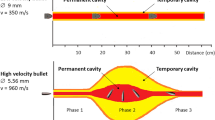
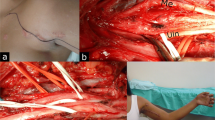
Abstract
Objectives
Ballistic injuries to peripheral nerves pose special challenges in terms of indications, timing and type of surgical intervention. The aim of the present work was to analyze our experience in the surgical treatment of peripheral nerve ballistic injuries with respect to the mechanism of injury (gunshot versus shrapnel), and identify common and dissimilar prognostic factors in both types of injury.
Methods
This study was conducted on 42 patients totaling 58 nerves. Twenty-two patients (32 nerves) were injured by gunshot and 20 patients (26 nerves) by shrapnel. Median postoperative follow-up was 33 months (range 12 months to 14 years).
Results
Overall postoperative outcome appears to be more favorable for gunshot-wound (GSW) patients than shrapnel-injured patients, especially in terms of neuropathic pain relief (75 % vs. 58 % respectively, p < 0.05). Presence of foreign particles in shrapnel injured patients has a negative impact on the surgical outcome in terms of rate of pain improvement (28 % compared to 67 % in patients with and without foreign particles, respectively). Nerve graft reconstruction, rather than neurolysis, seems to be the more beneficial treatment for shrapnel-induced neuropathic pain (100 % vs. 47 % in improvement rate, respectively). Early surgical intervention (median 2 months after injury) significantly relieved neuropathic pain in 83 % of shrapnel-injured patients compared to 58 % in patients operated later.
Conclusions
This study suggests that shrapnel injury is more destructive for nerve tissue than gunshot injury. Our impression is that early surgical intervention in shrapnel injuries and split nerve grafting (especially when small fragments are recognized in the nerve) significantly improve the patient’s functional activity and quality of life.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almogy G, Belzberg H, Mintz Y, Pikarsky AK, Zamir G, Rivkind AI (2004) Suicide bombing attacks: update and modifications to the protocol. Ann Surg 239(3):295–303
Bartlett CS (2003) Clinical update: gunshot wound ballistics. Clin Orthop Relat Res 408:28–57
Bartlett CS, Helfet DL, Hausman MR, Strauss E (2000) Ballistics and gunshot wounds: effects on musculoskeletal tissues. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 8(1):21–36
Cokluk C, Aydin K (2007) Ultrasound examination in the surgical treatment of lower extremity peripheral nerve injuries: part II. Turk Neurosurg 17(3):197–201
Covey DC (2002) Blast and fragment injuries of the musculoskeletal system. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84-A(7):1221–1234
Crabtree J (2006) Terrorist homicide bombings: a primer for preparation. J Burn Care Res 27(5):576–588
Dvali L, Mackinnon S (2003) Nerve repair, grafting, and nerve transfers. Clin Plast Surg 30(2):203–221
Eylon S, Mosheiff R, Liebergall M, Wolf E, Brocke L, Peyser A (2005) Delayed reaction to shrapnel retained in soft tissue. Injury 36(2):275–281
Graif M, Martinoli C, Rochkind S, Blank A, Trejo L, Weiss J, Kessler A, Derchi LE (2004) Sonographic evaluation of brachial plexus pathology. Eur Radiol 14(2):193–200
Hoogeveen JF, Troost D, Wondergem J, van der Kracht AH, Haveman J (1992) Hyperthermic injury versus crush injury in the rat sciatic nerve: a comparative functional, histopathological and morphometrical study. J Neurol Sci 108(1):55–64
Jandial R, Reichwage B, Levy M, Duenas V, Sturdivan L (2008) Ballistics for the neurosurgeon. Neurosurgery 62(2):472–480, discussion 480
Kato N, Htut M, Taggart M, Carlstedt T, Birch R (2006) The effects of operative delay on the relief of neuropathic pain after injury to the brachial plexus: a review of 148 cases. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 88(6):756–759
Kim DH, Kam AC, Chandika P, Tiel RL, Kline DG (2001) Surgical management and outcomes in patients with median nerve lesions. J Neurosurg 95(4):584–594
Kim DH, Kline DG (1995) Surgical outcome for intra- and extrapelvic femoral nerve lesions. J Neurosurg 83(5):783–790
Kim DH, Murovic JA, Tiel RL, Kline DG (2004) Penetrating injuries due to gunshot wounds involving the brachial plexus. Neurosurg Focus 16(5):E3
Kim DH, Murovic JA, Tiel RL, Kline DG (2004) Management and outcomes in 318 operative common peroneal nerve lesions at the Louisiana state university health sciences center. Neurosurgery 54(6):1421–1428, discussion 1428–1429
Kim DH, Murovic JA, Tiel RL, Kline DG (2006) Gunshot wounds involving the brachial plexus: surgical techniques and outcomes. J Reconstr Microsurg 22(2):67–72
Kline DG (1989) Civilian gunshot wounds to the brachial plexus. J Neurosurg 70(2):166–174
Lewin-Kowalik J, Marcol W, Kotulska K, Mandera M, Klimczak A (2006) Prevention and management of painful neuroma. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 46(2):62–67, discussion 67–68
Lynch CD, Pollock M (1998) Nerve thermal injury. Prog Brain Res 115:453–462
Millesi H, Meissl G, Berger A (1976) Further experience with interfascicular grafting of the median, ulnar, and radial nerves. J Bone Joint Surg Am 58(2):209–218
Nanobashvili J, Kopadze T, Tvaladze M, Buachidze T, Nazvlishvili G (2003) War injuries of major extremity arteries. World J Surg 27(2):134–139
Peleg K, Aharonson-Daniel L, Stein M, Michaelson M, Kluger Y, Simon D, Noji EK (2004) Gunshot and explosion injuries: characteristics, outcomes, and implications for care of terror-related injuries in Israel. Ann Surg 239(3):311–318
Rochkind S, Alon M (2000) Microsurgical management of old injuries of the peripheral nerve and brachial plexus. J Reconstr Microsurg 16(7):541–546
Rochkind S, Filmar G, Kluger Y, Alon M (2007) Microsurgical management of penetrating peripheral nerve injuries: pre, intra- and postoperative analysis and results. Acta Neurochir Suppl 100:21–24
Roganovic Z (2004) Missile-caused ulnar nerve injuries: outcomes of 128 repairs. Neurosurgery 55(5):1120–1129
Roganovic Z (2005) Missile-caused median nerve injuries: results of 81 repairs. Surg Neurol 63(5):410–418, discussion 418–9
Roganovic Z, Mandic-Gajic G (2006) Pain syndromes after missile-caused peripheral nerve lesions: part 2–treatment. Neurosurgery 59(6):1238–1249, discussion 1249–1251
Samardzic MM, Rasulic LG, Grujicic DM (1997) Gunshot injuries to the brachial plexus. J Trauma 43(4):645–649
Secer HI, Daneyemez M, Gonul E, Izci Y (2007) Surgical repair of ulnar nerve lesions caused by gunshot and shrapnel: results in 407 lesions. J Neurosurg 107(4):776–783
Secer HI, Daneyemez M, Tehli O, Gonul E, Izci Y (2008) The clinical, electrophysiologic, and surgical characteristics of peripheral nerve injuries caused by gunshot wounds in adults: a 40 year experience. Surg Neurol 69(2):143–152, discussion 152
Seddon HJ (1942) A classification of nerve injuries. Br Med J 2(4260):237–239
Seddon HJ (1949) The practical value of peripheral nerve repair. Proc R Soc Med 42(6):427–436
Seery JM, Valosen JM, Phillips JH, Slade DL, Seery AB, Parham MA, Chasen AB, Cutting PJ, Pizarro JM (2009) Effects of metal fragments on nerve healing in extremity injuries using a rat peroneal nerve model. J Am Coll Surg 209(2):278–283
Sheffy N, Mintz Y, Rivkind AI, Shapira SC (2006) Terror-related injuries: a comparison of gunshot wounds versus secondary-fragments-induced injuries from explosives. J Am Coll Surg 203(3):297–303
Stewart MP, Birch R (2001) Penetrating missile injuries of the brachial plexus. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 83(4):517–524
Stradiotti P, Curti A, Castellazzi G, Zerbi A (2009) Metal-related artifacts in instrumented spine. techniques for reducing artifacts in CT and MRI: state of the art. Eur Spine J 18(Suppl 1):102–108
Sunderland S (1951) A classification of peripheral nerve injuries producing loss of function. Brain 74(4):491–516
Suneson A, Hansson HA, Seeman T (1987) Peripheral high-energy missile hits cause pressure changes and damage to the nervous system: experimental studies on pigs. J Trauma 27(7):782–789
Tagliafico A, Altafini L, Garello I, Marchetti A, Gennaro S, Martinoli C (2010) Traumatic neuropathies: spectrum of imaging findings and postoperative assessment. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 14(5):512–522
Teitelbaum GP (1990) Metallic ballistic fragments: MR imaging safety and artifacts. Radiology 177(3):883
Vande Berg B, Malghem J, Maldague B, Lecouvet F (2006) Multi-detector CT imaging in the postoperative orthopedic patient with metal hardware. Eur J Radiol 60(3):470–479
Veselko M, Trobec R (2000) Intraoperative localization of retained metallic fragments in missile wounds. J Trauma 49(6):1052–1058
Volgas DA, Stannard JP, Alonso JE (2005) Current orthopaedic treatment of ballistic injuries. Injury 36(3):380–386
Vrettos BC, Rochkind S, Boome RS (1995) Low velocity gun shot wounds of the brachial plexus. J Hand Surg (Br) 20(2):212–214
Wightman JM, Gladish SL (2001) Explosions and blast injuries. Ann Emerg Med 37(6):664–678
Wilson RH (2003) Gunshots to the hand and upper extremity. Clin Orthop Relat Res 408:133–144
Wolf SJ, Bebarta VS, Bonnett CJ, Pons PT, Cantrill SV (2009) Blast injuries. Lancet 374(9687):405–415
Wolf YG, Rivkind A (2002) Vascular trauma in high-velocity gunshot wounds and shrapnel-blast injuries in Israel. Surg Clin N Am 82(1):237–244
Xu D, Pollock M (1994) Experimental nerve thermal injury. Brain 117(Pt 2):375–384
Yüksel F, Kişlaoğlu E, Durak N, Uçar C, Karacaoğlu E (1997) Prevention of painful neuromas by epineural ligatures, flaps and grafts. Br J Plast Surg 50(3):182–185
Zhu J, Liu F, Li D, Shao J, Hu B (2010) Preliminary study of the types of traumatic peripheral nerve injuries by ultrasound. Eur Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00330-010-1992-3
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shimon Rochkind and Ido Strauss contributed equally to the preparation of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rochkind, S., Strauss, I., Shlitner, Z. et al. Clinical aspects of ballistic peripheral nerve injury: shrapnel versus gunshot. Acta Neurochir 156, 1567–1575 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2139-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2139-0