Abstract
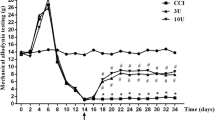
“Mirror pain” or mirror-image pain (MP) is pain opposite to the side of injury. Mechanism and frequency in humans are not known. There is no consent on therapy. Here we report that unilaterally injected botulinum toxin type A (BT-A) has bilateral effect in experimental MP, thus deserves to be investigated as therapy for this condition. We examined the localization of BT-A’s bilateral antinociceptive action in MP induced by 3 % carrageenan intramuscular injection in Wistar rats. BT-A was applied peripherally (5 U/kg), into ipsilateral or contralateral hind paw pad (i.pl.) and centrally (1 U/kg), at spinal (intrathecally, i.t.) or supraspinal (intracisternally, i.c.) level. Additionally, we examined the involvement of central opioid and GABAergic systems, as well as the contribution of peripheral capsaicin-sensitive neurons to BT-A’s bilateral antinociceptive effect. Ipsilateral i.pl. and i.t. BT-A reduced the bilateral mechanical sensitivity to von Frey filaments, while contralateral i.pl. and i.c. treatments had no effect on either tested side. Bilateral antinociceptive effect of ipsilateral i.pl. BT-A was prevented by μ-opioid antagonist naloxonazine (1.5 μg/10 μl) and GABAA antagonist bicuculline (1 μg/10 μl) if applied at the spinal level, in contrast to supraspinal application of the same doses. Local treatment of sciatic nerve with 2 % capsaicin 5 days following BT-A i.pl. injection caused desensitization of sciatic capsaicin-sensitive fibers, but did not affect bilateral antinociceptive effect of BT-A and the presence of cleaved SNAP-25 at the spinal cord slices. Present experiments suggest segmental actions of peripheral BT-A at spinal level, which are probably not solely dependent on capsaicin-sensitive neurons.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BT-A:
-
Botulinum toxin type A
- B:
-
Bicuculline
- N:
-
Naloxonazine
- SNAP-25:
-
Synaptosomal Associated Protein of 25 kDa
- clSNAP-25:
-
Cleaved SNAP-25
- MP:
-
Mirror pain
- ASIC3:
-
Acid-sensing ion channel 3
- CGRP:
-
Calcitonin gene-related polypeptide
- SP:
-
Substance P
- GABA:
-
γ-aminobutyric acid
- TRPV1:
-
Transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1
- CFA:
-
Complete Freund’s adjuvant
- IoNC:
-
Infraorbital nerve constriction
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- DRG:
-
Dorsal root ganglion
- RVM:
-
Rostral ventromedial medulla
- TNC:
-
Trigeminal nucleus caudalis
- TENS:
-
Transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation
- i.m.:
-
Intramuscular
- i.pl.:
-
Intraplantar
- i.t.:
-
Intrathecal
- i.c.:
-
Intracisternal
- i.c.v.:
-
Intracerebroventricular
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PBST:
-
Triton X-100 in phosphate buffered saline
- NGS:
-
Normal goat serum
References
Ainsworth L, Budelier K, Clinesmith M, Fiedler A, Landstrom R, Leeper BJ, Moeller L, Mutch S, O’Dell K, Ross J, Radhakrishnan R, Sluka KA (2006) Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) reduces chronic hyperalgesia induced by muscle inflammation. Pain 120(1–2):182–187. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2005.10.030
Antonucci F, Rossi C, Gianfranceschi L, Rossetto O, Caleo M (2008) Long-distance retrograde effects of botulinum neurotoxin A. J Neurosci 28(14):3689–3696. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.0375-08.2008
Bach-Rojecky L, Lacković Z (2009) Central origin of the antinociceptive action of botulinum toxin type A. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 94(2):234–238. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2009.08.012
Bach-Rojecky L, Relja M, Lacković Z (2005) Botulinum toxin type A in experimental neuropathic pain. J Neural Transm 112(2):215–219. doi:10.1007/s00702-004-0265-1
Bach-Rojecky L, Dominis M, Lacković Z (2008) Lack of anti-inflammatory effect of botulinum toxin type A in experimental models of inflammation. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 22(5):503–509. doi:10.1111/j.1472-8206.2008.00615.x
Bach-Rojecky L, Šalković-Petrišić M, Lacković Z (2010) Botulinum toxin type A reduces pain supersensitivity in experimental diabetic neuropathy: bilateral effect after unilateral injection. Eur J Pharmacol 633(1–3):10–14. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.01.020
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53(1):55–63. doi:10.1016/0165-0270(94)90144-9
Da Silva LF, Desantana JM, Sluka KA (2010) Activation of NMDA receptors in the brainstem, rostral ventromedial medulla, and nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis mediates mechanical hyperalgesia produced by repeated intramuscular injections of acidic saline in rats. J Pain 11(4):378–387. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2009.08.006
de la Llave-Rincón AI, Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Fernández-Carnero J, Padua L, Arendt-Nielsen L, Pareja JA (2009) Bilateral hand/wrist heat and cold hyperalgesia, but not hypoesthesia, in unilateral carpal tunnel syndrome. Exp Brain Res 198(4):455–463. doi:10.1007/s00221-009-1941-z
DeSantana JM, Da Silva LF, De Resende MA, Sluka KA (2009) Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation at both high and low frequencies activates ventrolateral periaqueductal grey to decrease mechanical hyperalgesia in arthritic rats. Neuroscience 163(4):1233–1241. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.06.056
Drinovac V, Bach-Rojecky L, Matak I, Lacković Z (2013) Involvement of μ-opioid receptors in antinociceptive action of botulinum toxin type A. Neuropharmacology 70:331–337. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.02.011
Drinovac V, Bach-Rojecky L, Lacković Z (2014) Association of antinociceptive action of botulinum toxin type A with GABA-A receptor. J Neural Transm 121(6):665–669. doi:10.1007/s00702-013-1150-6
Favre-Guilmard C, Auguet M, Chabrier PE (2009) Different antinociceptive effects of botulinum toxin type A in inflammatory and peripheral polyneuropathic rat models. Eur J Pharmacol 617(1–3):48–53. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.06.047
Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, de la Llave-Rincón AI, Fernández-Carnero J, Cuadrado ML, Arendt-Nielsen L, Pareja JA (2009) Bilateral widespread mechanical pain sensitivity in carpal tunnel syndrome: evidence of central processing in unilateral neuropathy. Brain 132(Pt 6):1472–1479. doi:10.1093/brain/awp050
Filipović B, Matak I, Bach-Rojecky L, Lacković Z (2012) Central action of peripherally applied botulinum toxin type A on pain and dural protein extravasation in rat model of trigeminal neuropathy. PLoS One 7(1):e29803. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0029803
Gale K, Casu M (1981) Dynamic utilization of GABA in substantia nigra: regulation by dopamine and GABA in the striatum, and its clinical and behavioral implications. Mol Cell Biochem 39:369–405. doi:10.1007/BF00232586
Gautam M, Benson CJ, Ranier JD, Light AR, Sluka KA (2012) ASICs do not play a role in maintaining hyperalgesia induced by repeated intramuscular acid injections. Pain Res Treat 2012:817347. doi:10.1155/2012/817347
Huang D, Yu B (2010) The mirror-image pain: an unclered phenomenon and its possible mechanism. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34(4):528–532. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.10.011
Huge V, Lauchart M, Förderreuther S, Kaufhold W, Valet M, Azad SC, Beyer A, Magerl W (2008) Interaction of hyperalgesia and sensory loss in complex regional pain syndrome type I (CRPS I). PLoS One 3(7):e2742. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002742
Jahn R, Fasshauer D (2012) Molecular machines governing exocytosis of synaptic vesicles. Nature 490(7419):201–207. doi:10.1038/nature11320
Jancalek R (2011) Signaling mechanisms in mirror image pain pathogenesis. Ann Neurosci 18(3):123–127. doi:10.5214/ans.0972-7531.11183010
Kalra A, Urban MO, Sluka KA (2001) Blockade of opioid receptors in rostral ventral medulla prevents antihyperalgesia produced by transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298(1):257–263
Koltzenburg M, Wall PD, McMahon SB (1999) Does the right side know what the left is doing? Trends Neurosci 22(3):122–127. doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(98)01302-2
Konopka KH, Harbers M, Houghton A, Kortekaas R, van Vliet A, Timmerman W, den Boer JA, Struys MM, van Wijhe M (2012) Bilateral sensory abnormalities in patients with unilateral neuropathic pain; a quantitative sensory testing (QST) study. PLoS One 7(5):e37524. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0037524
Lacković Z, Filipović B, Matak I, Helyes Z (2016) Botulinum toxin type A activity in cranial dura: implications for treatment of migraine and other headaches. Br J Pharmacol 173(2):279–291. doi:10.1111/bph.13366
Ledeboer A, Mahoney JH, Milligan ED, Martin D, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2006) Spinal cord glia and interleukin-1 do not appear to mediate persistent allodynia induced by intramuscular acidic saline in rats. J Pain 7(10):757–767. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2006.04.001
Ling GS, Simantov R, Clark JA, Pasternak GW (1986) Naloxonazine actions in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 129(1–2):33–38. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(86)90333-X
Matak I, Lacković Z (2014) Botulinum toxin A, brain and pain. Prog Neurobiol 119–120:39–59. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2014.06.001
Matak I, Bach-Rojecky L, Filipović B, Lacković Z (2011) Behavioral and immunohistochemical evidence for central antinociceptive activity of botulinum toxin A. Neuroscience 186:201–207. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.04.026
Matak I, Riederer P, Lacković Z (2012) Botulinum toxin’s axonal transport from periphery to the spinal cord. Neurochem Int 61(2):236–239. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2012.05.001
Matak I, Rossetto O, Lacković Z (2014) Botulinum toxin type A selectivity for certain types of pain is associated with capsaicin-sensitive neurons. Pain 155(8):1516–1526. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2014.04.027
Noble EP, Wurtman RJ, Axelrod J (1967) A simple and rapid method for injecting H3-norepinephrine into the lateral ventricle of the rat brain. Life Sci 6(3):281–291. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(67)90157-9
Pavone F, Luvisetto S (2010) Botulinum neurotoxin for pain management: insights from animal models. Toxins 2(12):2890–2913. doi:10.3390/toxins2122890
Pertovaara A (1988) Collateral sprouting of nociceptive C-fibers after cut or capsaicin treatment of the sciatic nerve in adult rats. Neurosci Lett 90(3):248–253. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(88)90197-8
Radhakrishnan R, Sluka KA (2009) Increased glutamate and decreased glycine release in the rostral ventromedial medulla during induction of a pre-clinical model of chronic widespread muscle pain. Neurosci Lett 457(3):141–145. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2009.03.086
Radhakrishnan R, Moore SA, Sluka KA (2003) Unilateral carrageenan injection into muscle or joint induces chronic bilateral hyperalgesia in rats. Pain 104(3):567–577. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(03)00114-3
Radhakrishnan R, Bement MK, Skyba D, Sluka KA, Kehl LJ (2004) Models of muscle pain: carrageenan model and acidic saline model. Curr Protoc Pharmacol Chapter 5, Unit 5.35. doi:10.1002/0471141755.ph0535s25
Ren K, Dubner R (1996) Enhanced descending modulation of nociception in rats with persistent hindpaw inflammation. J Neurophysiol 76(5):3025–3037
Shenker N, Haigh R, Roberts E, Mapp P, Harris N, Blake D (2003) A review of contralateral responses to a unilateral inflammatory lesion. Rheumatology 42(11):1279–1286. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg397
Skyba DA, King EW, Sluka KA (2002) Effects of NMDA and non-NMDA ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists on the development and maintenance of hyperalgesia induced by repeated intramuscular injection of acidic saline. Pain 98(1–2):69–78. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(01)00471-7
Skyba DA, Lisi TL, Sluka KA (2005) Excitatory amino acid concentrations increase in the spinal cord dorsal horn after repeated intramuscular injection of acidic saline. Pain 119(1–3):142–149. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2005.09.025
Sluka KA (2002) Stimulation of deep somatic tissue with capsaicin produces long-lasting mechanical allodynia and heat hypoalgesia that depends on early activation of the cAMP pathway. J Neurosci 22(13):5687–5693
Sluka KA, Kalra A, Moore SA (2001) Unilateral intramuscular injections of acidic saline produce a bilateral, long-lasting hyperalgesia. Muscle Nerve 24(1):37–46
Sluka KA, Price MP, Breese NM, Stucky CL, Wemmie JA, Welsh MJ (2003) Chronic hyperalgesia induced by repeated acid injections in muscle is abolished by the loss of ASIC3, but not ASIC1. Pain 106(3):229–239. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(03)00269-0
Sluka KA, Radhakrishnan R, Benson CJ, Eshcol JO, Price MP, Babinski K, Audette KM, Yeomans DC, Wilson SP (2007) ASIC3 in muscle mediates mechanical, but not heat, hyperalgesia associated with muscle inflammation. Pain 129(1–2):102–112. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2006.09.038
Tillu DV, Gebhart GF, Sluka KA (2008) Descending facilitatory pathways from the RVM initiate and maintain bilateral hyperalgesia after muscle insult. Pain 136(3):331–339. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2007.07.011
Werner MU, Ringsted TK, Kehlet H, Wildgaard K (2013) Sensory testing in patients with postthoracotomy pain syndrome: Part 1: mirror-image sensory dysfunction. Clin J Pain 29(9):775–783. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e318277b646
Zimmermann M (1983) Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 16(2):109–110
Acknowledgments
We thank Božica Hržan for excellent technical assistance and Ivica Matak for help in performing capsaicin experiment and advices in SNAP-25 immunohistochemistry. This work was supported by Croatian Science Foundation (IP-2014-09-4503), University of Zagreb financial support (Project BM005) and Croatian Ministry of Science, Education and Sports (Project No. 101-1010003- 0001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. Experiments were approved by the Ethical Committee of the University of Zagreb School of Medicine (permit No. 07-76/2005-43).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drinovac Vlah, V., Bach-Rojecky, L. & Lacković, Z. Antinociceptive action of botulinum toxin type A in carrageenan-induced mirror pain. J Neural Transm 123, 1403–1413 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-016-1605-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-016-1605-7