Abstract
Background
The Giant Intracranial Aneurysm Registry is a multicenter observational trial exclusively focusing on giant intracranial aneurysms (GIA). As no data exist on the interobserver variability in the radiological description of GIA, there is some uncertainty concerning the reliability of the GIA characteristics included in the registry. We have therefore designed a study to test the interobserver variability in the description of the specific GIA characteristics that are examined in the GIA registry.
Methods
Six different raters analyzed imaging of five GIA concerning GIA location, GIA size, GIA shape, GIA thrombosis, and the presence of perianeurysmal edema. Interobserver variability was examined using intraclass correlation and Fleiss’ kappa analysis.
Results
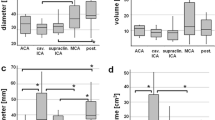
The intraclass correlation coefficient was 0.99 (95 % CI 0.97–1.0) for the largest GIA diameter and 0.98 (95 % CI 0.94–1.0) for the largest GIA diameter in an axial imaging slice. We found perfect interobserver agreement (Fleiss’ kappa 1.00) in the characterization of GIA location and the presence of perianeurysmal edema and almost perfect interobserver agreement for GIA thrombosis (Fleiss’ kappa 0.86, 95 % CI 0.63–1.00). Only moderate interobserver agreement was found in the description of GIA shape (Fleiss’ kappa 0.50, 95 % CI 0.27–0.73).
Conclusions
While GIA size, location, thrombosis, and the presence of perianeurysmal edema showed excellent interobserver agreement, the description of GIA shape was achieved with only moderate agreement. Data on GIA shape in multicenter studies, like the GIA registry, should therefore be discussed with caution and potentially reassessed in a centralized fashion.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez H (2009) Etiology of giant aneurysms and their treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:E8
Backes D, Vergouwen MD, Velthuis BK, van der Schaaf IC, Bor AS, Algra A, Rinkel GJ (2014) Difference in aneurysm characteristics between ruptured and unruptured aneurysms in patients with multiple intracranial aneurysms. Stroke 45:1299–1303
Baharoglu MI, Lauric A, Safain MG, Hippelheuser J, Wu C, Malek AM (2014) Widening and high inclination of the middle cerebral artery bifurcation are associated with presence of aneurysms. Stroke 45:2649–2655
Bor AS, Tiel Groenestege AT, terBrugge KG, Agid R, Velthuis BK, Rinkel GJ, Wermer MJ (2015) Clinical, radiological, and flow-related risk factors for growth of untreated, unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Stroke 46:42–48
Dengler J, Heuschmann PU, Endres M, Meyer B, Rohde V, Rufenacht DA, Vajkoczy P (2011) The rationale and design of the Giant Intracranial Aneurysm Registry: a retrospective and prospective study. Int J Stroke 6:266–270
Dengler J, Maldaner N, Bijlenga P, Burkhardt JK, Graewe A, Guhl S, Hong B, Hohaus C, Kursumovic A, Mielke D, Schebesch KM, Wostrack M, Rufenacht D, Vajkoczy P, Schmidt NO (2015) Perianeurysmal edema in giant intracranial aneurysms in relation to aneurysm location, size, and partial thrombosis. J Neurosurg. doi:10.3171/2014.10.JNS141560
Dengler J, Maldaner N, Bijlenga P, Burkhardt JK, Graewe A, Guhl S, Nakamura M, Hohaus C, Kursumovic A, Schmidt NO, Schebesch KM, Wostrack M, Vajkoczy P, Mielke D (2015) Quantifying unruptured giant intracranial aneurysms by measuring diameter and volume—a comparative analysis of 69 cases. Acta Neurochir 157:361–368
Dimmick S, Jones M, Steinfort B, Pines C, Faulder K (2009) Accuracy and interobserver reliability of three-dimensional rotational angiography versus mathematical models for volumetric measurement of intracranial aneurysms. J Clin Neurosci 16:1195–1198
Forbes G, Fox AJ, Huston J 3rd, Wiebers DO, Torner J (1996) Interobserver variability in angiographic measurement and morphologic characterization of intracranial aneurysms: a report from the International Study of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17:1407–1415
Froesen J, Piippo A, Paetau A, Kangasniemi M, Niemelä M, Hernesniemi J, Jääskeläinen J (2004) Remodeling of saccular cerebral artery aneurysm wall is associated with rupture: histological analysis of 24 unruptured and 42 ruptured cases. Stroke 35:2287–2293
Gonzalez NR, Duckwiler G, Jahan R, Murayama Y, Viñuela F (2008) Challenges in the endovascular treatment of giant intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 62(6 Suppl 3):1324–1335
Greving JP, Wermer MJ, Brown RD Jr, Morita A, Juvela S, Yonekura M, Ishibashi T, Torner JC, Nakayama T, Rinkel GJ, Algra A (2014) Development of the PHASES score for prediction of risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms: a pooled analysis of six prospective cohort studies. Lancet Neurol 13:59–66
Maldaner N, Guhl S, Mielke D, Musahl C, Schmidt NO, Wostrack M, Rüfenacht DA, Vajkoczy P, Dengler J (2015) Changes in volume of giant intracranial aneurysms treated by surgical strategies other than direct clipping. Acta Neurochir. doi:10.1007/s00701-015-2448-y
Rezek I, Lingineni RK, Sneade M, Molyneux AJ, Fox AJ, Kallmes DF (2014) Differences in the angiographic evaluation of coiled cerebral aneurysms between a core laboratory reader and operators: results of the Cerecyte Coil Trial. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:124–127
Suh SH, Cloft HJ, Huston J 3rd, Han KH, Kallmes DF (2014) Interobserver variability of aneurysm morphology: discrimination of the daughter sac. J Neurointerv Surg. doi:10.1136/neurintsurg-2014-011471
Tulamo R, Frösen J, Hernesniemi J, Niemelä M (2010) Inflammatory changes in the aneurysm wall: a review. J Neurointerv Surg 2:120–130
Viera AJ, Garrett JM (2005) Understanding interobserver agreement: the kappa statistic. Fam Med 37:360–363
Wiebers DO, Whisnant JP, Huston J 3rd, Meissner I, Brown RD Jr, Piepgras DG, Forbes GS, Thielen K, Nichols D, O’Fallon WM, Peacock J, Jaeger L, Kassell NF, Kongable-Beckman GL, Torner JC (2003) Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet 362:103–110
Acknowledgments
The Giant Intracranial Aneurysm Registry is funded by the Center for Stroke Research – Berlin.
Statement
All trials based on data from the Giant Intracranial Aneurysm Registry were approved by the ethics committees of all participating centers and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. All patients included gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
No parts of this project have been presented anywhere before.
Clinical Trial Registration-URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT02066493.
Appendix
Appendix
Giant intracranial aneurysm study group members
Vajkoczy P, Maldaner N, Uebelacker A, Dengler J
Department of Neurosurgery, Charité – Universitaetsmedizin Berlin
Endres M
Department of Neurology, Charité – Universitaetsmedizin Berlin
Bohner G, Wiener E, Bauknecht HC
Department of Neuroradiology, Charité – Universitaetsmedizin Berlin
Heuschmann PU, Malzahn U
Institute of Clinical Epidemiology and Biometry, University of Würzburg
Gläsker S, Zentner J, Van Velthoven V
Department of Neurosurgery, University Hospital Freiburg, Germany
Guhl S, Schroeder HWS
Department of Neurosurgery, University of Greifswald, Germany
Strowitzki M
Department of Neurosurgery, Trauma Center Murnau, Murnau, Germany
Etminan N, Haengghi D, Eicker S, Turowski B
Department of Neurosurgery, University of Düsseldorf, Germany
Schebesch KM, Brawanski A
Department of Neurosurgery, University of Regensburg, Germany
Wrede K, Sure U
Department of Neurosurgery, University of Essen, Germany
Schmidt NO, Regelsberger J, Westphal M
Department of Neurosurgery, University Medical Center, Hamburg Eppendorf, Germany
Mielke D, Rohde V
Department of Neurosurgery, Georg-August-University Goettingen, Germany
Hosch H, Moskopp D
Department of Neurosurgery Vivantes-Klinikum im Friedrichshain, Berlin, Germany
Joedicke A
Department of Neurosurgery Vivantes-Klinikum Neukoelln, Berlin, Germany
Hohaus C, Meisel HJ
Department of Neurosurgery, BG-Clinic Bergmannstrost, Halle, Germany.
Wostrack M, Meyer B, Lehmberg J
Department of Neurosurgery, Technical University of Munich, Germany
Musahl C, Hopf N
Department of Neurosurgery, Klinikum Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany
Winkler G, Spetzger U
Department of Neurosurgery, Klinikum Karlsruhe, Germany
Graewe A, Meier U
Department of Neurosurgery, Unfallkrankenhaus Berlin, Germany
Hong B, Nakamura M, Krauss J
Department of Neurosurgery, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany
Grote A, Simon M, Schramm J
Department of Neurosurgery, University Hospital Bonn, Bonn, Germany
Kursumovic A, Rath SA
Department of Neurosurgery and Interventional Neuroradiology, Donau-Isar-Klinikum,
Deggendorf, Germany
Marbacher S, Fathi A, Fandino J
Department of Neurosurgery, Kantonsspital Aarau, Aarau, Switzerland,
Familiari P, Raco A
Department of Neurosurgery, University of Rome “Sapienza”, Rome, Italy
BijlengaP, Schaller K
Service de Neurochirurgie, Faculté de Médecine de Genève and Hôpitaux Universitaire de Genève, Switzerland
Gruber A, Wang WT, Knosp E
Department of Neurosurgery, Medical University Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Hoffmann KT, Boxhammer E
Department of Neuroradiology, University of Leipzig, Leipzig, Germany
Rüfenacht DA
Department of Neuroradiology, Klinik Hirslanden, Zurich, Switzerland
Boccardi E, Piano M
Department of Neuroradiology, Ospedale Niguarda Ca’ Granda, Milano, Italy
Niemelä M, Nurminen V, Lehecka M, Hernesniemi J
Department of Neurosurgery, Helsinki University Central Hospital, Helsinki, Finland
Burkhardt JK, Bozinov O, Regli L
Department of Neurosurgery, University Hospital of Zurich, Switzerland
Shekhtman OD, Eliava SS
Burdenko Neurosurgical Institute, Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Moscow, Russia
N Kato, Irie K, Nishimura K, Kaku S, Arakawa H, Yuki I, Ishibashi T, Murayama Y
Department of Neurosurgery, Jikei University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan
Fiss I, Kombos T
Department of Spine Surgery and Neurosurgery, Helios Klinikum Hildesheim, Hildesheim, Germany
Pedro MT, König R, Wirtz R
Department of Neurosurgery, University Hospital of Ulm, Germany
Helthuis J, van der Zwan A
Department of Neurosurgery, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands
Cognard C, Gawlitza M
Department of Neuroradiology, Toulouse University Hospital, Toulouse, France
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wostrack, M., Mielke, D., Kato, N. et al. Interobserver variability in the characterization of giant intracranial aneurysms with special emphasis on aneurysm diameter and shape. Acta Neurochir 157, 1859–1865 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-015-2587-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-015-2587-1