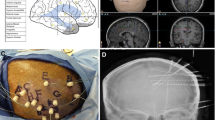
Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the safety and efficacy of stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG)-guided radiofrequency thermocoagulation (RFTC) for drug-resistant focal epilepsy and investigate the relationship between post-RFTC remission duration and delayed excision surgery effectiveness.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective analysis of 43 patients with drug-resistant focal epilepsy who underwent RFTC via SEEG electrodes. After excluding three, the remaining 40 were classified into subgroups based on procedures and outcomes. Twenty-four patients (60%) underwent a secondary excision surgery. We determined the predictive value of RFTC outcome upon subsequent surgical outcome by categorizing the delayed secondary surgery outcome as success (Engel I/II) versus failure (Engel III/IV). Demographic information, epilepsy characteristics, and the duration of seizure freedom after RFTC were assessed.
Results
Among 40 patients, 20% achieved Engel class I with RFTC alone, while 24 underwent delayed secondary excision surgery. Overall, 41.7% attained Engel class I, with a 66.7% success rate combining RFTC with delayed surgery. Seizure freedom duration was significantly longer in the success group (mean 4.9 months, SD = 2.7) versus the failure group (mean 1.9 months, SD = 1.1; P = 0.007). A higher proportion of RFTC-only and delayed surgical success group patients had preoperative lesional findings (p = 0.01), correlating with a longer time to seizure recurrence (p < 0.05). Transient postoperative complications occurred in 10%, resolving within a year.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that SEEG-guided RFTC is a safe and potential treatment option for patients with drug-resistant focal epilepsy. A prolonged duration of seizure freedom following RFTC may serve as a predictive marker for the success of subsequent excision surgery.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Bourdillon P, Cucherat M, Isnard J, Ostrowsky-Coste K, Catenoix H, Guénot M et al (2018) Stereo-electroencephalography-guided radiofrequency thermocoagulation in patients with focal epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsia 59:2296–2304
Bourdillon P, Devaux B, Job-Chapron AS, Isnard J (2018) SEEG-guided radiofrequency thermocoagulation. Neurophysiol Clin 48:59–64
Bourdillon P, Isnard J, Catenoix H, Montavont A, Rheims S, Ryvlin P et al (2016) Stereo-electro-encephalography-guided radiofrequency thermocoagulation: from in vitro and in vivo data to technical guidelines. World neurosurgery. 94:73–79
Bourdillon P, Isnard J, Catenoix H, Montavont A, Rheims S, Ryvlin P et al (2017) Stereo electroencephalography-guided radiofrequency thermocoagulation (SEEG-guided RF-TC) in drug-resistant focal epilepsy: Results from a 10-year experience. Epilepsia. 58:85–93
Bourdillon P, Rheims S, Catenoix H, Montavont A, Ostrowsky-Coste K, Isnard J et al (2020) Surgical techniques: Stereoelectroencephalography-guided radiofrequency-thermocoagulation (SEEG-guided RF-TC). Seizure 77:64–68
Catenoix H, Bourdillon P, Guénot M, Isnard J (2018) The combination of stereo-EEG and radiofrequency ablation. Epilepsy Res 142:117–120
Cossu M, Fuschillo D, Cardinale F, Castana L, Francione S, Nobili L et al (2014) Stereo-EEG-guided radio-frequency thermocoagulations of epileptogenic grey-matter nodular heterotopy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 85:611–617
Cossu M, Fuschillo D, Casaceli G, Pelliccia V, Castana L, Mai R et al (2015) Stereoelectroencephalography-guided radiofrequency thermocoagulation in the epileptogenic zone: a retrospective study on 89 cases. J Neurosurg 123:1358–1367
Dai Y, Zhang H, Fan X, Wei P, Shan Y, Zhao G (2023) Optimized SEEG-guided three-dimensional radiofrequency thermocoagulation for insular epilepsy. Acta Neurochirurgica 165:249–258
Dimova P, de Palma L, Job-Chapron AS, Minotti L, Hoffmann D, Kahane P (2017) Radiofrequency thermocoagulation of the seizure-onset zone during stereoelectroencephalography. Epilepsia. 58:381–392
d’Orio P, Revay M, Bevacqua G, Battista F, Castana L, Squarza S et al (2023) Stereo-electroencephalography (SEEG)-guided surgery in epilepsy with cingulate gyrus involvement: electrode implantation strategies and postoperative seizure outcome. J Clin Neurophysiol 40:516–528
Fan X, Shan Y, Lu C, An Y, Wang Y, Du J et al (2019) Optimized SEEG-guided radiofrequency thermocoagulation for mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis. Seizure 71:304–311
Gao R, Yu T, Xu C, Zhang X, Yan X, Ni D et al (2020) The value of magnetoencephalography for stereo-EEG-guided radiofrequency thermocoagulation in MRI-negative epilepsy. Epilepsy research 163:106322
Guénot M, Isnard J, Ryvlin P, Fischer C, Mauguière F, Sindou M (2004) SEEG-guided RF thermocoagulation of epileptic foci: feasibility safety, and preliminary results. Epilepsia 45:1368–1374
Isnard J, Taussig D, Bartolomei F, Bourdillon P, Catenoix H, Chassoux F et al (2018) French guidelines on stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG). Neurophysiol Clin 48:5–13
Kohlhase K, Zöllner JP, Tandon N, Strzelczyk A, Rosenow F (2021) Comparison of minimally invasive and traditional surgical approaches for refractory mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes. Epilepsia 62:831–845
Kwan P, Arzimanoglou A, Berg AT, Brodie MJ, Allen Hauser W, Mathern G et al (2010) Definition of drug resistant epilepsy: consensus proposal by the ad hoc Task Force of the ILAE Commission on Therapeutic Strategies. Epilepsia 51:1069–1077
Li H, Zhang M, Lin Z, Deng Z, Cao C, Zhan S et al (2023) Utility of hybrid PET/MRI in stereoelectroencephalography guided radiofrequency thermocoagulation in MRI negative epilepsy patients. Front Neurosci 17:1163946
Mercier MR, Dubarry AS, Tadel F, Avanzini P, Axmacher N, Cellier D et al (2022) Advances in human intracranial electroencephalography research, guidelines and good practices. NeuroImage 260:119438
Mirandola L, Mai RF, Francione S, Pelliccia V, Gozzo F, Sartori I et al (2017) Stereo-EEG: Diagnostic and therapeutic tool for periventricular nodular heterotopia epilepsies. Epilepsia 58:1962–1971
Moles A, Guénot M, Rheims S, Berthiller J, Catenoix H, Montavont A et al (2018) SEEG-guided radiofrequency coagulation (SEEG-guided RF-TC) versus anterior temporal lobectomy (ATL) in temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurol 265:1998–2004
Oliveira LP, Pérez-Enríquez C, Barguilla A, Langohr K, Conesa G, Infante N et al (2023) Stereo-electroencephalography-guided radiofrequency thermocoagulation in patients with MRI-negative focal epilepsy. J Neurosurg 138:837–846
Shields JA, Greven ACM, Shivamurthy VKN, Dickey AS, Matthews RE, Laxpati NG et al (2023) Stereoelectroencephalography-guided radiofrequency ablation of the epileptogenic zone as a treatment and predictor of future success of further surgical intervention. Epilepsia 64(8):2081–2093
Simula S, Garnier E, Contento M, Pizzo F, Makhalova J, Lagarde S et al (2023) Changes in local and network brain activity after stereotactic thermocoagulation in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy. Epilepsia 64:1582–1593
Tang B, Fu Y, Liu B, Yi Q (2022) Self-perceived burden and associated factors in Chinese adult epilepsy patients: A cross-sectional study. Front Neurol 13:994664
Voges J, Büntjen L, Schmitt FC (2018) Radiofrequency-thermoablation: General principle, historical overview and modern applications for epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 142:113–116
Wang R, Beg U, Padmanaban V, Abel TJ, Lipsman N, Ibrahim GM et al (2021) A systematic review of minimally invasive procedures for mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: too minimal, too fast? Neurosurgery 15(89):164–176
Wang Y, Xu J, Liu T, Chen F, Chen S, Xie Z et al (2020) Magnetic resonance-guided laser interstitial thermal therapy versus stereoelectroencephalography-guided radiofrequency thermocoagulation for drug-resistant epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsy Res 166:106397
Wei PH, An Y, Fan XT, Wang YH, Yang YF, Ren LK et al (2018) Stereoelectroencephalography-Guided Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation for Hypothalamic Hamartomas: Preliminary Evidence. World Neurosurg 114:e1073–e1078
Willems LM, Reif PS, Spyrantis A, Cattani A, Freiman TM, Seifert V et al (2019) Invasive EEG-electrodes in presurgical evaluation of epilepsies: Systematic analysis of implantation-, video-EEG-monitoring- and explantation-related complications, and review of literature. Epilepsy Behav: E&B 91:30–37
Yan H, Katz JS, Anderson M, Mansouri A, Remick M, Ibrahim GM et al (2019) Method of invasive monitoring in epilepsy surgery and seizure freedom and morbidity: a systematic review. Epilepsia 60:1960–1972
Zhu XR, Zhao T, Gu H, Gao YJ, Wang N, Zhao P et al (2019) High risk of anxiety and depression in caregivers of adult patients with epilepsy and its negative impact on patients’ quality of life. Epilepsy behav: E&B 90:132–136
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (NO: 2021YFF1200705).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Shaoya Yin conceived and designed the study. Weipeng Jin and Le Wang contributed to the surgery and provided technical support. Chuan Du and Yuzhang Wu conducted the clinical experiments, performed data analysis, interpreted the results, and drafted the manuscript. Guangrui Zhao and Deqiu Cui contributed to the surgery. Jingtao Yan and Guangfeng Li and performed data analysis. All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study has been approved by the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Huanhu Hospital (approval number NO. 2021–059), and has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, C., Jin, W., Wang, L. et al. Stereoelectroencephalography-guided radiofrequency thermocoagulation of the epileptogenic zone: a potential treatment and prognostic indicator for subsequent excision surgery. Acta Neurochir 166, 210 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-024-06106-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-024-06106-x