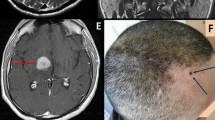
Abstract
We report a case of multiple brain abscesses’ puncture, employing the ROSA™ Brain surgical robot (Zimmer Biomet) and the O-arm® O2 Imaging System (Medtronic). A 51-year-old man was diagnosed with multiple supratentorial ring enhancing cystic lesions consistent with brain abscesses. A neurological deterioration occurred despite broad spectrum antibiotic therapy, due to mass effect of the abscesses. Stereotactic aspiration was performed using the described technique, allowing a single stage puncture of the cerebral lesions. In this case, the robot-assisted and image-guided procedure permitted an accurate, quick, and efficient targeting of the multiple abscesses for drainage.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT:
-
Computed tomographic
- DBS:
-
Deep brain stimulation
- DWI:
-
Diffusion-weighted imaging
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
References
Asquier-Khati A, Deschanvres C, Boutoille D et al (2020) Switch from parenteral to oral antibiotics for brain abscesses: a retrospective cohort study of 109 patients. J Antimicrob Chemother 75(10):3062–3066
Bjartmarz H, Rehncrona S (2007) Comparison of accuracy and precision between frame-based and frameless stereotactic navigation for deep brain stimulation electrode implantation. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 85(5):235–242
Brouwer MC, Coutinho JM, van de Beek D (2014) Clinical characteristics and outcome of brain abscess: systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 82(9):806–813
Brouwer MC, Tunkel AR, McKhann GM, van de Beek D (2014) Brain abscess. N Engl J Med 371(5):447–456
Cantiera M, Tattevin P, Sonneville R (2019) Brain abscess in immunocompetent adult patients. Rev Neurol (Paris) 175(7–8):469–474
Faria C, Erlhagen W, Rito M, De Momi E, Ferrigno G, Bicho E (2015) Review of robotic technology for stereotactic neurosurgery. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng 8:125–137
Fomenko A, Serletis D (2018) Robotic stereotaxy in cranial neurosurgery: a qualitative systematic review. Neurosurgery 83(4):642–650
González-Martínez J, Bulacio J, Thompson S, Gale J, Smithason S, Najm I, Bingaman W (2016) Technique, results, and complications related to robot-assisted stereoelectroencephalography. Neurosurgery 78(2):169–180
Kim LH, Feng AY, Ho AL, Parker JJ, Kumar KK, Chen KS, Grant GA, Henderson JM, Halpern CH (2020) Robot-assisted versus manual navigated stereoelectroencephalography in adult medically-refractory epilepsy patients. Epilepsy Res 159:106253
Kwoh YS, Hou J, Jonckheere EA, Hayati S (1988) A robot with improved absolute positioning accuracy for CT guided stereotactic brain surgery. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 35(2):153–160
Mamelak A, Mampalam T, Obana W, Rosenblum M (1995) Improved management of multiple brain abscesses: a combined surgical and medical approach: 76. Neurosurgery 36(1):76–86
Nathoo N, Nadvi SS, Narotam PK, van Dellen JR (2011) Brain abscess: management and outcome analysis of a computed tomography era experience with 973 patients. World Neurosurgery 75(5):716–726
Neudorfer C, Hunsche S, Hellmich M, El Majdoub F, Maarouf M (2018) Comparative study of robot-assisted versus conventional frame-based deep brain stimulation stereotactic neurosurgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 96(5):327–334
Philipp LR, Matias CM, Thalheimer S, Mehta SH, Sharan A, Wu C (2020) Robot-assisted stereotaxy reduces target error: a meta-analysis and meta-regression of 6056 trajectories. Neurosurgery. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyaa428
Sonneville R, Ruimy R, Benzonana N, Riffaud L, Carsin A, Tadié J-M, Piau C, Revest M, Tattevin P, ESCMID Study Group for Infectious Diseases of the Brain (ESGIB) (2017) An update on bacterial brain abscess in immunocompetent patients. Clin Microbiol Infect 23(9):614–620
Tattevin P, Bruneel F, Clair B, Lellouche F, de Broucker T, Chevret S, Bédos J-P, Wolff M, Régnier B (2003) Bacterial brain abscesses: a retrospective study of 94 patients admitted to an intensive care unit (1980 to 1999). Am J Med 115(2):143–146
Widmann G, Schullian P, Ortler M, Bale R (2012) Frameless stereotactic targeting devices: technical features, targeting errors and clinical results. Int J Med Robot 8(1):1–16
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Gaston Tabourel and Vincent Roualdes performed the neurosurgical procedures. Paul Le Turnier was consulted as infectious diseases specialist and did the clinical follow-up. Kevin Buffenoir and Vincent Roualdes initiated the project of a technical case report. Gaston Tabourel wrote the manuscript with input from all authors. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Statement of ethics
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. We did not seek Institutional Review Board approval for performing this surgical procedure, because the operation did not constitute research; the senior neurosurgeon deemed it to be necessary in the patient’s best interest.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Infection
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabourel, G., Le Turnier, P., Buffenoir, K. et al. Robot-assisted stereotactic multiple brain abscesses’ puncture: technical case report. Acta Neurochir 164, 845–851 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-021-04955-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-021-04955-4