. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 193(3):151–160. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2011.02.005
Rellecke J, Palazova M, Sommer W, Schacht A (2011) On the automaticity of emotion processing in words and faces: event-related brain potentials evidence from a superficial task. Brain Cognition 77(1):23–32. doi:10.1016/j.bandc.2011.07.001
Rutter M, Bailey A, Lord C (2003) The social communication questionnaire manual. Western Psychological Services, Los Angeles
Samyn V, Roeyers H, Bijttebier P, Rosseel Y, Wiersema JR (2015) Assessing effortful control in typical and atypical development: are questionnaires and neuropsychological measures interchangeable? A latent-variable analysis. Res Dev Disabil 36:587–599. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2014.10.018
Schmitz M, Cadore L, Paczko M, Kipper L, Chaves M, Rohde LA, Moura C, Knijnik M (2002) Neuropsychological performance in DSM-IV ADHD subtypes: an exploratory study with untreated adolescents. Can J Psychiatry-Rev Canadienne De Psychiatrie 47(9):863–869
Scime M, Norvilitis JM (2006) Task performance and response to frustration in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Psychol Sch 43(3):377–386. doi:10.1002/pits.20151
Shaffer D, Fisher P, Lucas CP, Dulcan MK, Schwab-Stone ME (2000) NIMH Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children version IV (NIMH DISC-IV): description, differences from previous versions, and reliability of some common diagnoses. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 39(1):28–38. doi:10.1097/00004583-200001000-00014
Shaw P, Stringaris A, Nigg J, Leibenluft E (2014) Emotion dysregulation in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Psychiat 171(3):276–293. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.13070966
Skirrow C, McLoughlin G, Kuntsi J, Asherson P (2009) Behavioral, neurocognitive and treatment overlap between attention-deficithyperactivity disorder and mood instability. Expert Rev Neurother 9(4):489–503. doi:10.1586/ERN.09.2
Sobanski E, Banaschewski T, Asherson P, Buitelaar J, Chen W, Franke B, Faraone SV (2010) Emotional lability in children and adolescents with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): clinical correlates and familial prevalence. J Child Psychol Psych 51(8):915–923. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02217.x
Spruyt A, De Houwer J, Tibboel H, Verschuere B, Crombez G, Verbanck P, Noel X (2013) On the predictive validity of automatically activated approach/avoidance tendencies in abstaining alcohol-dependent patients. Drug Alcohol Depen 127(1–3):81–86. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.06.019
Stringaris A, Goodman R (2009) Mood lability and psychopathology in youth. Psychol Med 39(8):1237–1245. doi:10.1017/S0033291708004662
Tsang TW, Kohn MR, Efron D, Clarke SD, Clark CR, Lamb C, Williams LM (2015) Anxiety in young people with ADHD: clinical and self-report outcomes. J Atten Disord 19(1):18–26. doi:10.1177/1087054712446830
Van Cauwenberge V, Sonuga-Barke EJS, Hoppenbrouwers K, Van Leeuwen K, Wiersema JR (2015) “Turning down the heat”: is poor performance of children with ADHD on tasks tapping “hot” emotional regulation caused by deficits in “cool” executive functions? Res Dev Disabil 47:199–207. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2015.09.012
van Mourik R, Oosterlaan J, Sergeant JA (2005) The Stroop revisited: a meta-analysis of interference control in AD/HD. J Child Psychol Psyc 46(2):150–165. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2004.00345.x
Walcott CM, Landau S (2004) The relation between disinhibition and emotion regulation in boys with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 33(4):772–782. doi:10.1207/s15374424jccp3304_12
Warreyn P, Raymaekers R, Roeyers H (2004) Handleiding vragenlijst sociale communicatie. SIG vzw, Destelbergen
Waschbusch DA (2002) A meta-analytic examination of comorbid hyperactive-impulsive-attention problems and conduct problems. Psychol Bull 128(1):118–150. doi:10.1037//0033-2909.128.1.118
Wechsler D (1991) Wechsler intelligence scale for children, 3rd edn. Psychological Corporation, New York
Willcutt EG (2012) The prevalence of DSM-IV attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analytic review. Neurotherapeutics 9(3):490–499. doi:10.1007/s13311-012-0135-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Professor Sonuga-Barke declares the following competing interests: fees for speaking, consultancy, research funding and conference support from Shire Pharma; speaker fees from Janssen Cilag, Consultancy from Neurotech solutions, Aarhus University, Copenhagen University and Berhanderling, Skolerne, Copenhagen, KU Leuven; book royalties from OUP and Jessica Kingsley.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Cauwenberge, V., Sonuga-Barke, E.J.S., Hoppenbrouwers, K. et al. Regulation of emotion in ADHD: can children with ADHD override the natural tendency to approach positive and avoid negative pictures?. J Neural Transm 124, 397–406 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-016-1631-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-016-1631-5