Abstract
Background
The optimal targets for deep brain stimulation (DBS) in patients with refractory chronic pain are not clearly defined. We applied sensory functional MRI (fMRI)- and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)-based DBS in chronic pain patients into 3 different targets to ascertain the most beneficial individual stimulation site.
Methods
Three patients with incapacitating chronic pain underwent DBS into 3 targets (periventricular gray (PVG), ventroposterolateral thalamus (VPL), and posterior limb of the internal capsule according to fMRI and DTI (PLIC). The electrodes were externalized and double-blinded tested for several days. Finally, the two electrodes with the best pain reduction were kept for permanent stimulation. The patients were then followed up for 12 months. Outcome measures comprised the numerical rating scale (NRS), short-form McGill’s score (SF-MPQ), and health-related quality of life (SF-36).
Results
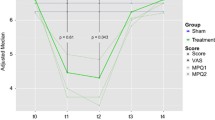
Continuous pain (mean NRS 6.6) was reduced to NRS 3.6 after 12 months. Only with stimulation of the PLIC pain attacks, that occurred at least 3 times a week (mean NRS 9.6) resolved in 2 patients and improved in one patient concerning both intensity (NRS 5) and frequency (twice a month). The mean SF-MPQ decreased from 92.7 to 50. The health-related quality of life improved considerably.
Conclusion
fMRI- and DTI-based DBS to the PLIC was the only target with a significant effect on pain attacks and seems to be the most promising target in chronic pain patients after brachial plexus injury. The combination with PVG or VPL can further improve patients’ outcome especially in terms of reducing the continuous pain.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu V, Vaz R, Rebelo V, Rosas MJ, Chamadoira C, Gillies MJ, Aziz TZ, Pereira EAC (2017) Thalamic deep brain stimulation for neuropathic pain: efficacy at three years follow-up. Neuromodulation 20:504–513
Adams JE, Hosobuchi Y, Fields HL (1974) Stimulation of internal capsule for relief of chronic pain. J Neurosurg 41:740–744
Boccard SGJ, Prangnell SJ, Pycroft L, Cheeran B, Moir L, Pereira EAC, Fitzgerald JJ, Green AL, Aziz TZ (2017) Long-term results of deep brain stimulation of the anterior cingulate cortex for neuropathic pain. World Neurosurg 106:625–637
Bouhassira D, Lanteri-Minet M, Attal N, Laurent B, Touboul C (2008) Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain 136:380–387
Farrell SM, Green A, Aziz T (2018) The current state of deep brain stimulation for chronic pain and its context in other forms of neuromodulation. Brain Sci 8
Gol A (1967) Relief of pain by electrical stimulation of the septal area. J NeurolSci 5:115–120
Gureje O, Von KM, Simon GE, Gater R (1998) Persistent pain and well-being: a World Health Organization study in primary care. JAMA 280:147–151
Hong JH, Son SM, Jang SH (2010) Identification of spinothalamic tract and its related thalamocortical fibers in human brain. Neurosci Lett 468:102–105
Hosobuchi Y, Adams JE, Linchitz R (1977) Pain relief by electrical stimulation of the central gray matter in humans and its reversal by naloxone. Science 197:183–186
Hunsche S, Sauner D, Runge MJ, Lenartz D, El MF, Treuer H, Sturm V, Maarouf M (2013) Tractography-guided stimulation of somatosensory fibers for thalamic pain relief. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 91:328–334
Marchand S (2008) The physiology of pain mechanisms: from the periphery to the brain. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 34:285–309
Mark VR, ERVIN FR (1965) Role of thalamotomy in treatment of chronic severe pain. Postgrad Med 37:563–571
Moriarty O, McGuire BE, Finn DP (2011) The effect of pain on cognitive function: a review of clinical and preclinical research. Prog Neurobiol 93:385–404
Narakas A (1978) Surgical treatment of traction injuries of the brachial plexus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 71–90
Parry CB (1980) Pain in avulsion lesions of the brachial plexus. Pain 9:41–53
Parry CB (1984) Pain in avulsion of the brachial plexus. Neurosurgery 15:960–965
Pereira EA, Aziz TZ (2014) Neuropathic pain and deep brain stimulation. Neurotherapeutics 11:496–507
Wang JY, Chang JY, Woodward DJ, Baccala LA, Han JS, Luo F (2007) Corticofugal influences on thalamic neurons during nociceptive transmission in awake rats. Synapse 61:335–342
Wilkinson HA (2000) Bilateral anterior cingulotomy for chronic noncancer pain. Neurosurgery 46:1535–1536
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The surgery of the three patients was done as an expanded access in off-label use.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the surgery and for publication of the results.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Functional Neurosurgery - Pain
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polanski, W.H., Zolal, A., Klein, J. et al. Somatosensory functional MRI tractography for individualized targeting of deep brain stimulation in patients with chronic pain after brachial plexus injury. Acta Neurochir 161, 2485–2490 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-04065-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-04065-2