Abstract
Background
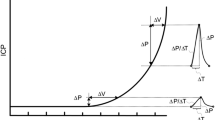
Monitoring of intracranial pressure (ICP) and ICP pulse wave amplitude (PWA) is an integrated part of neurosurgery. An increase in ICP usually leads to an increase in PWA. These findings have yet to be replicated during the positional shift from supine to upright, where we only know that ICP decreases. Our main aim is to clarify whether the positional shift also results in a change in pulse wave amplitude.
Method
Our database was retrospectively reviewed for subjects having had a standardized investigation of positional ICP. In all subjects, mean ICP and PWA were determined with both an automatic and a manual method and compared using Student’s t test. Finally, ICP and PWA were tested for correlation in both in supine and upright position.
Results
The study included 29 subjects. A significant change in ICP (Δ14.1 mmHg, p < 0.01) and no significant change in PWA (Δ0.4 mmHg, p = 0.06) were found. Furthermore, a linear correlation between ICP and PWA was found in both supine and upright positions (p < 0.01).
Conclusions
We found that during the positional shift from supine to upright, ICP is reduced while PWA remains unaffected. This indicates that the pressure-volume curve is shifted downward according to a hydrostatic pressure offset, while the slope of the curve does not change. In addition, the correlation between ICP and PWA in both supine and upright position validates the previous research on the matter.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andresen M, Hadi A, Petersen LG, Juhler M (2014) Effect of postural changes on ICP in healthy and ill subjects. Acta Neurochir 157(1):109–113
Avezaat CJJ, Van Eijndhoven JHM, Wyper DJ (1979) Cerebrospinal fluid pulse pressure and intracranial volume-pressure relationships. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 42(February):687–700
Avezaat CJJ, Van Eijndhoven JHM, Wyper DJ (1986) Clinical observations on the relationship between cerebrospinal fluid pulse pressure and intracranial pressure. Acta Neurochir 29:13–29
Brain Trauma Foundation, American Association of Neurological Surgeons JS on N and CC (1996) Guidelines for the treatment of severe head injury. J Neurotrauma 13:641–734
Brimioulle S, Moraine JJ, Norrenberg D, Kahn RJ (1997) Effects of positioning and exercise on intracranial pressure in a neurosurgical intensive care unit. Phys Ther 77(12):1682–1689
Carrera E, Kim DJ, Castellani G, Zweifel C, Czosnyka Z, Kasparowicz M, Smielewski P, Pickard JD, Czosnyka M (2010) What shapes pulse amplitude of intracranial pressure? J Neurotrauma. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2009.0951
Czosnyka M, Citerio G (2012) Brain compliance: the old story with a new ‘et cetera’. Intensive Care Med 38:925–927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-012-2572-6
Czosnyka M, Pickard JD (2004) Monitoring and interpretation of intracranial pressure. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75(6):813–821
Czosnyka M, Laniewski W, Batorski L, Zaworski W (1988) Analysis of intracranial pressure waveform during infusion test. Acta Neurochir 93:140–145
Czosnyka M, Hutchinson PJ, Balestreri M, Hiler M, Smielewski P, Pickard JD (2006) Monitoring and interpretation of intracranial pressure after head injury. Acta Neurochir Suppl 96:114–118
Czosnyka Z, Keong N, Kim DJ et al (2008) Pulse amplitude of intracranial pressure waveform in hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir Suppl. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-211-85,578-2_28
Eide PK (2008) Comparison of simultaneous continuous intracranial pressure (ICP) signals from ICP sensors placed within the brain parenchyma and the epidural space. Med Eng Phys 30(1):34–40
Eide PK, Brean A (2010) Cerebrospinal fluid pulse pressure amplitude during lumbar infusion in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus can predict response to shunting. Cerebrospinal Fluid Res 7(5). https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8454-7-5
Eide PK, Sæhle T (2010) Is ventriculomegaly in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus associated with a transmantle gradient in pulsatile intracranial pressure? Acta Neurochir 152(6):989–995
Eide PK, Sorteberg W (2007) Association among intracranial compliance, intracranial pulse pressure amplitude and intracranial pressure in patients with intracranial bleeds. Neurol Res 29(8):798–802
Feldman Z, Kanter M, Robertson C, Contant CF, Hayes C, Sheinberg MA, Villareal CA, Narayan RK, Grossman RG (1992) Effect of head elevation on intracranial pressure, cerebral perfusion pressure, and cerebral blood flow in head- injured patients. J Neurosurg 76:207–211
Foltz EL, Aine C (1981) Diagnosis of hydrocephalus by CSF pulse.Wave analysis: a clinical study. Surg Neurol 15(4):283–293
Kawoos U, McCarron RM, Auker CR, Chavko M (2015) Advances in intracranial pressure monitoring and its significance in managing traumatic brain injury. Int J Mol Sci 16(12):28979–28,997
Löfgren J, von Essen C, Zwetnow N (1973) The pressure-volume curve of the cerebrospinal fluid space in dogs. 557–74
Loman J, Myerson A, Goldman D (1935) Effects of alterations in posture on the cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Arch Neurol Psychiatr 33(6):1279–1295
Magnaes B (1976) Body position and cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Part 1: clinical studies on the effect of rapid postural changes. J Neurosurg 44(6):687–697. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1976.44.6.0687
Marmarou A, Shulman K (1975) Compartmental analysis of compliance and outflow resistance of the cerebrospinal fluid system. di:523–534
Matsumoto T, Nagai H, Kasuga Y, Kamiya K (1986) Changes in intracranial pressure (ICP) pulse wave following hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 82(1–2):50–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01456319
Mavrocordatos P, Bissonnette B, Ravussin P (2000) Effects of neck position and head elevation on intracranial pressure in anaesthetized neurosurgical patients: preliminary results. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 12(1):10–14. https://doi.org/10.1097/00008506-200001000-00003
Miller JD, Garibi J, Pickard JD (1973) A clinical study of intracranial volume pressure relationships. Br J Surg 60(4):316
Petersen LG, Petersen JCG, Andresen M, Secher NH, Juhler M (2016) Postural influence on intracranial and cerebral perfusion pressure in ambulatory neurosurgical patients. Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys 310(1):R100–R104
Petersen LG, Lawley JS, Lilja-cyron A et al (2019) Lower body negative pressure to safely reduce intracranial pressure. J Physiol 1:237–248
Portella G, Cormio M, Citerio G, Contant C, Kiening K, Enblad P, Piper I (2005) Continuous cerebral compliance monitoring in severe head injury: its relationship with intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure Statistical Methods. 707–713
Qvarlander S, Sundström N, Malm J, Eklund A (2019) Postural effects on intracranial pressure: modeling and clinical evaluation. 1474–1480
Raabe A, Czosnyka M, Piper I et al (1999) Monitoring of intracranial compliance: correction for a change in body position. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 141:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007010050263
Rosner MJ, Coley IB (1986) Cerebral perfusion pressure, intracranial pressure, and head elevation. J Neurosurg 65(5):636–641. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1986.65.5.0636
Vella MA, Crandall M, Patel MB, Surgery AC, Sciences S, Care SC, Surgery EG, Building MA (2018) Acute Management of Traumatic. Brain Inj 97(5):1015–1030
Wagshul ME, Eide PK, Madsen JR (2011) The pulsating brain: a review of experimental and clinical studies of intracranial pulsatility. Fluids Barriers CNS 8(1):5
Funding
NHN was supported by the Augustinos Foundation, grant number 18–4212. The funding source did not have any influence on data collection, interpretation of data, or the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.
Ethical approval
The project was approved by the Danish Data Protection Agency (approval number 2012–58-004). There was no need for ethics committee approval or patient consent, due to the study being retrospective and with no patient identifiable data.
Informed consent
For this type of study formal consent was not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on CSF Circulation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Norager, N.H., Olsen, M.H., Riedel, C.S. et al. Changes in intracranial pressure and pulse wave amplitude during postural shifts. Acta Neurochir 162, 2983–2989 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-020-04550-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-020-04550-z