Abstract
Background
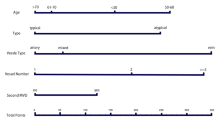
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery (GKRS) is an effective treatment option for medically refractory trigeminal neuralgia (TN). This study examines GKRS outcome in a large cohort of TN patients and highlights pretreatment factors associated with pain relief.
Methods
This is a single-center retrospective analysis of patients treated with GKRS for TN between 2011 and 2019. Pain relief was assessed at 1 year, and 2–3 years following GKRS. Multivariable analysis identified several factors that predicted pain relief. These predicting factors were applied to establish a pain relief scoring system.
Results
A total of 162 patients met inclusion criteria. At 1 year post-GKRS, the breakdown of Barrow Neurological Institute (BNI) score for pain relief was as follows: 77 (48%) score of I, 13 (8%) score of II, 37 (23%) score of III, 22 (14%) score of IV, and 13 (8%) score of V. Factors that were significantly associated with pain-free outcome at 1 year were: Typical form of TN (OR = 2.2 [1.1, 4.9], p = 0.049), No previous microvascular decompression (OR = 4.4 [1.6, 12.5], p = 0.005), Response to medical therapy (OR = 2.7 [1.1, 6.1], p = 0.018), and Seniority > 60 years (OR = 2.8 [1.4, 5.5], p = 0.003). The term “Trigeminal Neuralgia-RadioSurgery” was used to create the TN-RS acronym representing the significant factors. A stepwise increase in the median predicted probability of pain-free outcome at 1 year from 3% for patients with a score of 0 to 69% for patients with a maximum score of 4.
Conclusion
The TN-RS scoring system can assist clinicians in identifying patients that may benefit from GNRS for TN by predicting 1-year pain-free outcomes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data for this study can be shared upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Code and statistical analysis in this study can be shared upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- GKRS:
-
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery
- TN:
-
Trigeminal neuralgia
- BNI:
-
Barrow Neurological Institute
- SRS:
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery
- MVD:
-
Microvascular decompression
References
Barzaghi LR, Albano L, Scudieri C, Gigliotti CR, del Vecchio A, Mortini P (2021) Factors affecting long-lasting pain relief after Gamma Knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: a single institutional analysis and literature review. Neurosurg Rev 44(5):2797–2808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01474-9
Bijlenga P, Gondar R, Schilling S et al (2017) PHASES score for the management of intracranial aneurysm: a cross-sectional population-based retrospective study. Stroke 48(8):2105–2112. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.017391
Chen JCT, Greathouse HE, Girvigian MR, Miller MJ, Liu A, Rahimian J. Prognostic factors for radiosurgery treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000297100.34508.0B
Dhople AA, Adams JR, Maggio WW, Naqvi SA, Regine WF, Kwok Y (2009) Long-term outcomes of Gamma Knife radiosurgery for classic trigeminal neuralgia: implications of treatment and critical review of the literature: Clinical article. J Neurosurg 111(2):351–358. https://doi.org/10.3171/2009.2.JNS08977
Eller JL, Raslan AM, Burchiel KJ (2005) Trigeminal neuralgia: definition and classification. Neurosurg Focus 18(5). https://doi.org/10.3171/FOC.2005.18.5.4
Fatima N, Meola A, Ding VY, et al (2021) The Stanford stereotactic radiosurgery experience on 7000 patients over 2 decades (1999–2018): looking far beyond the scalpel. J Neurosurg 1–17. https://doi.org/10.3171/2020.9.JNS201484
Foreman PM, Enriquez-Marulanda A, Mooney JH, et al (2018) Whole blood aggregometry prior to pipeline embolization device treatment of intracranial aneurysms: defining an optimal platelet inhibition cutoff value for clopidogrel. J Neurosurg 1–8. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.6.JNS181044
Gorgulho A (2012) Radiation mechanisms of pain control in classical trigeminal neuralgia. Surg Neurol Int 3(Suppl 1):S17. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.91606
Goyal S, Kedia S, Kumar R et al (2021) Role of Gamma Knife radiosurgery in trigeminal neuralgia—its long term outcome and prediction using Artificial neural Network model. J Clin Neurosci 92:61–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2021.07.017
Helis CA, Hughes RT, Munley MT et al (2020) Results of a third Gamma Knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 134(3):1237–1243. https://doi.org/10.3171/2020.2.JNS192876
Kondziolka D, Zorro O, Lobato-Polo JE et al (2010) Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: Clinical article. J Neurosurg 112(4):758–765. https://doi.org/10.3171/2009.7.JNS09694
Li L, Seaman SC, Bathla G et al (2020) Microvascular decompression versus stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: a single-institution experience. World Neurosurg 143:e400–e408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2020.07.161
Little AS, Shetter AG, Shetter ME, Kakarla UK, Rogers CL (2009) Salvage gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery for surgically refractory trigeminal neuralgia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74(2):522–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJROBP.2008.08.048
Liu M, Wood JN (2011) The roles of sodium channels in nociception: implications for mechanisms of neuropathic pain. Pain Med 12(SUPPL. 3):S93–S99. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1526-4637.2011.01158.X/2/PME_1158_F1.JPEG
Loeser JD, Calvin WH, Howe JF (2009) The pathophysiology of trigeminal neuralgia. Clin Neurosurg 24:2359–2419. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-69960-6_140
Longhi M, Rizzo P, Nicolato A, Foroni R, Reggio M, Gerosa M (2007) Gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia results and potentially predictive parameters—part I: idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 61(6):1254–1261. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000306104.68635.D4
Maesawa S, Salame C, Flickinger JC, Pirris S, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD (2001) Clinical outcomes after stereotactic radiosurgery for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 94(1):14–20. https://doi.org/10.3171/JNS.2001.94.1.0014
Marshall K, Chan MD, McCoy TP, et al (2012) Predictive variables for the successful treatment of trigeminal neuralgia with gamma knife radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 70(3). https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0B013E3182320D36
Park H, Jeong SS, Chung HT, Lee EJ (n.d.) Treatment planning factors associated with long-term outcomes of gamma knife surgery in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2021.05.008
Park H, Jeong SS, Chung HT, Lee EJ (2021) Treatment planning factors associated with long-term outcomes of Gamma Knife surgery in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. World Neurosurg 151:e899–e910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2021.05.008
Régis J, Constantin T, Resseguier N et al (2016) Long-term safety and efficacy of Gamma Knife surgery in classical trigeminal neuralgia: a 497-patient historical cohort study. J Neurosurg 124:1079–1087. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.2.JNS142144
Rogers CL, Shetter AG, Fiedler JA, Smith KA, Han PP, Speiser BL (2000) Gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: the initial experience of the Barrow Neurological Institute. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47(4):1013–1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-3016(00)00513-7
Schisterman EF, Perkins NJ, Liu A, Bondell H (2005) Optimal cut-point and its corresponding Youden Index to discriminate individuals using pooled blood samples. Epidemiology 16(1):73–81. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ede.0000147512.81966.ba
Taich ZJ, Goetsch SJ, Monaco E, et al (2016) Stereotactic radiosurgery treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: clinical outcomes and prognostic factors. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.02.067
Tuleasca C, Paddick I, Hopewell JW et al (2020) Establishment of a therapeutic ratio for gamma knife radiosurgery of trigeminal neuralgia: the critical importance of biologically effective dose versus physical dose. World Neurosurg 134:e204–e213. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WNEU.2019.10.021
Tuleasca C, Régis J, Sahgal A et al (2019) Stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: a systematic review. J Neurosurg 130(3):733–757. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.9.JNS17545
Verheul JB, Hanssens PEJ, Lie S te, Leenstra S, Piersma H, Beute GN (2010) Gamma Knife surgery for trigeminal neuralgia: a review of 450 consecutive cases: clinical article. J Neurosurg 113(Special_Supplement):160–167. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.7.GKS10978
Vittinghoff E, McCulloch CE (2007) Relaxing the rule of ten events per variable in logistic and Cox regression. Am J Epidemiol 165(6):710–718. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwk052
Wilson TA, Karlsson B, Huang L, Ramanathan D, Oyoyo U, Boling W (2020) Optimizing radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: impact of radiation dose and anatomic target on patient outcomes. World Neurosurg 143:e482–e491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2020.07.206
Xu R, Xie ME, Jackson CM (2021) Trigeminal neuralgia: current approaches and emerging interventions. J Pain Res 14:3437–3463. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S331036
Young RF, Vermeulen S, Posewitz A (1998) Gamma knife radiosurgery for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 70 Suppl 1(SUPPL. 1):192–199. https://doi.org/10.1159/000056422
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by AO, JF, GK, CP, CG, CC, and LS. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AO, JF, GK, and CC. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This retrospective chart review study involving human participants was in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The Human Investigation Committee (IRB) of Swedish Neuroscience Institute approved this study.
Consent to participate
No identifying patient information was presented in this study.
Consent for publication
Authors are responsible for correctness of the statements provided in the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Orlev, A., Feghali, J., Kimchi, G. et al. TN-RS: a novel scoring system predicts Gamma Knife Radiosurgery outcome for trigeminal neuralgia patients. Acta Neurochir 165, 3895–3903 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-023-05835-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-023-05835-9