Summary.
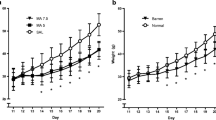
C57/BL6 mice were administered either 7.5 mg Fe2+/kg or vehicle (saline) postnatally on days 10–12 after birth. From 61 days of age onwards for 21 days, groups of mice were administered either clozapine (1 or 5 mg/kg, s.c.) or haloperidol (1 mg/kg, s.c.) or vehicle (Tween-80). Twenty-four hours after the final injection of either neuroleptic compound or vehicle, spontaneous motor activity was measured over a 60-min interval. Following this, each animal was removed, injected apomorphine (1 mg/kg, s.c.) and replaced in the same test chamber. It was found that postnatal administration of Fe2+ at the 7.5 mg/kg dose level reduced activity during the initial 20-min periods (0–20 and 20–40 min) and then induced hyperactivity during the final 20-min period over all three parameters of activity. Subchronic treatment with the higher, 5 mg/kg, dose of clozapine abolished or attenuated the hypoactivity in by postnatal Fe2+ during the 1st two 20-min periods over all three parameters of activity. Subchronic treatment with the higher, 5 mg/kg, dose of clozapine abolished or attenuated the hyperactivity in by postnatal Fe2+ during the 3rd and final 20-min period. Subchronic administration of haloperidol, without postnatal iron, increased the level of both locomotion (1st 20 min) and rearing (2nd 20 min) activity. Postnatal administration of Fe2+ at the 7.5 mg/kg dose increased the levels of both locomotion and rearing, but not total activity, following administration of apomorphine (1 mg/kg). Subchronic administration of clozapine, at both the 1 and 5 mg/kg doses, reduced the increased locomotor activity caused by postnatal Fe2+, whereas clozapine, 5 mg/kg, elevated further the postnatal Fe2+-induced increased in rearing. Subchronic administration of clozapine, at both the 1 and 5 mg/kg doses, and haloperidol, 1 mg/kg, increased the level of locomotor following administration of apomorphine (1 mg/kg) in mice treated postnatally with vehicle, whereas only clozapine increased the level of rearing. Correlational analyses indicated that both apomorphine-induced locomotion and rearing were highly correlated with the total iron content in the basal ganglia, thereby offering direct evidence of the linear relationship between iron content in the basal ganglia and the behavioural expression of DA D2-receptor supersensitivity in mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T Archer A Fredriksson G Jonsson T Lewander AK Mohammed SB Ross U Soderberg (1986) ArticleTitleCentral noradrenaline depletion antagonizes aspects of d-amphetamine-induced hyperactivity in the rat. Psychopharmacology 88 141–146 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00652230 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XitFyqurs%3D Occurrence Handle3081924
T Archer N Schröder A Fredriksson (2003) ArticleTitleNeurobehavioural deficits following postnatal iron overload. II. Instrumental learning performance. Neurotox Res 5 77–94 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3srmtFWisQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle14628858
D Ben-Shachar MB Youdim (1990) ArticleTitleNeuroleptic-induced supersensitivity and brain iron. I. Iron deficiency and neuroleptic-induced dopamine D2 receptor supersensitivity. J Neurochem 54 1136–1141 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXhvFWkur8%3D Occurrence Handle1968955
D Ben-Shachar E Livne I Spanier R Zuk MB Youdim (1993) ArticleTitleIron modulates neuroleptic-induced effects related to the dopaminergic system. Isr J Med Sci 29 587–592 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuD2c3gtlA%3D Occurrence Handle7901181
D Ben-Shachar B Pinhassi MB Youdim (1991) ArticleTitlePrevention of neuroleptic-induced dopamine D2 receptor supersensitivity by chronic iron salt treatment. Eur J Pharmacol 202 177–183 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0014-2999(91)90292-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXmsVOqtL8%3D Occurrence Handle1687031
RG Bolles PJ Woods (1964) ArticleTitleThe ontogeny of behaviour in the albino rat. Anim Behav 12 427–441 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0003-3472(64)90062-4
A Campbell RJ Baldessarini (1981) ArticleTitleTolerance to behavioural effects of haloperidol. Life Sci 29 1341–1346 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0024-3205(81)90677-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXlvVSqu7g%3D Occurrence Handle7197320
BA Campbell LD Lytle HC Fibiger (1969) ArticleTitleOntogeny of adrenergic arousal and cholinergic inhibitory mechanisms in the rat. Science 166 635–637 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3cXhtFaksA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle5823302
Davison AN, Dobbing J (1968) Applied neurochemistry. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 178–221, 253–316
DT Dexter A Carayon F Javoy-Agid Y Agid FR Wells SE Daniel AJ Lees P Jenner CD Marsden (1991) ArticleTitleAlterations in the levels of iron, ferritin and other trace metals in Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases affecting the basal ganglia. Brain 114 1953–1975 Occurrence Handle1832073
DT Dexter FR Wells F Agid Y Agid AJ Lees P Jenner CD Marsden (1987) ArticleTitleIncreased nigral iron content in postmortem parkinsonian brain [letter]. Lancet 2 1219–1220 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BieD28vmtlI%3D Occurrence Handle2890848
BP Drayer W Olanow P Burger GA Johnson R Herfkens S Riederer (1986) ArticleTitleParkinson plus syndrome: diagnosis using high field MR imaging of brain iron. Radiology 159 493–498 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BimC2sfktlI%3D Occurrence Handle3961182
AJ Dwork G Lawler PA Zybert M Durkin M Osman N Willson AI Barkai (1990) ArticleTitleAn autoradiographic study of the uptake and distribution of iron by the brain of the young rat. Brain Res 518 31–39 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0006-8993(90)90950-G Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXltFaqsb8%3D Occurrence Handle2390723
PH Evans (1993) ArticleTitleFree radicals in brain metabolism and pathology. Br Med Bull 49 577–587 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXltFaguw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle8221024
A Fredriksson N Schroder T Archer (2003) ArticleTitleNeurobehavioural deficits following postnatal iron overload. I. Spontaneous motor activity. Neurotoxicity Res 5 53–76 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3srmtFWisw%3D%3D
A Fredriksson N Schroder P Eriksson I Izquierdo T Archer (1999) ArticleTitleNeonatal iron exposure induces neurobehavioural dysfunctions in adult mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 159 25–30 Occurrence Handle10.1006/taap.1999.8711 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXltFSgs70%3D Occurrence Handle10448122
A Fredriksson N Schroder P Eriksson I Izquierdo T Archer (2000) ArticleTitleMaze learning and motor activity deficits in adult mice induced by iron exposure during a critical postnatal period. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 119 65–74 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXltVCnug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10648873
A Fredriksson N Schroder P Eriksson I Izquierdo T Archer (2001) ArticleTitleNeonatal iron potentiates adult MPTP-induced neurodegenerative and functional deficits. Parkinsonism Rel Dis 7 97–105
M Gerlach D Ben-Shachar P Riederer MB Youdim (1994) ArticleTitleAltered brain metabolism of iron as a cause of neurodegenerative diseases? J Neurochem 63 793–807 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXlsFCgtLo%3D Occurrence Handle7519659
J Glowinski LL Iversen (1966) ArticleTitleRegional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]norepinephrine, [3H]dopamine and [3H]dopa in various regions of the brain. J Neurochem 13 655–669 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF28Xks1Kqtrw%3D Occurrence Handle5950056
MM Iqbal A Rahman Z Husain SZ Mahmud WG Ryan JM Feldman (2003) ArticleTitleClozapine: a clinical review of adverse effects and management. Ann Clin Psychiat 15 33–48
Janetzky B, Reichmann H, Youdim MBH, Riederer P (1997) Iron and oxidative damage in neurodegenerative diseases. In: Beal MF, Howell H, Bodis-Wollner I (eds) Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 407–421
E Kienzl L Puchinger K Jellinger W Linert H Stachelberger RF Jameson (1995) ArticleTitleThe role of transition metals in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 134 IssueIDSuppl 69–78 Occurrence Handle8847547
Kirk R (1995) Experimental design: procedures for the behavioural sciences. Brooks/Cole, Belmont, CA
P Laduron K De Bie J Leysen (1977) ArticleTitleSpecific effect of haloperidol on dopamine turnover in the frontal cortex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 296 183–185 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00508472 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2sXktFGqs78%3D Occurrence Handle834317
JA Lieberman (1998) ArticleTitleMaximizing clozapine therapy: managing side effects. J Clin Psychiatry 59 38–43 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXis1Srtro%3D Occurrence Handle9541337
DC Mash J Pablo BE Buck J Sanchez-Ramos WJ Weiner (1991) ArticleTitleDistribution and number of transferrin receptors in Parkinson’s disease and in MPTP-treated mice. Exp Neurol 114 73–81 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0014-4886(91)90086-R Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXmt12ls7o%3D Occurrence Handle1915737
T Matsumoto H Uchimura M Hirano J Soo Kim H Yokoo M Shimomura T Nakahara K Inoue K Oomagari (1983) ArticleTitleDifferential effects of acute and chronic administration of haloperidol on homovanillic acid levels in discrete levels of rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 89 27–33 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXktFKnurw%3D Occurrence Handle6861888
RG McKenzie MJ Zigmond (1985) ArticleTitleChronic neuroleptic treatment increased D-2 but not D-1 receptors in the rat striatum. Eur J Pharmacol 113 159–165
HR Meltzer S Matsubara JC Lee (1989) ArticleTitleClassification of typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs on the basis of D1–D2 and serotonin PK1 values. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 251 3238–3246
CW Olanow (1992) ArticleTitleMagnetic-resonance-imaging in parkinsonism. Neurol Clin 10 405–420 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2B287lt1M%3D Occurrence Handle1584182
PK Randall (1985) ArticleTitleQuantification of dopaminergic supersensitivity using apomorphine induced behaviour in the mouse. Life Sci 37 1419–1423 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0024-3205(85)90081-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXlsFCjt70%3D Occurrence Handle4046742
PK Randall JA Severson CE Finch (1981) ArticleTitleAging and the regulation of striatal dopaminergic mechanisms in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 219 695–700 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXmtFGitLo%3D Occurrence Handle7197719
H Reichmann B Janetzky P Riederer (1995) ArticleTitleIron-dependent enzymes in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Suppl) 46 157–164 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XitVKht7Y%3D
GP Reynolds JE Brown JE McCall AVP McKay (1992) ArticleTitleDopamine receptor abnormalities in the striatum and pallidum in tardive dyskinesia: a postmortem study. J Neural Transm 87 225–230 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01245368 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2B2MrptFA%3D
E Richelson A Elson (1984) ArticleTitleAntagonism of neurotransmitter receptors of normal human brain in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol 103 197–214 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0014-2999(84)90478-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXls1emu74%3D Occurrence Handle6149136
P Riederer E Sofic WD Rausch B Schmidt GP Reynolds K Jellinger MB Youdim (1989) ArticleTitleTransition metals, ferritin, glutathione, and ascorbic acid in parkinsonian brains. J Neurochem 52 515–520 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXhtFals78%3D Occurrence Handle2911028
Rozenzweig MR, Leiman AL, Breedlove SM, (1999) Biological psychology: an introduction to behavioural, cognitive and clinical neuroscience. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA
B Scatton (1977) ArticleTitleDifferential regional development of the tolerance to increase in dopamine turnover upon repeated neuroleptic administration. Eur J Pharmacol 46 363–369 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0014-2999(77)90230-8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXhtFGgsrg%3D Occurrence Handle590344
N Schroder A Fredriksson M Vianna R Roesler I Izquierdo T Archer (2001) ArticleTitleMemory deficits in adult rats following postnatal iron administration. Behav Brain Res 124 77–85 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXksVyltL8%3D Occurrence Handle11423168
Strong R, Mattamal M, Andorn A (1993) Free radicals in aging. In: Yu B (ed) Free radicals, the aging brain, and age-related neurodegenerative disorders. CRC Press, Florida, pp 223–246
KF Swaiman (1991) ArticleTitleHallervorden-Spatz syndrome and brain iron metabolism. Arch Neurol 48 1285–1293 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyB28zotlE%3D Occurrence Handle1845035
D Tarsy RJ Baldessarini (1974) ArticleTitleBehavioural supersensitivity to apomorphine following treatment with drugs which interfere with synaptic function of catecholamines. Neuropharmacology 13 927–940 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0028-3908(74)90084-7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2MXmvValtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle4474641
EM Taylor EH Morgan (1990) ArticleTitleDevelopmental changes in transferrin and iron uptake by the brain in the rat. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 55 35–42 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXlt12kur0%3D Occurrence Handle2208639
EM Taylor A Crowe EH Morgan (1991) ArticleTitleTransferrin and iron uptake by the brain: effects of altered iron status. J Neurochem 57 1584–1592 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXmsFCrtrs%3D Occurrence Handle1919575
JL Waddington (1990) ArticleTitleNeuroleptic/dopamine receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 183 106
PF Von Voigtlander EG Losey HF Triezenberg (1975) ArticleTitleIncreased sensitivity to dopaminergic agents after chronic neuroleptic treatment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 193 88–94 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2MXktVSks7o%3D
MB Youdim D Ben-Shachar P Riederer (1991) ArticleTitleIron in brain function and dysfunction with emphasis on Parkinson’s disease. Eur Neurol 31 34–40 Occurrence Handle1649757
MB Youdim D Ben-Shachar P Riederer (1993) ArticleTitleThe possible role of iron in the etiopathology of Parkinson’s disease [published erratum appears in Mov Disord (1993) 8(2): 255]. Mov Disord 8 1–12 Occurrence Handle10.1002/mds.870080102 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyC38rlvVA%3D Occurrence Handle8419792
MB Youdim E Grunblatt S Mandel (1999) ArticleTitleThe pivotal role of iron in NF-kappa B activation and nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Prospects for neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease with iron chelators. Ann NY Acad Sci 890 7–25 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXnsVCquw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10668410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fredriksson, A., Eriksson, P. & Archer, T. Postnatal iron-induced motor behaviour alterations following chronic neuroleptic administration in mice. J Neural Transm 113, 137–150 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-005-0307-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-005-0307-3