Abstract
Object
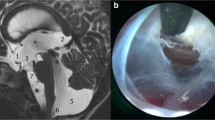
One of the critical steps for the success of intraventricular neuroendoscopic procedures is the entry into the third ventricle and passage of the endoscopy system through the foramen of Monro (FM). A diameter larger than that of the instrument used is considered a prerequisite for safely performing the technique, as damage to this structure can lead to alterations in the fornix and vascular structures. When the foramen diameter is narrow and there is no obstruction/stenosis, the role of foraminoplasty in reducing the risk of complications has not been adequately assessed in the literature.
Methods
A review of endoscopic procedures conducted at our center since 2018 was undertaken. Cases in which preoperative imaging indicated a FM diameter < 6 mm and foraminoplasty technique was applied were examined to determine the technical and functional success of the procedure. The technical success was determined by completing the neuroendoscopic procedure with the absence of macroscopic lesions in the various structures comprising the foramen and without complications in the follow-up imaging tests. Functional success was defined as the absence of cognitive/memory alterations during the 3-month postoperative follow-up. Additionally, a review of the various forms of foraminoplasty described in the literature is conducted.
Results
In our cohort, six patients were identified with a preoperative FM diameter < 6 mm without obstruction or stenosis. Foraminoplasty was planned for these cases to facilitate various intraventricular neuroendoscopic procedures. In all instances, the technique was successfully performed without causing macroscopic damage to the structures comprising the foramen. Follow-up visits included various cognitive tests to assess potential sequelae related to microscopic damage to the fornix. None of the patients exhibited anomalies.
Conclusion
Foraminoplasty in patients with a narrow FM without signs of stenosis/obstruction is a useful technique to reduce the risk of complications during the passage of the endoscopy system through this structure, enabling the safe performance of neuroendoscopic procedures.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data have been acquired from the database of our Hospital.
Code availability
Not Applicable.
Abbreviations
- CT :
-
Computed Tomography
- MRI :
-
Magnetic Resonance Image
- FM :
-
Foramen of Monro
- F :
-
French
References
(2018) Application of the Lotta ventriculoscopic system in clinical practice. Endo:Press Germany, second edition 47-48
Benabarre A, Ibáñez J, Boget T, Obiols J, Martínez-Aran A, Vieta E (2001) Neuropsychological and psychiatric complications in endoscopic third ventriculostomy: a clinical case report. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 71:268–271
Bonanni R, Carlesimo GA, Caltagirone C (2004) Amnesia following endoscopic third ventriculostomy: a single case study. Eur Neurol 51(2):118–120
Bouras T, Sgouros S (2011) Complications of endoscopic third ventriculostomy. J Neurosurg Pediatr 7(6):643–649
Ebrahimzadeh K, Maloumeh EN, Samadian M, Rezaei O (2018) Endoscopic strategy in surgical treatment of adult idiopathic bilateral occlusion of the foramen of Monro and review of the literature. World Neurosurg 115:e610–e619
Elkheshin S, Zohdi A (2022) Endoscopic Monro Foraminoplasty, types, techniques and complications avoidance. Interdiscip Neurosurg 29:101579
Guil-Ibáñez JJ, Parrón-Carreño T, Saucedo L, Masegosa-González J (2023) Neuronavigated foraminoplasty, shunt removal, and endoscopic third ventriculostomy in a 54-year-old patient with third shunt malfunction episode: how I do it. Acta Neurochir. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-023-05777-2.7
Jean WC, Tai AX, Hogan E, Herur-Raman A, Felbaum DR, Leonardo J, Syed HR (2019) An anatomical study of the foramen of Monro: implications in management of pineal tumors presenting with hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir 161(5):975–983
Kalhorn SP, Strom RG, Harter DH (2011) Idiopathic bilateral stenosis of the foramina of Monro treated using endoscopic foraminoplasty and septostomy. Neurosurg Focus 30(4):E5
Konar SK, Shukla D, Devi BI (2018) Neuroendoscopic management of coexisting congenital agenesis of bilateral foramen of monro with aqueductal stenosis and Chiari malformation: Case report and review of the literature. World Neurosurg 118:55–58
Migliorati K, Muratori A, Fontanella MM, Panciani PP (2018) Adult bilateral idiopathic occlusion of foramina of Monro: is foraminoplasty really safe and effective? BMJ Case Rep 2018:bcr2018226332
Mori H, Koike T, Fujimoto T, Nishiyama K, Yoshimura J, Tanaka R (2007) Endoscopic stent placement for treatment of secondary bilateral occlusion of the Monro foramina following endoscopic third ventriculostomy in a patient with aqueductal stenosis. Case report. J Neurosurg 107(2):416–420
Oertel J, Linsler S, Emmerich C, Keiner D, Gaab M, Schroeder H, Senger S (2017) Results of combined intraventricular neuroendoscopic procedures in 130 cases with special focus on fornix contusions. World Neurosurg 108:817–825
Punt J (2004) Third ventriculostomy in shunt malfunction. In: Cinalli G, Maixner WJ, Sainte-Rose C (eds) Pediatric Hydrocephalus. Springer-Verlag, Milan, pp 389–396
Schonauer C, Johnson R, Chiriatti S, de Falco R, Albanese V, Tessitore E, Barbagallo GM (2014) Adult idiopatic occlusion of Monro foramina: intraoperative endoscopic reinterpretation of radiological data and review of the literature. Br J Neurosurg 28(6):717–721
Schroeder HW, Niendorf WR, Gaab MR (2002) Complications of endoscopic third ventriculostomy. J Neurosurg 96(6):1032–1040
Sharifi G, Alavi E, Rezaee O, Jahanbakhshi A, Faramarzi F (2012) Neuroendoscopic foraminoplasty for bilateral idiopathic occlusion of foramina of Monro. Turk Neurosurg 22(2):265–268
Soleman J, Guzman R (2020) Neurocognitive Complications after Ventricular Neuroendoscopy: A Systematic Review. Behav Neurol 2020:2536319
Soni JP, Gupta BD, Soni M, Singh RN, Purohit NN, Gupta M, Dabi DR, Nemal KR (1995) Normal parametros of ventricular system in healthy Infants. Indian Pediatr Mayo de 32(5):549–555
Tirado-Caballero J, Rivero-Garvia M, Moreno-Madueño G, Gómez-González E, Márquez-Rivas J (2021) Cranial expansion and aqueductoplasty for combined isolated fourth ventricle and slit-ventricle syndrome: a surgical alternative. Child’s Nerv Syst : ChNS : Off J Int Soc Pediatr Neurosurg 37(3):885–894
Tirakotai W, Riegel T, Schulte DM, Bertalanffy H, Hellwig D (2004) Neuroendoscopic stent procedure in obstructive hydrocephalus due to both foramina of monro occluding craniopharyngioma: technical note. Surg Neurol 61(3):293–296
Torres-Corzo J, Rangel-Castilla L, Nakaji P (2019) Neuroendoscopic surgery. Thieme
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guil-Ibañez JJ: Conception, data gathering, writing, and production.
Gomar-Alba M; García-Pérez F; Saucedo L; Narro-Donate JM; Vargas-López AJ; Parrón-Carreño T; Castro-De Luna GM; Contreras Jiménez A; Masegosa-González J;: Reviewers.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Details of previous presentation(s): The authors declare that this manuscript has not been previously published in whole or in part or submitted elsewhere for review.
Authors declare that they have no personal or institutional financial interest in drugs, materials, or devices described in their submissions.
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments.
Consent to participate and publications
Informed consent to participate and for publication was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Written informed consent was obtained from the parents as legal guardians.
Conflict of Interest/Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 476436 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guil-Ibáñez, J.J., Gomar-Alba, M., García-Pérez, F. et al. Neuroendoscopic access to the third ventricle in patients with narrow foramen of monro without stenosis/obstruction: role of foraminoplasty. Acta Neurochir 166, 197 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-024-06077-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-024-06077-z