Abstract
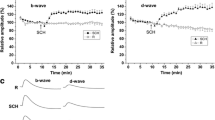
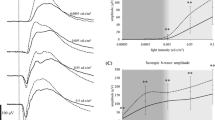
The effects of dopamine receptor blockade by sulpiride (D2-class antagonist) and sulpiride plus SCH 23390 (D1-class antagonist) on the V − log I function of the electroretinographic (ERG) b- and d-waves were investigated in light-adapted frog eyes. Sulpiride significantly decreased the absolute sensitivity of the b- and d-waves. The amplitude of the both waves was diminished over the whole intensity range studied. A similar effect on the b-, but not d-wave amplitude was seen during the perfusion with sulpiride plus SCH 23390. The effect on the d-wave amplitude depended on stimulus intensity. The threshold of the d-wave was not significantly altered. The suprathreshold d-wave amplitude was enhanced at the lower stimulus intensities and remained unchanged at the higher ones. The results obtained indicate that the action of endogenous dopamine on the photopic ERG shows clear ON–OFF asymmetry. Participation of different classes of dopamine receptors is probably responsible for this difference.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barton AC, Black LE, Sibley DR (1991) Agonist-induced desensitization of D2 dopamine receptors in human Y-79 retinoblastoma cells. Mol Pharmacol 39:650–658
Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR (2011) The physiology, signaling and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 63:182–217
Boatright JH, Hoel MJ, Iuvone PM (1989) Stimulation of endogenous dopamine release and metabolism in amphibian retina by light- and K+-evoked depolarization. Brain Res 482:164–168
Bodis-Wollner I, Marx MS, Ghilardi MF (1989) Systemic haloperidol administration increases the amplitude of the light- and dark-adapted ERG in the monkey. Clin Vision Sci 4:19–26
Boelen MK, Boelen MG, Marshak DW (1998) Light-stimulated release of dopamine from the primate retina is blocked by 1-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid (APB). Vis Neurosci 15:97–103
Citron MC, Erinoff L, Rickman DW, Brecha NC (1985) Modification of electroretinograms in dopamine-depleted retinas. Brain Res 345:186–191
Dong CJ, McReynolds JS (1991) The relationship between light, dopamine release and horizontal cell coupling in the mudpuppy retina. J Physiol 440:291–309
Fain GL (1976) Sensitivity of toad rods: dependence on wave-length and background illumination. J Physiol 261:71–101
Gardner B, Liu ZF, Jiang D, Sibley DR (2001) The role of phosphorylation/dephosphorylation in agonist-induced desensitization of D1 dopamine receptor function: evidence for a novel pathway for receptor dephosphorylation. Mol Pharmacol 59:310–321
Gibson CJ (1990) A simple perfusion system for measuring endogenous retinal dopamine release. J Neurosci Methods 32:75–79
Godley BF, Wurtman RJ (1988) Release of endogenous dopamine from the superfused rabbit retina in vitro: effect of light stimulation. Brain Res 452:393–395
Hampson EC, Vaney DI, Weiler R (1992) Dopaminergic modulation of gap junction permeability between amacrine cells in mammalian retina. J Neurosci 12:4911–4922
He S, Weiler R, Vaney DI (2000) Endogenous dopaminergic regulation of horizontal cell coupling in the mammalian retina. J Comp Neurol 418:33–40
Herrmann R, Heflin SJ, Hammond T, Lee B, Wang J, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG, Eggers ED, Frishman LJ, McCall MA, Arshavsky VY (2011) Rod vision is controlled by dopamine-dependent sensitization of rod bipolar cells by GABA. Neuron 72:101–110
Holopigian K, Clewner L, Seiple W, Kupersmith MJ (1994) The effects of dopamine blockade on the human flash electroretinogram. Doc Ophthalmol 86:1–10
Hood DC, Hock PA (1975) Light adaptation of the receptors: increment threshold function for the frog’s rods and cones. Vision Res 15:545–553
Hu EH, Pan F, Volgyi B, Bloomfield SA (2010) Light increases the gap junctional coupling of retinal ganglion cells. J Physiol 588:4145–4163
Huppe-Gourgues F, Coude G, Lachapelle P, Casanova C (2005) Effects of intravitreal administration of dopaminergic ligands on the b-wave amplitude of the rabbit electroretinogram. Vision Res 45:137–145
Ito K, Haga T, Lameh J, Sadée W (1999) Sequestration of dopamine D2 receptors depends on coexpression of G-protein-coupled receptor kinases 2 or 5. Eur J Biochem 260:112–119
Jackson CR, Ruan GX, Aseem F, Abey J, Gamble K, Stanwood G, Palmiter RD, Iuvone PM, McMahon DG (2012) Retinal dopamine mediates multiple dimensions of light-adapted vision. J Neurosci 32:9359–9368
Jaffe MJ, Levinson PD, Zimmlichman R, Coen JC, Karson CN, de Monasterio FM (1987) The effect of metoclopramide on the ganzfeld electroretinogram. Vision Res 27:1693–1700
Kim DY, Jung CS (2012) Gap junction contributions to the goldfish electroretinogram at the photopic illumination level. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 16:219–224
Kirsh M, Wagner HJ (1989) Release pattern of endogenous dopamine in teleost retinae during light adaptation and [harmacological stimulation. Vision Res 29:147–154
Ko F, Seeman P, Sun WS, Kapur S (2002) Dopamine D2 receptors internalize in their low-affinity state. Neuroreport 13:1017–1020
Kolbinger W, Weiler R (1993) Modulation of endogenous dopamine release in the turtle retina: effects of light, calcium, and neurotransmitters. Vis Neurosci 10:1035–1041
Kondo M, Piao CH, Tanikawa A, Horiguchi M, Terasaki H, Miyake Y (2000) Amplitude decrease of photopic ERG b-wave at higher stimulus intensities in humans. Jpn J Ophthalmol 44:20–28
Kramer SG (1971) Dopamine: a retinal neurotransmitter I. Retinal uptake, storage, and light-stimulated release of H3-dopamine in vivo. Invest Ophthal Vis Sci 10:438–452
Kroeze WK, Hufeisen SJ, Popadak BA, Renock SM, Steinberg S, Ernsberger P, Jayathilake K, Meltzer HY, Roth BL (2003) H1-histamine receptor affinity predicts short-term weight gain for typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs. Neuropsychopharmacol 28:519–526
Kupenova TN (2011) An inductive algorithm for smooth approximation of functions. Commun JINR, Dubna, E11-2011-97
Kupenova P, Belcheva S (1981) Effects of haloperidol, methylergometrine and phentolamine on the frog ERG. Experientia 37:852–854
Kupenova P, Popova E, Vitanova L (2008) GABAa and GABAc receptor mediated influences on the intensity-response functioned of the b- and d-wave in the frog ERG. Vision Res 48:882–892
Kupenova P, Vitanova L, Popova E (2010) GABAa and GABAc receptor-mediated modulation of responses to color stimuli: electroretinographic study in the turtle Emys orbicularis. J Neural Transm 117:431–444
Lasater EM, Dowling JE (1985) Dopamine decreases conductance of the electrical junctions between cultured retinal horizontal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3025–3029
Lavoie J, Illiano P, Sotnikova TD, Gainetdinov RR, Beaulieu JM, Hébert M (2013) The electroretinogram as a biomarker of central dopamine and serotonin: potential relevance to psychiatric disorders. Biol Psychiatry. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.11.024
Li L, Dowling JE (2000) Effects of dopamine depletion on visual sensitivity of zebrafish. J Neurosci 20:1893–1903
Li X, Schaeffel F, Konrad K, Eberhart Z (1996) A dose related response of 6-OHDA on chicken spectral sensitivity and oscillatory potentials of recording electroretinograms. Chin Med J 109:762–770
Lin ZS, Yazulla S (1994a) Depletion of retinal dopamine increases brightness perception in goldfish. Vis Neurosci 11:683–693
Lin ZS, Yazulla S (1994b) Depletion of retinal dopamine does not affect the ERG b-wave increment threshold function in goldfish in vivo. Vis Neurosci 11:695–702
Mills SL, Xia X-B, Hoshi H, Firth SI, Rice ME, Frishman LJ, Marshak DW (2007) Dopaminergic modulation of tracer coupling in a ganglion-amacrine cell network. Vis Neurosci 24:593–608
Mizota A, Adachi-Usami E (1993) Electroretinographic effects of haloperidol on the mouse retina. Doc Ophthalmol 85:151–160
Mora-Ferrer C, Behrend K (2004) Dopaminergic modulation of photopic temporal transfer properties in goldfish retina investigated with the ERG. Vision Res 44:2067–2081
Muresan Z, Besharse JC (1993) D2-like dopamine receptors in amphibian retina: localization with fluorescent ligands. J Comp Neurol 331:149–160
Naarendorp R, Hitchock PF, Sieving PA (1993) Dopaminergic modulation of rod pathway signals does not affect the scotopic ERG of cat at dark-adapted threshold. J Neurophysiol 70:1681–1691
Naka KI, Rushton WAH (1966) S-potentials from colour units in the retina of fish (Cyprinidae). J Physiol 185:536–555
Nakagawa T, Kurasaki S, Masuda T, Ukai K, Kubo S, Kadono H (1988) Effects of some psychotropic drugs on the b-wave of the electroretinogram in isolated rabbit retina. Jpn J Pharmacol 46:97–100
Negishi K, Teranishi T, Kato S (1983) A GABA antagonist, bicuculline, exerts its uncoupling action on external horizontal cells through dopamine cells in carp retina. Neurosci Lett 37:261–266
Oliver P, Jolicoeur FB, Lafond G, Drumheller A, Brunette JR (1987) Effects of retinal dopamine depletion on the rabbit electroretinogram. Doc Ophthalmol 66:359–371
Parkinson D, Rando RR (1983) Effect of light on dopamine turnover and metabolism in rabbit retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 24:384–388
Piccolino M, Neyton J, Gerschenfeld HM (1984) Decrease of gap junction permeability induced by dopamine and cyclic adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate in horizontal cells of turtle retina. J Neurosci 4:2477–2488
Popova E (2000) Glycinergic and GABAergic control of intensity-response function of frog ERG waves under different conditions of light stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand 170:225–242
Popova E, Kupenova P (2009) Contribution of proximal retinal neurons to b- and d-wave of frog electroretinogram under different conditions of light adaptation. Vision Res 49:2001–2010
Popova E, Kupenova P (2010) Contribution of voltage-gated sodium channels to b- and d-waves of frog electroretinogram under different conditions of light adaptation. Vision Res 50:88–98
Popova E, Kupenova P (2011) Effects of dopamine D1 receptor blockade on the intensity-response function of ERG b- and d-waves under different conditions of light adaptation. Vision Res 51:1627–1636
Popova E, Kupenova P, Vitanova L, Mitova L (1995) ERG OFF response in frog retina : light adaptation and the effect of 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate. Acta Physiol Scand 154:377–386
Puppala D, Maaswinkel H, Mason B, Legan SJ, Li L (2004) An in vivo microdialysis study of light.dark-modulation of vitreal dopamine release in zebrafish. J Neurocytol 33:193–201
Schneider T, Zrenner E (1991) Effects of D-1 and D-2 dopamine antagonists on ERG and optic nerve response of the cat. Exp Eye Res 52:425–430
Skrandies W, Wässle H (1988) Dopamine and serotonin in cat retina: electroretinography and histology. Exp Brain Res 71:231–240
Ueno S, Kondo M, Niwa Y, Terasaki H, Miyake Y (2004) Luminance dependence of neural components that underlies the primate photopic electroretinogram. IOVS 45:1033–1040
Vaquero CF, Pignatelli A, Partida GJ, Ishida AT (2001) A dopamine-and protein kinase A-dependent mechanism for network adaptation in retinal ganglion cells. J Neurosci 21:8624–8635
Veruki M (1997) Dopaminergic neurons in the rat retina express dopamine D2/3 receptors. Eur J Neurosci 9:1096–1100
Wali N, Leguire LE (1992) The photopic hill: a new phenomenon of the light adapted electroretinogram. Doc Ophthalmol 80:335–345
Walkembach J, Brüss M, Urban BW, Barann M (2005) Interactions of metoclopramide and ergotamine with human 5-HT3A receptors and human 5-HT reuptake carriers. Br J Pharmacol 146:543–552
Wang Y, Harsanyi K, Mangel SC (1997) Endogenous activation of dopamine D2 receptors regulates dopamine release in the fish retina. J Neurophysiol 78:439–449
Witkovsky P (2004) Dopamine and retinal function. Doc Ophthalmol 108:17–40
Witkovsky P, Stone S, Besharse JC (1988) The effects of dopamine and related ligands on photoreceptor to horizontal cell transfer in the Xenopus retina. Biomed Res 9(suppl 2):93–107
Witkovsky P, Nicholson C, Rice ME, Bohmaker K, Meller E (1993) Extracellular dopamine concentration in the retina of the clawed frog, Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5667–5671
Yazulla S, Lin ZS, Studholme KM (1996) Dopaminergic control of light-adaptive synaptic plasticity and role in goldfish visual behavior. Vision Res 36:4045–4057
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant № 14/2012 from the Council for Medical Science, Medical University Sofia.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Popova, E. Effects of dopamine receptor blockade on the intensity-response function of electroretinographic b- and d-waves in light-adapted eyes. J Neural Transm 121, 233–244 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-013-1103-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-013-1103-0