Abstract
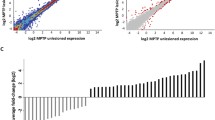
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most prevalent, progressive neurodegenerative disease and is characterized by the irreversible and selective loss of nigrostriatal dopaminergic (DA) neurons. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), which is a potent protective factor for DA neurons, is considered a promising neuroprotective candidate for PD. microRNAs (miRNAs) have been shown to be involved in a number of neurodegenerative diseases. Both miRNAs and GDNF affect DA neuronal processes, but the molecular crosstalk between these molecules remains unclear. The present study aimed to evaluate whether GDNF modulates miRNA expression. We used microarray analysis and real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) to investigate miRNAs expression in 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-injured MN9D cells treated with GDNF for 30 min, 1 h, or 3 h. Our results showed that GDNF treatment led to differential expression of 143 miRNAs. To further identify mechanisms by which GDNF exerts its effects, we compared miRNAs and mRNAs microarray data at the 1-h time point. We found that various biological processes and pathways were regulated at the miRNA level following GDNF treatment. Collectively, these results provide evidence of the capacity of GDNF to influence miRNAs expression, suggesting a new mechanism of GDNF action.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambros V (2003) MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell 113(6):673–676
Antony PM, Diederich NJ, Balling R (2011) Parkinson’s disease mouse models in translational research. Mamm Genome 22(7–8):401–419
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297
Beck KD, Valverde J, Alexi T, Poulsen K, Moffat B, Vandlen RA, Rosenthal A, Hefti F (1995) Mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons protected by GDNF from axotomy-induced degeneration in the adult brain. Nature 373(6512):339–341
Bové J, Prou D, Perier C, Przedborski S (2005) Toxin-induced models of Parkinson’s disease. NeuroRx 2(3):484–494
Braydich-Stolle L, Nolan C, Dym M, Hofmann MC (2005) Role of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in germ-line stem cell fate. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1061:94–99
Chapman EJ, Carrington JC (2007) Specialization and evolution of endogenous small RNA pathways. Nat Rev Genet 8(11):884–896
Chen CX, Huang SY, Zhang L, Liu YJ (2005) Synaptophysin enhances the neuroprotection of VMAT2 in MPP+-induced toxicity in MN9D cells. Neurobiol Dis 19(3):419–426
Choi HK, Won L, Roback JD, Wainer BH, Heller A (1992) Specific modulation of dopamine expression in neuronal hybrid cells by primary cells from different brain regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89(19):8943–8947
Crews L, Mizuno H, Desplats P, Rockenstein E, Adame A, Patrick C, Winner B, Winkler J, Masliah E (2008) Alpha-synuclein alters Notch-1 expression and neurogenesis in mouse embryonic stem cells and in the hippocampus of transgenic mice. J Neurosci 28(16):4250–4260
Dietz GP, Valbuena PC, Dietz B, Meuer K, Müeller P, Weishaupt JH, Bähr M (2006) Application of a blood-brain-barrier-penetrating form of GDNF in a mouse model for Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 1082(1):61–66
Gill SS, Patel NK, Hotton GR, O’Sullivan K, McCarter R, Bunnage M, Brooks DJ, Svendsen CN, Heywood P (2003) Direct brain infusion of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in Parkinson disease. Nat Med 9(5):589–595
Giraldez AJ, Mishima Y, Rihel J, Grocock RJ, Van Dongen S, Inoue K, Enright AJ, Schier AF (2006) Zebrafish MiR-430 promotes deadenylation and clearance of maternal mRNAs. Science 312(5770):75–79
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS, Bartel DP (2010) Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature 466(7308):835–840
Holtz WA, Turetzky JM, O’Malley KL (2005) Microarray expression profiling identifies early signaling transcripts associated with 6-OHDA-induced dopaminergic cell death. Antioxid Redox Signal 7(5–6):639–648
Horita Y, Honmou O, Harada K, Houkin K, Hamada H, Kocsis JD (2006) Intravenous administration of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor gene-modified human mesenchymal stem cells protects against injury in a cerebral ischemia model in the adult rat. J Neurosci Res 84(7):1495–1504
Huang JC, Babak T, Corson TW, Chua G, Khan S, Gallie BL, Hughes TR, Blencowe BJ, Frey BJ, Morris QD (2007) Using expression profiling data to identify human microRNA targets. Nat Methods 4(12):1045–1049
Ihle JN (1996) STATs: signal transducers and activators of transcription. Cell 84(3):331–334
Joung JG, Hwang KB, Nam JW, Kim SJ, Zhang BT (2007) Discovery of microRNA mRNA modules via population-based probabilistic learning. Bioinformatics 23(9):1141–1147
Kim EK, Choi EJ (2010) Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802(4):396–405
Kuure S, Sainio K, Vuolteenaho R, Ilves M, Wartiovaara K, Immonen T, Kvist J, Vainio S, Sariola H (2005) Crosstalk between Jagged1 and GDNF/Ret/GFRalpha1 signalling regulates ureteric budding and branching. Mech Dev 122(6):765–780
Liang Q, Liou AK, Ding Y, Cao G, Xiao X, Perez RG, Chen J (2004) 6-Hydroxydopamine induces dopaminergic cell degeneration via a caspase-9-mediated apoptotic pathway that is attenuated by caspase-9dn expression. J Neurosci Res 77(5):747–761
Lin LF, Doherty DH, Lile JD, Bektesh S, Collins F (1993) GDNF: a glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Science 260(5111):1130–1132
Linsley PS, Schelter J, Burchard J, Kibukawa M, Martin MM, Bartz SR, Johnson JM, Cummins JM, Raymond CK, Dai H, Chau N, Cleary M, Jackson AL, Carleton M, Lim L (2007) Transcripts targeted by the microRNA-16 family cooperatively regulate cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol 27(6):2240–2252
Liu X, Wang T, Wakita T, Yang W (2010) Systematic identification of microRNA and messenger RNA profiles in hepatitis C virus-infected human hepatoma cells. Virology 398(1):57–67
Marsden CD, Olanow CW (1998) The causes of Parkinson’s disease are being unraveled and rational neuroprotective therapy is close to reality. Ann Neurol 44(3 Suppl 1):S189–S196
Miska EA (2005) How microRNAs control cell division, differentiation and death. Curr Opin Genet Dev 15(5):563–568
Mouradian MM (2012) MicroRNAs in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 46(2):279–284
Nutt JG, Burchiel KJ, Comella CL, Jankovic J, Lang AE, Laws ER Jr, Lozano AM, Penn RD, Simpson RK Jr, Stacy M, Wooten GF (2003) Randomized, double-blind trial of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) in PD. Neurology 60(1):69–73
Pascual A, Hidalgo-Figueroa M, Piruat JI, Pintado CO, Gómez-Díaz R, López-Barneo J (2008) Absolute requirement of GDNF for adult catecholaminergic neuron survival. Nat Neurosci 11(7):755–761
Patel S, Singh V, Kumar A, Gupta YK, Singh MP (2006) Status of antioxidant defense system and expression of toxicant responsive genes in striatum of maneb- and paraquat-induced Parkinson’s disease phenotype in mouse: mechanism of neurodegeneration. Brain Res 1081(1):9–18
Schratt GM, Tuebing F, Nigh EA, Kane CG, Sabatini ME, Kiebler M, Greenberg ME (2006) A brain-specific microRNA regulates dendritic spine development. Nature 439(7074):283–289
Simon AR, Rai U, Fanburg BL, Cochran BH (1998) Activation of the JAK-STAT pathway by reactive oxygen species. Am J Physiol 275(6 Pt 1):C1640–C1652
Singh MP, Patel S, Dikshit M, Gupta YK (2006) Contribution of genomics and proteomics in understanding the role of modifying factors in Parkinson’s disease. Indian J Biochem Biophys 43(2):69–81
Singh C, Ahmad I, Kumar A (2007) Pesticides and metals induced Parkinson’s disease: involvement of free radicals and oxidative stress. Cell Mol Biol 53(5):19–28
Singhal NK, Srivastava G, Patel DK, Jain SK, Singh MP (2011) Melatonin or silymarin reduces maneb- and paraquat-induced Parkinson’s disease phenotype in the mouse. J Pineal Res 50(2):97–109
Slevin JT, Gerhardt GA, Smith CD, Gash DM, Kryscio R, Young B (2005) Improvement of bilateral motor functions in patients with Parkinson disease through the unilateral intraputaminal infusion of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurosurg 102(2):216–222
Smith MP, Cass WA (2007) GDNF reduces oxidative stress in a 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 412(3):259–263
Subramaniam S, Strelau J, Unsicker K (2008) GDNF prevents TGF-beta-induced damage of the plasma membrane in cerebellar granule neurons by suppressing activation of p38-MAPK via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. Cell Tissue Res 331(2):373–383
Tansey MG, McCoy MK, Frank-Cannon TC (2007) Neuroinflammatory mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease: potential environmental triggers, pathways, and targets for early therapeutic intervention. Exp Neurol 208(1):1–25
Tomac A, Lindqvist E, Lin LF, Ogren SO, Young D, Hoffer BJ, Olson L (1995) Protection and repair of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system by GDNF in vivo. Nature 373(6512):335–339
Vo N, Klein ME, Varlamova O, Keller DM, Yamamoto T, Goodman RH, Impey S (2005) A cAMP-response element binding protein-induced microRNA regulates neuronal morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(45):16426–16431
Yang F, Feng L, Zheng F, Johnson SW, Du J, Shen L, Wu CP, Lu B (2001) GDNF acutely modulates excitability and A-type K(+) channels in midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Nat Neurosci 4(11):1071–1078
Yoong LF, Wan G, Too HP (2006) Glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor and neurturin regulate the expressions of distinct miRNA precursors through the activation of GFRalpha2. J Neurochem 98(4):1149–1158
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81101899) and a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Higher Education Institution (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Chen, H., Chen, F. et al. Effects of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor on microRNA expression in a 6-hydroxydopamine-injured dopaminergic cell line. J Neural Transm 120, 1511–1523 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-013-1031-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-013-1031-z