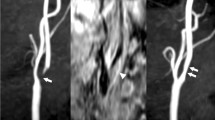
Abstract
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have been widely used to treat chronic myeloid leukemia. Nilotinib and ponatinib, which are second- and third-generation TKIs, have been reported to cause cerebrovascular arterial complications. Here, we present two cases of moyamoya disease presenting with symptomatic ischemic stroke during new-generation TKI treatment. We judged that new-generation TKI treatment was a factor in symptomatic ischemic stroke of unknown moyamoya disease in both cases. Noninvasive examinations using magnetic resonance imaging or carotid ultrasonography should be performed before and during new-generation TKI treatment in order to prevent symptomatic ischemic stroke.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Due to the nature of this research, participants of this study did not agree for their data to be shared publicly, so supporting data is not available.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Alshiekh-Nasany R, Zidan A, Martinez C (2016) Extensive intracranial arterial stenosis in conjunction with the use of tyrosine kinase inhibitor nilotinib. Clin Case Rep 4:1184–1186
Chen CJ, Sorace BJ, Shakeri A, Park MS, Southerland AM, Worrall BB, Kalani MYS (2018) Tyrosine kinase inhibitor induced rapidly progressive vasculopathy after intracranial stent placement. J Neuro Interventional Surg 10:e28
Coon EA, Zalewski NL, Hoffman EM, Tefferi A, Flemming KD (2013) Nilotinib treatment-associated cerebrovascular disease and stroke. Am J Hematol 88:534–535
Fujiwara S, Fukumoto S, Miyazaki Y, Aso K, Ichikawa H, Onoue S, Iwata S, Ohue S (2021) A case of multiple arterial stenoses due to long-term nilotinib exposure. Jpn J Neurosurg 30:804–810
Gomez-Galvan JB, Borrego S, Tovar N, Llull L (2017) Nilotinib as a risk factor for ischemic stroke: a series of three cases. Neurol Engl Ed 32:411–413
Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration (2017) Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1995–2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol 3(4):524–548
Haguet H, Douxfil J, Mullier F, Chatelain C, Graux C, Dogne J (2017) Risk of arterial and venous occlusive events in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with new generation BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Opin Drug Saf 16(1):5–12
Hirayama A, Sorimachi T, Yokota K, Shigematsu H, Srivatanakul K, Matsumae M (2022) New-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor-associated asymptomatic cerebrovascular stenosis: two illustrative cases. Acta Neurochir 164:1623–1626
Jager NGL, Stuurman FE, Baars JW, Opdam FL (2014) Cerebrovascular events during nilotinib treatment. Neth J Med 72:2
Kuroda S, Fujimura M, Takahashi J, Kataoka H, Ogasawara K, Iwama T, Tominaga T, Miyamoto S (2022) Diagnostic criteria for moyamoya disease - 2021 revised version. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 62:307–312
Kuroda S, Houkin K (2008) Moyamoya disease: current concepts and future perspectives. Lancet Neurol 7:1056–1066
Manouchehri A, Kanu E, Mauro MJ, Aday AW, Linder JR, Moslehi J (2020) Tyrosine kinase inhibitors in leukemia and cardiovascular events: form mechanism to patient care. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 40:301–308
Moslehi JJ, Deininger (2015) Tyrosine kinase inhibitors-associated cardiovascular toxicity in chronic myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 33:4210–4218
Nakaya A, Ebitani M, Monzen T, Nagano T, Saito F, Yaoita Y (2019) A case of recurrent cerebral infarction during treatment of oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor for chronic myelogenous leukemia. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 59:418–424
O’Hare T, Deininger MWN, Eide CA, Clackson T, Druker BJ (2011) Targeting the BCR-ABL signaling pathway in therapy-resistant philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 17:212–221
Ozaki T, Nakamura H, Izutsu N, Masaie H, Ishikawa J, Kinoshita M (2017) Intracranial stenting for nilotinib treatment-associated cerebrovascular stenosis in chronic myeloid leukemia. Interv Neuroradiol 23:527–530
Rai Y, Hara T (2023) Tyrosine kinase inhibitor-associated cerebral arterial occlusive disease treated with high-flow bypass surgery: a case report. NMC Case Rep J 10:61–66
Shinya Y, Miyawaki S, Imai H, Hongo H, Ono H, Takenobu A, Nakatomi H, Teraoka A, Saito N (2017) Genetic analysis of ring finger protein 213 (RNF213) c.14576G > A in intracranial atherosclerosis of the anterior and posterior circulations. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 26:2638–2644
Suzuki K, Yamamoto J, Kakeda S, Takamatsu S, Miyaoka R, Kitagawa T, Saito T, Nakano Y, Nishizawa S (2019) Vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging findings and surgical treatment in nilotinib-associated cerebrovascular disease: a case report. Mol Clin Oncol 10:239–243
Uemura M, Kanazawa M, Yamagishi T, Nagai T, Takahashi M, Koide S, Tada M, Simbo J, Isami A, Makino K, Masuko M, Nikkuni K, Okamoto K, Igarashi S, Morita K, Onodera O (2020) Role of RNF213 p.4810K variant in the development of intracranial arterial disease in patients treated with nilotinib. J Neurol Sci 408:116577
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to the study concept or the data analysis or interpretation, drafted the manuscript or revised it critically for important intellectual content, approved the final version of the manuscript to be published, and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The manuscript is written in accordance with the 1964 WMA Declaration of Helsinki. All the procedures being performed and treatment received were part of routine care.
Consent for publication
Informed consent was obtained from the patients about the publication of the case details and any associated images.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nakajima, H., Miyake, R., Hongo, T. et al. Moyamoya disease presenting with symptomatic ischemic stroke during new-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment: two illustrative cases. Acta Neurochir 165, 3637–3641 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-023-05858-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-023-05858-2