Abstract
Background
Decompressive craniectomy (DC) is a common neurosurgical intervention for severe traumatic brain injury (TBI), as well as malignant stroke, malignancy and infection. DC necessitates subsequent cranioplasty. There are significant demographic differences between TBI and non-TBI patients undergoing cranioplasty, which may influence their relative risk profiles for infection, aseptic bone flap resorption (aBFR) and re-operation.
Objective
Perform a meta-analysis to determine the relative infection, aBFR and re-operation risk profiles of TBI patients as compared to other indications for DC.
Methods
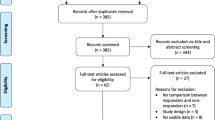
A systematic review and meta-analysis was performed in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines. PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE and Google Scholar were searched until 26/11/2020. Studies detailing rates of infection, re-operation and/or aBFR in specific materials and the post-TBI population were included, while studies in paediatrics or craniosynostosis repair were excluded.
Results
Twenty-six studies were included. There was no difference in relative risk of infection between TBI and non-TBI cohorts (RR 0.81, 95% CI 0.57–1.17), with insignificant heterogeneity (I2 = 33%). TBI was a risk factor for aBFR (RR 1.54, 95% CI 1.25–1.89), with no significant heterogeneity (I2 = 13%). TBI was a risk factor for re-operation in the autologous sub-group (RR 1.49, 95% CI 1.05–2.11) but not in the alloplastic sub-group (RR = 0.86, 95% CI 0.34–2.18). Heterogeneity was insignificant (I2 = 11%).
Conclusion
TBI is a risk factor for aBFR and re-operation following cranioplasty. Use of an alloplastic graft for primary cranioplasty in these patients may partially mitigate this increased risk.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agner C, Dujovny M, Gaviria M (2002) Neurocognitive assessment before and after cranioplasty. Acta Neurochir 144(10):1033–1040
Al-Tamimi YZ, Sinha P, Trivedi M, Robson C, Al-Musawi TA, Hossain N, Mumford C, Towns G. Comparison of acrylic and titanium cranioplasty. Br J Neurosurg. 2012 Aug;26(4):510-3. https://doi.org/10.3109/02688697.2011.633640
Alkhaibary A, Alharbi A, Abbas M, Algarni A, Abdullah JM, Almadani WH, Khairy I, Alkhani A, Aloraidi A, Khairy S (2020) Predictors of surgical site infection in autologous cranioplasty: a retrospective analysis of subcutaneously preserved bone flaps in abdominal pockets. World Neurosurg 133:e627–e632
Alonso-Coello P, Schünemann HJ, Moberg J et al (2016) GRADE Evidence to Decision (EtD) frameworks: a systematic and transparent approach to making well informed healthcare choices. 1: Introduction. BMJ. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i2016
Ashayeri K, Jackson EM, Huang J, Brem H, Gordon CR (2016) Syndrome of the trephined: a systematic review. Neurosurgery 79(4):525–533
Banham-Hall N, Kothwal K, Pipkin J, Bentley J, Dickens GL (2013) Prevalence of low bone mineral density in inpatients with traumatic brain injury receiving neurobehavioural rehabilitation: a postoperative, observational study. Physiotheraphy 99(4):328–334
Bobinski L, Koskinen LOD, Lindvall P (2013) Complications following cranioplasty using autologous bone or polymethylmethacrylate - retrospective experience from a single center. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115(9):1788–1791
Bramlett HM, Dietrich WD (2015) Long-term consequences of traumatic brain injury: current status of potential mechanisms of injury and neurological outcomes. J Neurotrauma 32(23):1834–1848
Von Der Brelie C, Stojanovski I, Meier U, Lemcke J (2015) Open traumatic brain injury is a strong predictor for aseptic bone necrosis after cranioplasty surgery: a retrospective analysis of 219 patients. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg 77(1):19–24
Brommeland T, Rydning PN, Pripp AH, Helseth E (2015) Cranioplasty complications and risk factors associated with bone flap resorption. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med 23(1):75
Catania A, Lonati C, Sordi A, Gatti S (2009) Detrimental consequences of brain injury on peripheral cells. Brain Behav Immun 23(7):877–884
Cheng CH, Lee HC, Chen CC, Cho DY, Lin HL (2014) Cryopreservation versus subcutaneous preservation of autologous bone flaps for cranioplasty: comparison of the surgical site infection and bone resorption rates. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 124:85–89
Cheng YK, Weng HH, Yang JT, Lee MH, Wang TC, Chang CN (2008) Factors affecting graft infection after cranioplasty. J Clin Neurosci 15(10):1115–1119
Corallo F, Marra A, Bramanti P, Calabrò RS (2014) Effect of cranioplasty on functional and neuropsychological recovery after severe acquired brain injury: fact or fake? Considerations on a single case. Funct Neurol 29(4):273–275
Corliss B, Gooldy T, Vaziri S, Kubilis P, Murad G, Fargen K (2016) Complications after in vivo and ex vivo autologous bone flap storage for cranioplasty: a comparative analysis of the literature. World Neurosurg 96:510–515
DiStefano C, Sturiale C, Trentini P, Bonora R, Rossi D, Cervigni G, Piperno R (2012) Unexpected neuropsychological improvement after cranioplasty: a case series study. Br J Neurosurg 26(6):827–831
Dobran M, Nasi D, Polonara G, Paracino R, Mancini F, Della CM, Jonis G, Campa S, Lattanzi S, Iacoangeli M (2020) Clinical and radiological risk factors of autograft cranioplasty resorption after decompressive craniectomy for traumatic brain injury. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 196:105979
Dujovny M, Fernandez P, Alperin N, Betz W, Misra M, Mafee M (1997) Post-cranioplasty cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamic changes: Magnetic resonance imaging quantitative analysis. Neurol Res 19(3):311–316
Dünisch P, Walter J, Sakr Y, Kalff R, Waschke A, Ewald C (2013) Risk factors of aseptic bone resorption: a study after autologous bone flap reinsertion due to decompressive craniotomy - Clinical article. J Neurosurg 118(5):1141–1147
Fan MC, Wang QL, Sun P, Zhan SH, Guo P, Deng WS, Dong Q (2018) Cryopreservation of autologous cranial bone flaps for cranioplasty: a large sample retrospective study. World Neurosurg 109:e853–e859
Göttsche J, Mende KC, Schram A, Westphal M, Amling M, Regelsberger J, Sauvigny T, Hahn M. Cranial bone flap resorption-pathological features and their implications for clinical treatment. Neurosurg Rev. 2020 Oct 12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-020-01417-w
Halani SH, Chu JK, Malcolm JG, Rindler RS, Allen JW, Grossberg JA, Pradilla G, Ahmad FU (2017) Effects of cranioplasty on cerebral blood flow following decompressive craniectomy: a systematic review of the literature. Neurosurgery 81(2):204–216
Hamböck M, Hosmann A, Seemann R, Wolf H, Schachinger F, Hajdu S, Widhalm H (2020) The impact of implant material and patient age on the long-term outcome of secondary cranioplasty following decompressive craniectomy for severe traumatic brain injury. Acta Neurochir 162(4):745–753
Hersh DS, Anderson HJ, Woodworth GF, Martin JE, Khan YM (2021) Bone flap resorption in pediatric patients following autologous cranioplasty. Oper Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.1093/ons/opaa452
Hofmeijer J, Kappelle LJ, Algra A, Amelink GJ, van Gijn J, van der Worp HB (2009) Surgical decompression for space-occupying cerebral infarction (the Hemicraniectomy after middle cerebral artery infarction with life-threatening edema trial [HAMLET]): a multicentre, open, randomised trial. Lancet Neurol 8(4):326–333
Honeybul S, Ho KM (2016) Cranioplasty: morbidity and failure. Br J Neurosurg 30(5):523–528
Honeybul S, Janzen C, Kruger K, Ho KM (2013) The impact of cranioplasty on neurological function. Br J Neurosurg 27(5):636–641
Honeybul S, Morrison DA, Ho KM, Lind CRP, Geelhoed E (2017) A randomized controlled trial comparing autologous cranioplasty with custom-made titanium cranioplasty. J Neurosurg 126(1):81–90
Honeybul S, Morrison DA, Ho KM, Lind CRP, Geelhoed E (2018) A randomised controlled trial comparing autologous cranioplasty with custom-made titanium cranioplasty: long-term follow-up. Acta Neurochir 160(5):885–891
Hutchinson PJ, Kolias AG, Timofeev IS et al (2016) Trial of decompressive craniectomy for traumatic intracranial hypertension. N Engl J Med 375(12):1119–1130
Iaccarino C, Kolias A, Adelson PD, Rubiano AM, Viaroli E, Buki A, Cinalli G, Fountas K, Khan T, Signoretti S, Waran V, Adeleye AO, Amorim R, Bertuccio A, Cama A, Chesnut RM, De Bonis P, Estraneo A, Figaji A, Florian SI, Formisano R, Frassanito P, Gatos C, Germanò A, Giussani C, Hossain I, Kasprzak P, La Porta F, Lindner D, Maas AIR, Paiva W, Palma P, Park KB, Peretta P, Pompucci A, Posti J, Sengupta SK, Sinha A, Sinha V, Stefini R, Talamonti G, Tasiou A, Zona G, Zucchelli M, Hutchinson PJ, Servadei F. Consensus statement from the international consensus meeting on post-traumatic cranioplasty. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2021 Feb;163(2):423-440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-020-04663-5
Jüttler E, Bösel J, Amiri H, Schiller P, Limprecht R, Hacke W, Unterberg A (2011) DESTINY II: DEcompressive Surgery for the Treatment of malignant INfarction of the middle cerebral arterY II. Int J Stroke 6(1):79–86
Jüttler E, Schwab S, Schmiedek P, Unterberg A, Hennerici M, Woitzik J, Witte S, Jenetzky E, Hacke W (2007) Decompressive surgery for the treatment of malignant infarction of the middle cerebral artery (DESTINY): a randomized, controlled trial. Stroke 38(9):2518–2525
Kim BW, Kim TU, Hyun JK (2017) Effects of early cranioplasty on the restoration of cognitive and functional impairments. Ann Rehabil Med 41(3):354–361
Kim JH, Kim JH, Kwon TH, Chong K, Hwang SY, Yoon WK (2018) Aseptic bone flap resorption after cranioplasty with autologous bone: incidence, risk factors, and clinical implications. World Neurosurg 115:e111–e118
Klinger DR, Madden C, Beshay J, White J, Gambrell K, Rickert K (2014) Autologous and acrylic cranioplasty: a review of 10 years and 258 cases. World Neurosurg 82(3):E525–E530
Korhonen TK, Salokorpi N, Niinimäki J, Serlo W, Lehenkari P, Tetri S (2019) Quantitative and qualitative analysis of bone flap resorption in patients undergoing cranioplasty after decompressive craniectomy. J Neurosurg 130(1):312–321
Korhonen TK, Tetri S, Huttunen J, Lindgren A, Piitulainen JM, Serlo W, Vallittu PK, Posti JP (2019) Predictors of primary autograft cranioplasty survival and resorption after craniectomy. J Neurosurg 130(5):1672–1679
Kriegel RJ, Schaller C, Clusmann H (2007) Cranioplasty for large skull defects with PMMA (Polymethylmethacrylate) or tutoplast® processed autogenic bone grafts. Zentralbl Neurochir 68(4):182–189
Kwiecien GJ, Rueda S, Couto RA, Hashem A, Nagel S, Schwarz GS, Zins JE, Gastman BR (2018) Long-term outcomes of cranioplasty: titanium mesh is not a long-term solution in high-risk patients. Ann Plast Surg 81(4):423–426
Lee SH, Yoo CJ, Lee U, Park CW, Lee SG, Kim WK (2014) Resorption of autogenous bone graft in cranioplasty: resorption and reintegration failure. Korean J Neurotrauma 10(1):10
Liang ES, Tipper G, Hunt L, Gan PYC (2016) Cranioplasty outcomes and associated complications: a single-centre observational study. Br J Neurosurg 30(1):122–127
Liu L, Lu ST, Liu AH et al (2020) Comparison of complications in cranioplasty with various materials: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.1080/02688697.2020.1742291
Maas AIR, Menon DK, Adelson PD et al (2017) Traumatic brain injury: integrated approaches to improve prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol 16(12):987–1048
Malcolm JG, Mahmooth Z, Rindler RS, Allen JW, Grossberg JA, Pradilla G, Ahmad FU (2018) Autologous cranioplasty is associated with increased reoperation rate: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World Neurosurg 116:60–68
Malcolm JG, Rindler RS, Chu JK, Chokshi F, Grossberg JA, Pradilla G, Ahmad FU (2018) Early cranioplasty is associated with greater neurological improvement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Neurosurg 82(3):278–288
Malcolm JG, Rindler RS, Chu JK, Grossberg JA, Pradilla G, Ahmad FU (2016) Complications following cranioplasty and relationship to timing: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Neurosci 33:39–51
McGuinness LA, Higgins JPT (2020) Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): an R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res Synth Methods 12(1):55–61
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339(7716):332–336
Moreira-Gonzalez A, Jackson IT, Miyawaki T, Barakat K, DiNick V (2003) Clinical outcome in cranioplasty: critical review in long-term follow-up. J Craniofac Surg 14(2):144–153
Morton RP, Abecassis IJ, Hanson JF et al (2016) Predictors of infection after 754 cranioplasty operations and the value of intraoperative cultures for cryopreserved bone flaps. J Neurosurg 125(3):766–770
Mrad MA, Murrad K, Antonyshyn O (2017) Analyzing the cost of autogenous cranioplasty versus custom-made patient-specific alloplastic cranioplasty. J Craniofac Surg 28(5):1260–1263
Mukherjee S, Thakur B, Haq I, Hettige S, Martin AJ (2014) Complications of titanium cranioplasty - a retrospective analysis of 174 patients. Acta Neurochir 156(5):989–998
Mustroph CM, Malcolm JG, Rindler RS, Chu JK, Grossberg JA, Pradilla G, Ahmad FU (2017) Cranioplasty infection and resorption are associated with the presence of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World Neurosurg 103:686–693
National Institue For Health and Care Excellence (2014) Head injury: assessment and early management [CG176]
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) (2019) Stroke and transient ischaemic attack in over 16s: diagnosis and initial management [NG128]
Posti JP, Yli-Olli M, Heiskanen L, Aitasalo KMJ, Rinne J, Vuorinen V, Serlo W, Tenovuo O, Vallittu PK, Piitulainen JM (2018) Cranioplasty after severe traumatic brain injury: effects of trauma and patient recovery on cranioplasty outcome. Front Neurol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00223
Rashidi A, Sandalcioglu IE, Luchtmann M (2020) Aseptic bone-flap resorption after cranioplasty - incidence and risk factors. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0228009
Rocque BG, Agee BS, Thompson EM, Piedra M, Baird LC, Selden NR, Greene S, Deibert CP, Hankinson TC, Lew SM, Iskandar BJ, Bragg TM, Frim D, Grant G, Gupta N, Auguste KI, Nikas DC, Vassilyadi M, Muh CR, Wetjen NM, Lam SK. Complications following pediatric cranioplasty after decompressive craniectomy: a multicenter retrospective study. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2018 Sep;22(3):225-232. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.3.PEDS17234
Schoekler B, Trummer M (2014) Prediction parameters of bone flap resorption following cranioplasty with autologous bone. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 120:64–67
Schuss P, Vatter H, Marquardt G, Imöhl L, Ulrich CT, Seifert V, Güresir E (2012) Cranioplasty after decompressive craniectomy: the effect of timing on postoperative complications. J Neurotrauma 29(6):1090–1095
Schuss P, Vatter H, Oszvald Á, Marquardt G, Imöhl L, Seifert V, Güresir E (2013) Bone flap resorption: risk factors for the development of a long-term complication following cranioplasty after decompressive craniectomy. J Neurotrauma 30(2):91–95
Schütz A, Murek M, Stieglitz LH, Bernasconi C, Vulcu S, Beck J, Raabe A, Schucht P (2019) ACE-inhibitors: a preventive measure for bone flap resorption after autologous cranioplasty? J Neurosurg 131(5):1607–1614
Schwarz F, Dünisch P, Walter J, Sakr Y, Kalff R, Ewald C (2016) Cranioplasty after decompressive craniectomy: is there a rationale for an initial artificial bone-substitute implant? A single-center experience after 631 procedures. J Neurosurg 124(3):710–715
Singleton Q, Vaibhav K, Braun M et al (2019) Bone marrow derived extracellular vesicles activate osteoclast differentiation in traumatic brain injury induced bone loss. Cells 8(1):63
Smith, Comiskey C, Carroll (2016) Prevalence of and risk factors for osteoporosis in adults with acquired brain injury. Ir J Med Sci 185(2):473–481
Song J, Liu M, Mo X, Du H, Huang H, Xu GZ (2014) Beneficial impact of early cranioplasty in patients with decompressive craniectomy: evidence from transcranial Doppler ultrasonography. Acta Neurochir 156(1):193–198
Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC et al (2016) ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i4919
Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ et al (2019) RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l4898
Turner-Stokes L, Pick A, Nair A, Disler PB, Wade DT (2015) Multi-disciplinary rehabilitation for acquired brain injury in adults of working age. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004170.pub3
Vahedi K, Vicaut E, Mateo J et al (2007) Sequential-design, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial of early decompressive craniectomy in malignant middle cerebral artery infarction (DECIMAL Trial). Stroke 38(9):2506–2517
van de Vijfeijken SECM, Groot C, Ubbink DT et al (2019) Factors related to failure of autologous cranial reconstructions after decompressive craniectomy. J Cranio-Maxillofac Surg 47(9):1420–1425
van de Vijfeijken SECM, Münker TJAG, Spijker R et al (2018) Autologous bone is inferior to alloplastic cranioplasties: safety of autograft and allograft materials for cranioplasties, a systematic review. World Neurosurg 117:443–452.e8
Wiggins A, Austerberry R, Morrison D, Ho KM, Honeybul S (2013) Cranioplasty with custom-made titanium plates-14 years experience. Neurosurgery 72(2):248–256
Wilson L, Stewart W, Dams-O’Connor K, Diaz-Arrastia R, Horton L, Menon DK, Polinder S (2017) The chronic and evolving neurological consequences of traumatic brain injury. Lancet Neurol 16(10):813–825
Wui SH, Kim KM, Ryu YJ, Kim I, Lee SJ, Kim J, Kim C, Park S (2016) The autoclaving of autologous bone is a risk factor for surgical site infection after cranioplasty. World Neurosurg 91:43–49
Yadla S, Campbell PG, Chitale R, Maltenfort MG, Jabbour P, Sharan AD (2011) Effect of early surgery, material, and method of flap preservation on cranioplasty infections: a systematic review. Neurosurgery 68(4):1124–1130
Yeap M-C, Chen C-C, Liu Z-H et al (2019) Postcranioplasty seizures following decompressive craniectomy and seizure prophylaxis: a retrospective analysis at a single institution. J Neurosurg 131(3):936–940
Yeap MC, Tu PH, Liu ZH et al (2019) Long-term complications of cranioplasty using stored autologous bone graft, three-dimensional polymethyl methacrylate, or titanium mesh after decompressive craniectomy: a single-center experience after 596 procedures. World Neurosurg 128:e841–e850
Zhang Q, Yuan Y, Li X, Sun T, Zhou Y, Yu H, Guan J (2018) A large multicenter retrospective research on embedded cranioplasty and covered cranioplasty. World Neurosurg 112:e645–e651
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept and design: JH, MA, and DP O’B
Screening and data collation: JH and AM
Statistical analysis: JH
Interpretation of data: JH, MA, AM, and DP O’B
Writing: JH, MA, AM, and DP O’B
Review and revision of manuscript: JH, MA, AM, and DP O’B
All authors reviewed the manuscript prior to final submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Brain trauma
Supplementary information
ESM 1
Itemised search strategy for each database. (PDF 145 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henry, J., Amoo, M., Murphy, A. et al. Complications of cranioplasty following decompressive craniectomy for traumatic brain injury: systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Neurochir 163, 1423–1435 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-021-04809-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-021-04809-z