Abstract
Background
Epilepsy, a disease characterized by recurrent seizures, is a common chronic neurologic condition. Antiepileptic drugs (AED) are the mainstay of treatment for epilepsy. Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) surgery is an adjuvant therapy for the treatment of drug refractory epilepsy (DRE). VNS revision and implant removal surgeries remain common.
Methods
Using a single neurosurgeon data registry for epilepsy surgery, we retrospectively analyzed a total of 824 VNS surgeries. Patients were referred to two Level IV Comprehensive Epilepsy centers (from 08/1997 to 08/2022) for evaluation. Patients were divided into four groups: new device placement, revision surgery, removal surgery, and battery replacement for end-of-life of the generator. The primary endpoint was to analyze the reasons that led patients to undergo revision and removal surgeries. The time period from the index surgery to the removal surgery was also calculated.
Results
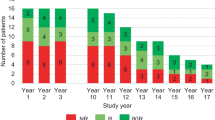
The median age of patients undergoing any type of surgery was 34 years. The primary reason for revision surgeries was device malfunction, followed by patients’ cosmetic dissatisfaction. There was no statistical sex-difference in revision surgeries. The median age and body mass index (BMI) of patients who underwent revision surgery were 38 years and 26, respectively. On the other hand, the primary reason for removal was lack of efficacy, followed again by cosmetic dissatisfaction. The survival analysis showed that 43% of VNS device remained in place for 5 years and 50% of the VNS devices were kept for 1533 days or 4.2 years.
Conclusions
VNS therapy is safe and well-tolerated. VNS revision and removal surgeries occur in less than 5% of cases. More importantly, attention to detail and good surgical technique at the time of the index surgery can increase patient satisfaction, minimize the need for further surgeries, and improve acceptance of the VNS technology.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and material are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Code availability
Code is available upon request from the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- AED:
-
Antiepileptic drugs
- VNS:
-
Vagus nerve stimulation
- DRE:
-
Drug refractory epilepsy
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration
- MRI:
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- PNES:
-
Psychogenic non-epileptic seizures
- EEG:
-
Electroencephalogram
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
References
Aalbers MW, Rijkers K, Klinkenberg S, Majoie M, Cornips EM (2015) Vagus nerve stimulation lead removal or replacement: surgical technique, institutional experience, and literature overview. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 157(11):1917–1924
Afra P, Adamolekun B, Aydemir S, Watson GDR (2021) Evolution of the vagus nerve stimulation (vns) therapy system technology for drug-resistant epilepsy. Front Med Technol 3:696543
Agarwal G, Wilfong AA, Edmonds JL Jr (2011) Surgical revision of vagus nerve stimulation electrodes in children. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 144(1):123–124
Air EL, Ghomri YM, Tyagi R, Grande AW, Crone K, Mangano FT (2009) Management of vagal nerve stimulator infections: do they need to be removed? J Neurosurg Pediatr 3(1):73–78
Baaj AA, Benbadis SR, Tatum WO, Vale FL (2008) Trends in the use of vagus nerve stimulation for epilepsy: analysis of a nationwide database. Neurosurg Focus 25(3):E10
Benbadis SR, Tatum WO, Vale FL (2000) When drugs don’t work: an algorithmic approach to medically intractable epilepsy. Neurology 55(12):1780–1784
Beghi E (2020) The epidemiology of epilepsy. Neuroepidemiology 54(2):185–191
Champeaux C, Landre E, Chassoux F, Mann MW, Devaux B, Turak B (2017) Vagus nerve stimulation removal or replacement involving the lead and the electrode: surgical technique, institutional experience and outcome. World Neurosurg 99:275–281
Couch JD, Gilman AM, Doyle WK (2016) Long-term expectations of vagus nerve stimulation: a look at battery replacement and revision surgery. Neurosurgery 78(1):42–46
Engel J Jr (2014) Approaches to refractory epilepsy. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 17(Suppl 1):S12–S17
Englot DJ, Rolston JD, Wright CW, Hassnain KH, Chang EF (2016) Rates and predictors of seizure freedom with vagus nerve stimulation for intractable epilepsy. Neurosurgery 79(3):345–353
Espinosa J, Aiello MT, Naritoku DK (1999) Revision and removal of stimulating electrodes following long-term therapy with the vagus nerve stimulator. Surg Neurol 51(6):659–664
Fisher RS (2017) The new classification of seizures by the international league against epilepsy 2017. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 17(6):48
Fitchett A, Mastitskaya S, Aristovich K (2021) Selective Neuromodulation of the Vagus Nerve. Front Neurosci 15:685872
Gigliotti MJ, Mao G, Dupre DA, Wilberger J (2018) Vagal nerve stimulation: indications for revision in adult refractory epilepsy. World Neurosurg 120:e1047–e1053
Giordano F, Zicca A, Barba C, Guerrini R, Genitori L (2017) Vagus nerve stimulation: surgical technique of implantation and revision and related morbidity. Epilepsia 58(Suppl 1):85–90
Grolemund GWH (2011) Dates and times made easy with lubridate. J Stat Softw 40(3):1–25
Guekht A, Brodie M, Secco M, Li S, Volkers N, Wiebe S (2021) The road to a World Health Organization global action plan on epilepsy and other neurological disorders. Epilepsia 62(5):1057–1063
Johnson RL, Wilson CG (2018) A review of vagus nerve stimulation as a therapeutic intervention. J Inflamm Res 11:203–213
Koutroumanidis M, Binnie CD, Hennessy MJ, Alarcon G, Elwes RD, Toone BK et al (2003) VNS in patients with previous unsuccessful resective epilepsy surgery: antiepileptic and psychotropic effects. Acta Neurol Scand 107(2):117–121
Krahl SE, Clark KB (2012) Vagus nerve stimulation for epilepsy: a review of central mechanisms. Surg Neurol Int 3(Suppl 4):S255–S259
Liechty PG, Tubbs RS, Blount JP (2006) The use of a sump antibiotic irrigation system to save infected hardware in a patient with a vagal nerve stimulator: technical note. Surg Neurol 65(1):48–9 (discussion 9-50)
Lulic D, Ahmadian A, Baaj AA, Benbadis SR, Vale FL (2009) Vagus nerve stimulation. Neurosurg Focus 27(3):E5. https://doi.org/10.3171/2009.6.FOCUS09126
Ng WH, Donner E, Go C, Abou-Hamden A, Rutka JT (2010) Revision of vagal nerve stimulation (VNS) electrodes: review and report on use of ultra-sharp monopolar tip. Childs Nerv Syst 26(8):1081–1084
Ohemeng KK, Parham K (2020) Vagal nerve stimulation: indications, implantation, and outcomes. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 53(1):127–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2019.09.008
O’Reardon JP, Cristancho P, Peshek AD (2006) Vagus nerve stimulation (vns) and treatment of depression: to the brainstem and beyond. Psychiatry (Edgmont) 3(5):54–63
Orosz I, McCormick D, Zamponi N, Varadkar S, Feucht M, Parain D et al (2014) Vagus nerve stimulation for drug-resistant epilepsy: a European long-term study up to 24 months in 347 children. Epilepsia 55(10):1576–1584
Patel NC, Edwards MS (2004) Vagal nerve stimulator pocket infections. Pediatr Infect Dis J 23(7):681–683
Perez-Carbonell L, Faulkner H, Higgins S, Koutroumanidis M, Leschziner G (2020) Vagus nerve stimulation for drug-resistant epilepsy. Pract Neurol 20(3):189–198
Revesz D, Rydenhag B, Ben-Menachem E (2016) Complications and safety of vagus nerve stimulation: 25 years of experience at a single center. J Neurosurg Pediatr 18(1):97–104
Sjoberg DDWK, Curry M, Lavery JA, Larmarange J (2021) Reproducible summary tables with the gtsummary package. R J 13:570–580
Spindler P, Vajkoczy P, Schneider UC (2021) Surgical revision after vagus nerve stimulation. A case series. Epilepsy Behav Rep 15:100437
Strzelczyk A, Griebel C, Lux W, Rosenow F, Reese JP (2017) The burden of severely drug-refractory epilepsy: a comparative longitudinal evaluation of mortality, morbidity, resource use, and cost using german health insurance data. Front Neurol 8:712
Spooner A, Chen E, Sowmya A, Sachdev P, Kochan NA, Trollor J et al (2020) A comparison of machine learning methods for survival analysis of high-dimensional clinical data for dementia prediction. Sci Rep 10(1):20410
Spuck S, Tronnier V, Orosz I, Schonweiler R, Sepehrnia A, Nowak G et al (2010) Operative and technical complications of vagus nerve stimulator implantation. Neurosurgery 67(2 Suppl Operative):489–94
Terry M. Therneau PMG (2000) Modeling survival data: extending the cox model. New York
Therneau T (2023) A Package for Survival Analysis in R. R package version 35–5
Trezza A, Landi A, Grioni D, Pirillo D, Fiori L, Giussani C et al (2017) Adverse effects and surgical complications in pediatric patients undergoing vagal nerve stimulation for drug-resistant epilepsy. Acta Neurochir Suppl 124:43–47
Vale FL, Ahmadian A, Youssef AS, Tatum WO, Benbadis SR (2011) Long-term outcome of vagus nerve stimulation therapy after failed epilepsy surgery. Seizure 20(3):244–248
Waseem H, Raffa SJ, Benbadis SR, Vale FL (2014) Lead revision surgery for vagus nerve stimulation in epilepsy: outcomes and efficacy. Epilepsy Behav 31:110–113
Wickham HAM, Bryan J, Chang W, McGowan LD, François R, Grolemund G, Hayes A, Henry L, Hester J, Kuhn M, Pedersen TL, Miller E, Bache SM, Müller K, Ooms J, Robinson D, Seidel DP, Spinu V, Takahashi K, Vaughan D, Wilke C, Woo K, Yutani H (2019) Welcome to the tidyverse. J Open Source Softw 4(43):1686
Wozniak SE, Thompson EM, Selden NR (2011) Vagal nerve stimulator infection: a lead-salvage protocol. J Neurosurg Pediatr 7(6):671–675
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LK: writing original paper, methodology, and writing—review and editing. LVG: investigation and writing—review and editing. KP: investigation and writing—review and editing. MK: data curation and writing—review and editing. FLV: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, writing—review and editing, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This retrospective chart review study involving human participants was in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The Human Investigation Committee (IRB) of Medical College of Georgia, Augusta University (MCG-AU), and the University of South Florida (USF) approved this study.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaoutzani, L., Goldman, L.V., Piper, K. et al. Revision and removal of vagus nerve stimulation systems: twenty-five years’ experience. Acta Neurochir 165, 3913–3920 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-023-05875-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-023-05875-1