Abstract
Objective
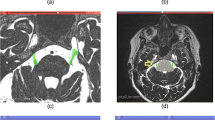
To explore whether segmentation and 3D modeling are more accurate in the preoperative detection of the neurovascular relationship (NVR) in patients with trigeminal neuralgia (TN) compared to MRI fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition (FIESTA).
Method
Segmentation and 3D modeling using 3D Slicer were conducted for 40 patients undergoing MRI FIESTA and microsurgical vascular decompression (MVD). The NVR, as well as the offending vessel determined by MRI FIESTA and 3D Slicer, was reviewed and compared with intraoperative manifestations using SPSS.
Results
The k agreement between the MRI FIESTA and operation in determining the NVR was 0.232 and that between the 3D modeling and operation was 0.6333. There was no significant difference between these two procedures (χ2 = 8.09, P = 0.088). The k agreement between the MRI FIESTA and operation in determining the offending vessel was 0.373, and that between the 3D modeling and operation was 0.922. There were significant differences between two of them (χ2 = 82.01, P = 0.000). The sensitivity and specificity for MRI FIESTA in determining the NVR were 87.2 % and 100 %, respectively, and for 3D modeling were both 100 %.
Conclusion
The segmentation and 3D modeling were more accurate than MRI FIESTA in preoperative verification of the NVR and offending vessel. This was consistent with surgical manifestations and was more helpful for the preoperative decision and surgical plan.

Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Love S, Coakham HB (2001) Trigeminal neuralgia: pathology and pathogenesis. Brain 124:2346–2360
Barker FG 2nd, Janetta PJ, Bissonette DJ, Larkins MV, Jho HD (1996) The long-term outcome of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. N Engl J Med 334:1077–1083
Sindou M, Leston J, Decullier E, Chapuis F (2007) Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: long-term effectiveness and prognostic factors in a series of 362 consecutive patients with clear-cut neurovascular conflicts who underwent pure decompression. J Neurosurg 106(6):1144–1153
Benes L, Shiratori K, Gurschi M, Sure U, Tirakotai W, Krischek B, Bertalanffy H (2005) Is preoperative high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging accurate in predicting neurovascular compression in patients with trigeminal neuralgia? A single-blind study. Neurosurg Rev 28(2):131–136
Zeng Q, Zhou Q, Liu Z, Li C, Ni S, Xue F (2013) Preoperative detection of the neurovascular relationship in trigeminal neuralgia using three-dimensional fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition (FIESTA) and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA). J Clin Neurosci 20(1):107–111
Fedorov A, Beichel R, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Finet J, Fillion-Robin JC, Pujol S, Bauer C, Jennings D, Fennessy F, Sonka M, Buatti J, Aylward S, Miller JV, Pieper S, Kikinis R (2012) 3D slicer as an image computing platform for the Quan imaging network. Magn Reson Imaging 30:1323–1341
Chun-Cheng Q, Qing-Shi Z, Ji-Qing Z, Zhi-Gang W (2009) A single-blinded pilot study assessing neurovascular contact by using high-resolution MR imaging inpatients with trigeminal neuralgia. Eur J Radiol 69:459–463
Ni S, Su W, Li X, Zeng Q, Liu Y, Zhu S, Wu C (2009) Enhanced three-dimensional fast spoiled gradient recalled MRI combined with magnetic resonance angiography for preoperative assessment of patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J Clin Neurosci 16:1555–1559
Leal PR, Hermier M, Froment JC, Souza MA, Cristino-Filho G, Sindou M (2010) Preoperative demonstration of the neurovascular compression characteristics with special emphasis on the degree of compression, using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging: a prospective study, with comparison to surgical findings, in 100 consecutive patients who underwent microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 152(5):817–825
Vergani F, Panaretos P, Penalosa A, English P, Nicholson C, Jenkins A (2011) Preoperative MRI/MRA for microvascular decompression in trigeminal neuralgia: consecutive series of 67 patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 153(12):2377–2381
Chavhan GB, Babyn PS, Jankharia BG, Cheng HL, Shroff MM (2008) Steady-state MR imaging sequences: physics, classification, and clinical applications. Radiographics 28:1147–1160
Mikami T, Minamida Y, Yamaki T, Koyanagi I, Nonaka T, Houkin K (2005) Cranial nerve assessment in posteriorfossa tumors with fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition (FIESTA). Neurosurg Rev 28:261–266
Patel NK, Aquilina K, Clarke Y, Renowden SA, Coakham HB (2003) How accurate ismagnetic resonance angiography in predicting neurovascular compression inpatientswith trigeminal neuralgia? A prospective, single-blinded comparativestudy. Br J Neurosurg 17(1):60–64
Montano N, Conforti G, Di Bonaventura R, Meglio M, Fernandez E, Papacci F (2015) Advances in diagnosis and treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Ther Clin Risk Manag 11:289–299
Satoh T, Onoda K, Date I (2007) Preoperative simulation for microvascualr decompression in patients with idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: visualization with three-dimensional magnetic cisternogram and angiogram fusion imaging. Neurosurgery 60:104–114
Xu X-h, Chen X-l, Zhang J, Zheng Y, Sun G-c, Yu X-g, Xu B-n (2014) Comparison of the Tada formula with software slicer precise and Low-cost method for volume assessment of intracerebral hematoma. Stroke 45:3433–3435
Lorenzoni J, Davidb P, Levivierc M (2012) Patterns of neurovascular compression in patients with classic trigeminal neuralgia: a high-resolution MRI-based study. Eur J Radiol 81:1851–1857
Masur H, Papke K, Bongartz G, Vollbretcht K (1995) The significance of three-dimensional MR-defined neurovascular compression for the pathogenesis of trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurol 242:93–98
Levy EI, Jannetta PJ (2002) Microvascular decompression. In: Kim J, Burchiel (eds) Surgical management of pain. Thieme, New York, pp 878–886
Nakajima N, Jun W, Tamotsu M, Jo H, Nobuhiko H (2007) Surface rendering-based virtual intraventricular endoscopy: Retrospective feasibility study and comparison to volume rendering-based approach. Neuroimage 37(Suppl 1):S89–S99
Awaji M, Okamoto K, Nishiyama K (2007) Magnetic resonance cisternography for preoperative evaluation of arachnoid cysts. Neuroradiology 49(9):721–726
Duffner F, Schiffbauer H, Glemser D, Skalej M, Freudenstein D (2003) Anatomy of the cerebral ventricular system for endoscopic neurosurgery: a magnetic resonance study. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145(5):359–368
Tirakotai W, Tirakotai O, Sure U, Riegel T, Bertalanffy H, Hellwig D (2004) The evolution of stereotactic guidance in neuroendoscopy. Childs Nerv Syst 20(11-12):790–795
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors certify that they have NO affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Kai-wei Han, Dan-feng Zhang and Ji-gang Chen contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Kw., Zhang, Df., Chen, Jg. et al. Presurgical visualization of the neurovascular relationship in trigeminal neuralgia with 3D modeling using free Slicer software. Acta Neurochir 158, 2195–2201 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-016-2936-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-016-2936-8