Summary.
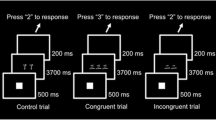
The Continuous Performance Test (CPT) is an appropriate instrument for assessment of correlates at the brain electrical activity level of attention and response to stimulant medication. The aim of the study was to confirm at the electrophysiological level the clinical effectiveness of methylphenidate (MPH) in children with attention deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD); to this end, a comparative study of hyperactive and healthy control children was undertaken, employing a modified CPT test.
Twenty-one channel ERPs from 17 hyperactive boys, with and without MPH treatment, and from 20 healthy control children were analyzed with reference-independent techniques. The resulting quasi-stabile microstates correspond to the time ranges of the conventional ERP components P100, P200 and P300 (with the subcomponents P3a and P3b) and could be discriminated by means of data-based segmentation. The P3a amplitudes of the hyperactive children, in each case with and without MPH medication, were compared with those of healthy controls.
P3a segment amplitudes were significantly lower in non-medicated ADHD patients than in healthy children, both following positive and inhibitory stimulus conditions. A significant medication effect was detected following MPH treatment: segment 3 amplitudes in MPH-treated hyperactive children were not significantly different from those of healthy controls.
MPH exerts a highly potent effect on stimulus recognition and resulting consequences. Application of the CPT-OX enables the reliable measurement of electrophysiological correlates of the clinical effectiveness of MPH under different stimulus conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received November 5, 2002; accepted January 27, 2003 Published online May 5, 2003
Authors' address: J. Seifert, M.D., Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, University Hospital Würzburg, Füchsleinstrasse 15, D-97080 Wuerzburg, Germany, e-mail: kjp@nervenklinik.uni-wuerzburg.de
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seifert, J., Scheuerpflug, P., Zillessen, KE. et al. Electrophysiological investigation of the effectiveness of methylphenidate in children with and without ADHD. J Neural Transm 110, 821–829 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-003-0818-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-003-0818-8