Abstract
Background
The management of craniopharyngiomas is challenging, usually requiring multidisciplinary care. We evaluated the long-term clinical and radiologic outcomes of Gamma Knife radiosurgery (GKRS) for craniopharyngiomas.
Methods
This retrospective study involved patients managed with GKRS for a craniopharyngioma during the period of 1989 to 2019. Patient clinical and radiologic data, tumor characteristics, and procedural details were analyzed.
Results
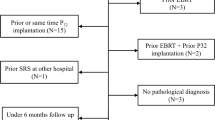
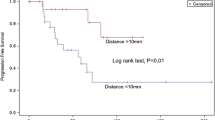
Thirty-eight consecutive patients (24 males; mean patient age at GKRS = 30.82 years [SD ± 20.45 years]) were treated with GKRS for craniopharyngioma. Overall survival rates at 5 and 10 years were 84.1% and 80.1%, respectively. Progression-free survival at 5 years was 48.1%, and, at 10 years, it was 29.8%. Risk factors for post-GKRS clinical deterioration were increasing number of isocenters used (p = 0.04 (HR1.32, CI 1–1.73)), increasing margin dose [p = 0.02 (HR1.52, CI 1.31–1.84)], and maximum dose > 35 Gy [p = 0.002 (HR1.35, CI 1.11–1.63)].
Conclusion
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) appears a safe and effective management option in selected craniopharyngioma patients. Increasing margin dose and maximum dose > 35 Gy are associated with an increased risk for post-SRS neurologic deficit. Further, well-designed studies are necessary to determine the optimal timing and SRS parameters and to identify which patients with craniopharyngioma will benefit the most from SRS.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiou SM, Lunsford LD, Niranjan A, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC (2001) Stereotactic radiosurgery of residual or recurrent craniopharyngioma, after surgery, with or without radiation therapy. Neuro Oncol 3(3):159–166
Chung W-Y, Pan DH-C, Shiau C-Y, Guo W-Y, Wang L-W (2000) Gamma knife radiosurgery for craniopharyngiomas. J Neurosurg 93(supplement_3):47–56
Dho Y-S, Kim YH, Kim JW, Park C-K, Chung H-T, Kim S-K, Paek SH, Wang K-C, Kim DG (2018) Optimal strategy of gamma knife radiosurgery for craniopharyngiomas. J Neurooncol 140(1):135–143
Effenterre RV, Boch A-L (2002) Craniopharyngioma in adults and children: a study of 122 surgical cases. J Neurosurg 97(1):3–11
Fahlbusch R, Honegger J, Paulus W, Huk W, Buchfelder M (1999) Surgical treatment of craniopharyngiomas: experience with 168 patients. J Neurosurg 90(2):237–250
Gopalan R, Dassoulas K, Rainey J, Sherman JH, Sheehan JP (2008) Evaluation of the role of Gamma Knife surgery in the treatment of craniopharyngiomas. Neurosurg Focus 24(5):E5
Hasegawa T, Kobayashi T, Kida Y (2010) Tolerance of the optic apparatus in single-fraction irradiation using stereotactic radiosurgery: evaluation in 100 patients with craniopharyngioma. Neurosurgery 66(4):688–694; discussion 694-695
Hoffman HJ, Silva MD, Humphreys RP, Drake JM, Smith ML, Blaser SI (1992) Aggressive surgical management of craniopharyngiomas in children. J Neurosurg 76(1):47–52
Jane JA, Laws ER (2006) Craniopharyngioma Pituitary 9(4):323–326
Kalapurakal JA, Goldman S, Hsieh YC, Tomita T, Marymont MH (2003) Clinical outcome in children with craniopharyngioma treated with primary surgery and radiotherapy deferred until relapse. Med Pediatr Oncol 40(4):214–218
Karavitaki N, Brufani C, Warner JT, Adams CBT, Richards P, Ansorge O, Shine B, Turner HE, Wass JaH (2005) Craniopharyngiomas in children and adults: systematic analysis of 121 cases with long-term follow-up. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 62(4):397–409
Kim SK, Wang KC, Shin SH, Choe G, Chi JG, Cho BK (2001) Radical excision of pediatric craniopharyngioma: recurrence pattern and prognostic factors. Childs Nerv Syst 17(9):531–536; discussion 537
Kobayashi T, Kida Y, Mori Y, Hasegawa T (2005) Long-term results of gamma knife surgery for the treatment of craniopharyngioma in 98 consecutive cases. J Neurosurg 103(6 Suppl):482–488
Kobayashi T, Tsugawa T, Hatano M, Hashizume C, Mori Y, Shibamoto Y (2015) Gamma knife radiosurgery of craniopharyngioma: results of 30 cases treated at Nagoya Radiosurgery Center. Nagoya J Med Sci 77(3):447–454
Lee C-C, Yang H-C, Chen C-J, Hung Y-C, Wu H-M, Shiau C-Y, Guo W-Y, Pan DH-C, Chung W-Y, Liu K-D (2014) Gamma Knife surgery for craniopharyngioma: report on a 20-year experience. J Neurosurg 121(Suppl):167–178
Lin LL, Naqa IE, Leonard JR, Park TS, Hollander AS, Michalski JM, Mansur DB (2008) Long-term outcome in children treated for craniopharyngioma with and without radiotherapy. J Neurosurg Pediatr 1(2):126–130
Losa M, Pieri V, Bailo M, Gagliardi F, Barzaghi LR, Gioia L, Del Vecchio A, Bolognesi A, Mortini P (2018) Single fraction and multisession Gamma Knife radiosurgery for craniopharyngioma. Pituitary 21(5):499–506
Maira G, Anile C, Rossi GF, Colosimo C (1995) Surgical treatment of craniopharyngiomas: an evaluation of the transsphenoidal and pterional approaches. Neurosurgery 36(4):715–724
Müller HL (2014) Craniopharyngioma. Endocr Rev 35(3):513–543
Müller HL, Merchant TE, Warmuth-Metz M, Martinez-Barbera J-P, Puget S (2019) Craniopharyngioma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 5(1):1–19
Niranjan A, Kano H, Mathieu D, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2010) Radiosurgery for craniopharyngioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78(1):64–71
Ogino A, Lunsford LD, Long H, Johnson S, Faramand A, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Kano H (2021) Stereotactic radiosurgery as the primary management for patients with Koos grade IV vestibular schwannomas. J Neurosurg 1(aop):1–9
Ogino A, Niranjan A, Kano H, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2021) Optimizing stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with recurrent or residual craniopharyngiomas. J Neurooncol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03806-7
Saleem MA, Hashim ASM, Rashid A, Ali M (2013) Role of gamma knife radiosurgery in multimodality management of craniopharyngioma. Acta Neurochir Suppl 116:55–60
Schoenfeld A, Pekmezci M, Barnes MJ et al (2012) The superiority of conservative resection and adjuvant radiation for craniopharyngiomas. J Neurooncol 108(1):133–139
Stripp DCH, Maity A, Janss AJ et al (2004) Surgery with or without radiation therapy in the management of craniopharyngiomas in children and young adults. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58(3):714–720
Tsugawa T, Kobayashi T, Hasegawa T et al (2020) Gamma Knife surgery for residual or recurrent craniopharyngioma after surgical resection: a multi-institutional retrospective study in Japan. Cureus 12(2):e6973
Ulfarsson E, Lindquist C, Roberts M, Rähn T, Lindquist M, Thorén M, Lippitz B (2002) Gamma knife radiosurgery for craniopharyngiomas: long-term results in the first Swedish patients. J Neurosurg 97(5 Suppl):613–622
Varlotto J, DiMaio C, Grassberger C et al (2016) Multi-modality management of craniopharyngioma: a review of various treatments and their outcomes. Neurooncol Pract 3(3):173–187
Xu Z, Yen C-P, Schlesinger D, Sheehan J (2011) Outcomes of Gamma Knife surgery for craniopharyngiomas. J Neurooncol 104(1):305–313
Yang I, Sughrue ME, Rutkowski MJ, Kaur R, Ivan ME, Aranda D, Barani IJ, Parsa AT (2010) Craniopharyngioma: a comparison of tumor control with various treatment strategies. Neurosurg Focus 28(4):E5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Brain Tumors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pikis, S., Mantziaris, G., Lavezzo, K. et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for craniopharyngiomas. Acta Neurochir 163, 3201–3207 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-021-04990-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-021-04990-1