Abstract
Background
Trigeminal neuralgia (TGN) caused by the vertebrobasilar artery (VBA) is uncommon. The abducens nerve root is frequently dislocated by a tortuous VBA near the trigeminal nerve root. This unusual location of the root is not well known. This study aimed to investigate the location of the stretched abducens nerve root.
Methods
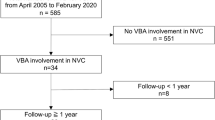
The objective is 26 patients with VBA-related TGN who underwent microvascular decompression (MVD). We retrospectively investigated the course of the abducens nerve root with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with three-dimensional (3D) imaging and surgical findings. The displacement of the abducens nerve root on the affected side was compared to the contralateral side.
Results
The abducens nerve root was distorted by a tortuous VBA (46.2%) or the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (53.8%). The average length of the cisternal segment was stretched to 23.4 mm versus 12.4 mm on the contralateral side. The peak point of the elevated abducens nerve root was mostly located rostro-medial (65.4%) or caudo-medial (34.6%) to the neurovascular compression site of the trigeminal nerve with a mean distance of 9.1 mm. Contact with the trigeminal nerve root was observed in 7 patients (26.9%). Three-dimensional imaging was consistent with the surgical findings and useful in predicting the location of the abducens nerve root. No abducens nerve palsy was noted in our series.
Conclusions
The abducens nerve root is located near the trigeminal nerve root in VBA-related TGN. Preoperative understanding of the unusual course of the abducens nerve root contributes to avoiding accidental nerve injury during MVD.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arishima H, Kikuta KI (2017) Magnetic resonance imaging findings of isolated abducent nerve palsy induced by vascular compression of vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia. J Neurosci Rural Pract 8:124–127
Choudhari KA (2005) Isolated abducent nerve palsy after microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: case report. Neurosurgery 57:1317
De Ridder D, Menovsky T (2007) Neurovascular compression of the abducent nerve causing abducent palsy treated by microvascular decompression. Case report. J Neurosurg 107:1231–1234
El-Ghandour NM (2010) Microvascular decompression in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia caused by vertebrobasilar ectasia. Neurosurgery 67:330–337
Giray S, Pelit A, Kizilkilic O, Karatas M (2005) Isolated abducens nerve palsy caused by contralateral vertebral artery dolichoectasia. Neurol India 53:246–247
Goldenberg-Cohen N, Miller NR (2004) Noninvasive neuroimaging of basilar artery dolichoectasia in a patient with an isolated abducens nerve paresis. Am J Ophthalmol 137:365–367
Goto Y, Inoue T (2020) Surgical management of the trigeminocerebellar artery in microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown) 19:379–384
Grigoryan YA, Sitnikov AR, Grigoryan GY (2016) Trigeminal neuralgia and hemifacial spasm associated with vertebrobasilar artery tortuosity. Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko 80:44–56
Honey CM, Kaufmann AM (2018) Trigeminal neuralgia due to vertebrobasilar artery compression. World Neurosurg 118:e155–e160
Inoue T, Shitara S, Goto Y, Prasetya M, Fukushima T (2020) Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia attributable to the vertebrobasilar artery: decompression technique and significance of separation from the nerve root. Acta Neurochir (Wien)
Kato H, Nakajima M, Ohnaka Y, Ishihara K, Kawamura M (2010) Recurrent abducens nerve palsy associated with neurovascular compression. J Neurol Sci 295:135–136
Linskey ME, Jho HD, Jannetta PJ (1994) Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia caused by vertebrobasilar compression. J Neurosurg 81:1–9
Liu J, Chen Z, Feng T, Jiang B, Yuan Y, Yu Y (2019) Biomedical glue sling technique in microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia caused by atherosclerotic vertebrobasilar artery: a description of operative technique and clinical outcomes. World Neurosurg 128:e74–e80
Ma X, Sun X, Yao J, Ni S, Gong J, Wang J, Li X (2013) Clinical analysis of trigeminal neuralgia caused by vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia. Neurosurg Rev 36:573–577
Miyamoto S, Matsuda M, Ishikawa E, Matsumura A (2020) Microvascular decompression for abducens nerve palsy due to neurovascular compression from both the vertebral artery and anterior inferior cerebellar artery: a case report. Surg Neurol Int 15:242
Miyazaki S, Fukushima T, Tamagawa T, Morita A (1987) Trigeminal neuralgia due to compression of the trigeminal root by a basilar artery trunk. Report of 45 cases. Neurol Med Chir 27:742–748 (Jpn)
Narai H, Manabe Y, Deguchi K, Iwatsuki K, Sakai K, Abe K (2000) Isolated abducens nerve palsy caused by vascular compression. Neurology 55:453–454
Ohhashi G, Irie K, Tani S, Ogawa T, Abe T, Hata Y (2001) Isolated abducens nerve palsy caused by the compression of the basilar artery: a case report. No To Shinkei 53:69–72
Ohtsuka K, Sone A, Igarashi Y, Akiba H, Sakata M (1996) Vascular compressive abducens nerve palsy disclosed by magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Ophthalmol 122:416–419
Ono K, Arai H, Endo T, Tsunoda A, Sato K, Sakai T, Makita J (2004) Detailed MR imaging anatomy of the abducent nerve: evagination of CSF into Dorello canal. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:623–626
Sandvand KA, Ringstad G, Kerty E (2008) Periodic abducens nerve palsy in adults caused by neurovascular compression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79:100–102
Smoker WR, Price MJ, Keyes WD, Corbett JJ, Gentry LR (1986) High-resolution computed tomography of the basilar artery: 1. normal size and position. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 7:55–60
Sun S, Jiang W, Wang J, Gao P, Zhang X, Jiao L, Liu W, Shu K, Lei T (2017) Clinical analysis and surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia caused by vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia: A retrospective study. Int J Surg 41:183–189
Taniguchi A, Ii Y, Kobayashi H, Maeda M, Tomimoto H (2011) Bilateral abducens nerve palsy by compression from bilateral anterior inferior cerebellar artery. J Neurol 258:2271–2273
Tsai TH, Demer JL (2011) Nonaneurysmal cranial nerve compression as cause of neuropathic strabismus: evidence from high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Ophthalmol 152:1067–1073
Tuzcu EA, Bayarogullari H, Coskun M, Yilmaz C, Ilhan N, Daglioglu MC, Aras M (2013) Bilateral abducens paralysis secondary to compression of abducens nerve roots by vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia. Neuroophthalmology 37:254–256
Wang X, Wang H, Chen S, Liang H, Wang H, Xu M, Xu L (2019) The long-term clinical outcomes of microvascular decompression for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia compressed by the vertebra-basilar artery: a case series review. BMC Neurol 19:217
Yamazaki T, Yamamoto T, Hatayama T, Zaboronok A, Ishikawa E, Akutsu H, Matsuda M, Kato N, Matsumura A (2015) Abducent nerve palsy treated by microvascular decompression: a case report and review of the literature. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 157:1801–1805
Yang XS, Li ST, Zhong J, Zhu J, Du Q, Zhou QM, Jiao W, Guan HX (2012) Microvascular decompression on patients with trigeminal neuralgia caused by ectatic vertebrobasilar artery complex: technique notes. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 154:793–797
Yousry I, Camelio S, Wiesmann M, Schmid UD, Moriggl B, Brückmann H, Yousry TA (1999) Detailed magnetic resonance imaging anatomy of the cisternal segment of the abducent nerve: Dorello's canal and neurovascular relationships and landmarks. J Neurosurg 91:276–283
Zhu Y, Thulborn K, Curnyn K, Goodwin J (2005) Sixth cranial nerve palsy caused by compression from a dolichoectatic vertebral artery. J Neuroophthalmol 25:134–135
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. Lori Radcliffe for her assistance with English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Functional Neurosurgery – Pain.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, T., Shitara, S., Shima, A. et al. Location of the abducens nerve stretched by a tortuous vertebrobasilar artery in trigeminal neuralgia. Acta Neurochir 163, 1027–1036 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-021-04742-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-021-04742-1