Abstract
Background
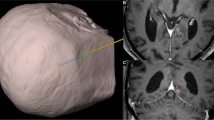
Brain biopsies are required to establish a definitive histological diagnosis for brain lesions that have been identified on imaging in order to guide further treatment for patients.
Objective
Various navigation systems are in use but little up to date evidence is available regarding the safety and accuracy of a frameless, electromagnetic technique to target brain lesions.
Methods
Data was collected retrospectively on all patients that had brain biopsies at our institution from 01/01/2010 to 31/12/2017. Operation notes, neuropathology reports, and clinical notes on electronic patient record were used to determine whether biopsy of adequate identifiable abnormal tissue was achieved, whether a definitive diagnosis was established, any adverse events occurred, and if a repeat biopsy was carried out.
Results
Three hundred seventy-one AxiEM (Medtronic, Minneapolis, USA)-guided brain tumor biopsies were performed in this 8-year period. Three hundred forty-nine (94.07%) procedures provided definitive tissue diagnosis, 22 (5.93%) were non diagnostic; in 6 cases (1.62%), repeat biopsy was performed and adverse events which caused clinical compromise were observed in 4 patients (1.08%).
Conclusions
The AxiEM is a fast, effective, and safe frameless and pinless neuronavigational system. It offers a high degree of accuracy required for the establishment of a definitive diagnosis, permitting optimal further treatment, and thus improving patient outcomes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin DV, Lozanne K, Parry PV, Engh JA, Seelman K, Mintz A (2011) Image-guided frameless stereotactic needle biopsy in awake patients without the use of rigid head fixation. J Neurosurg 114:1414–1420
Bekelis K, Radwan TA, Desai A, Roberts DW (2012) Frameless robotically targeted stereotactic brain biopsy: feasibility, diagnostic yield, and safety. J Neurosurg 116:1002–1006
Clark S, Sangra M, Hayhurst C (2008) The use of noninvasive electromagnetic neuronavigation for slit ventricle syndrome and complex hydrocephalus in a pediatric population. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2:430–434
Dammers R, Haitsma IK, Schouten JW, Kros JM, Avezaat CJJ, Vincent AJPE (2008) Safety and efficacy of frameless and frame-based intracranial biopsy techniques. Acta Neurochir 150:23
Dorward NL, Paleologos TS, Alberti O, Thomas DG (2002) The advantages of frameless stereotactic biopsy over frame-based biopsy. Br J Neurosurg 16:110–118
Frati A, Pichierri A, Bastianello S, Raco A, Santoro A, Esposito V et al (2011) Frameless stereotactic cerebral biopsy: our experience in 296 cases. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 89:234–245
Georgiopoulos M, Ellul J, Chroni E, Constantoyannis C (2018) Efficacy, safety, and duration of a frameless fiducial-less brain biopsy versus frame-based stereotactic biopsy: a prospective randomized study. J Neurol Surg 79:31–38
Harrison SE, Shooman D, Grundy PL (2012) A prospective study into the safety and efficacy of frameless, pinless electromagnetic image-guided biopsy of cerebral lesions: electromagnetic image-guided biopsy of cerebral lesions. Neurosurgery 70:29–33
Lefranc M, Capel C, Pruvot-Occean A-S, Fichten A, Desenclos C, Toussaint P et al (2015) Frameless robotic stereotactic biopsies: a consecutive series of 100 cases. J Neurosurg 122:342–352
Lu Y, Yeung C, Radmanesh A, Wiemann R, Black PM, Golby AJ (2015) Comparative effectiveness of frame-based, frameless, and intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging-guided brain biopsy techniques. World Neurosurg 83:261–268
Mascott CR (2006) In vivo accuracy of image guidance performed using optical tracking and optimized registration. J Neurosurg 105:4
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (2006) Guidance on cancer services: improving outcomes for people with brain and other CNS tumors https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/csg10/resources/improving-outcomes-for-people-with-brain-and-other-central-nervous-system-tumours-update-27841361437. Accessed 8 Jan 2019
Reavey-Cantwell JF, Bova FJ, Pincus DW (2006) Frameless, pinless stereotactic neurosurgery in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr 104(6):392–395
Shooman D, Belli A, Grundy PL (2010) Image-guided frameless stereotactic biopsy without intraoperative neuropathological examination. J Neurosurg 113:170–178
Spetzger U, Laborde G, Gilsbach JM (1995) Frameless neuronavigation in modern neurosurgery. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 38:163–166
Verploegh ISC, Volovici V, Haitsma IK, Schouten JW, Dirven CM, Kros JM et al (2015) Contemporary frameless intracranial biopsy techniques: might variation in safety and efficacy be expected. Acta Neurochir 157:2011–2016
Watanabe E, Watanabe T, Manaka S, Mayanagi Y, Takakura K (1987) Three-dimensional digitizer (neuronavigator): new equipment for computed tomography-guided stereotaxic surgery. Surg Neurol 27:543–547
Woodworth GF, McGirt MJ, Samdani A, Garonzik I, Olivi A, Weingart JD (2006) Frameless image-guided stereotactic brain biopsy procedure: diagnostic yield, surgical morbidity, and comparison with the frame-based technique. J Neurosurg 104:233–237
Zhang QJ, Wang WH, Wei XP, Yu YG (2013) Safety and efficacy of frameless stereotactic brain biopsy techniques. Chin Med Sci J 28:113–116
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee (name of institute/committee) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Brain Tumors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giamouriadis, A., Perera, D., Safdar, A. et al. Safety and accuracy of frameless electromagnetic-navigated (AXIEMTM)-guided brain lesion biopsies: a large single-unit study. Acta Neurochir 161, 2587–2593 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-04093-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-04093-y