Abstract
Background
Thin aneurysm wall thickness (AWT) is thought to portend an elevated risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is biased by AWT overestimations. Previously, this suspected bias has been qualitatively described but never quantified. We aimed to quantify the overestimation of AWT by MRI when compared to the gold standard of AWT as measured by light microscopy of fresh aneurysm specimens (without any embedding procedure). This analysis should help to define the clinical potential of MRI estimates of AWT.
Methods
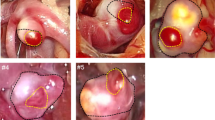
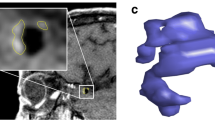
3-Tesla (3T) MRI (contrast-enhanced T1 Flash sequences; resolution: 0.4x0.4x1.5 mm3) was performed in 13 experimental aneurysms. After MR acquisition, the aneurysms were retrieved, longitudinally sectioned and calibrated micrographs were obtained immediately. AWT at the dome, AWT at the neck and parent vessel wall thickness (PVT) were measured on precisely correlated MR-images and histologic micrographs by blinded independent investigators. Parameters were statistically compared (Wilcoxon test, Spearman's correlation).
Results
AWT was assessed and reliably measured using MRI. Interobserver variability was not significant for either method. MR overestimation was only significant below the image resolution threshold: AWT at the dome (0.24 ± 0.06 mm vs. MR 0.30 ± 0.08 mm; p = 0.0078; R = 0.6125), AWT at the neck (0.25 ± 0.07 mm vs. MR 0.29 ± 0.07 mm; p = 0.0469; R = 0.7451), PVT (0.46 ± 0.06 mm vs. MR 0.48 ± 0.06 mm; p = 0.5; R = 0.8568).
Conclusion
In this experimental setting, MR overestimations were minimal (mean 0.02 mm) above the image resolution threshold. When AWT is classified in ranges defined by the MR resolution threshold, clinical usage may be beneficial. Further quantitative and comparative experimental and human studies are warranted to confirm these findings.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abruzzo T, Shengelaia G, Dawson R, Owens D, Cawley C, Gravanis M (1998) Histologic and morphologic comparison of experimental aneurysms with human intracranial aneurysms. AJNR:1309–1314
Boussel L, Wintermark M, Martin A, Dispensa B, VanTijen R, Leach J, Rayz V, Acevedo-Bolton G, Lawton M, Higashida R, Smith W, Young W, Saloner D (2008) Monitoring serial change in the lumen and outer wall of vertebrobasilar aneurysms. AJNR 29:259–264
Bouzeghrane F, Naggara O, Kallmes D, Berenstein A, Raymond J, Centres atICoN (2010) In vivo experimental intracranial aneurysm models: a systematic review. AJNR 31:418–423
Canham P, Finlay H, Tong S (1996) Stereological analysis of the layered collagen of human intracranial aneurysms. J Microsc 183:170–180
Cebral J, Mut F, Weir J, Putman C (2011) Quantitative characterization of the hemodynamic environment in ruptured and unruptured brain aneurysms. AJNR 32:145–151
Cloft HJ, Altes TA, Marx WF, Raible RJ, Hudson SB, Helm GA, Mandell JW, Jensen ME, Dion JE, Kallmes DF (1999) Endovascular creation of an in vivo bifurcation aneurysm model in rabbits. Radiology 213:223–228
Costalat V, Sanchez M, Ambard D, Thines L, Lonjon N, Nicoud F, Brunel H, Lejeune J, Dufour H, Bouillot P, Lhaldky J, Kouri K, Segnarbieux F, Maurage C, Lobotesis K, Villa-Uriol M, Zhang C, Frangi A, Mercier G, Bonafé A, Sarry L, Jourdan F (2011) Biomechanical wall properties of human intracranial aneurysms resected following surgical clipping (IRRAs Project). J Biomech 44:2685–2691
Frösen J, Piippo A, Paetau A, Kangasniemi M, Niemelä M, Hernesniemi J, Jääskeläinen J (2004) Remodeling of saccular cerebral artery aneurysm wall is associated with rupture: histological analysis of 24 unruptured and 42 ruptured cases. Stroke 35:2287–2293
Griffith T (1994) Modulation of blood flow and tissue perfusion by endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Exp Physiolo 79:873–913
Kallmes DF, Helm GA, Hudson SB, Altes TA, Do HM, Mandell JW, Cloft HJ (1999) Histologic evaluation of platinum coil embolization in an aneurysm model in rabbits. Radiology 213:217–222
Kataoka K, Taneda M, Asai T, Kinoshita A, Ito M, Kuroda R (1999) Structural fragility and inflammatory response of ruptured cerebral aneurysms. A comparative study between ruptured and unruptured cerebral aneurysms. Stroke 30:1396–1401
Lall R, Eddleman C, Bendok B, Batjer H (2009) Unruptured intracranial aneurysms and the assessment of rupture risk based on anatomical and morphologic factors: sifting through the sands of data. Neurosurg Focus 26(E2):1–5
Marbacher S, Erhardt S, Ai Schläppi J, Coluccia D, Remonda L, Fandino J, Sherif C (2011) Complex Bi-Lobular, Bi-Saccular, and Broad-Necked Microsurgical Aneurysms Formation in the Rabbit Bifurcation Model for the Study of Upcoming Endovascular Techniques. AJNR 32:772–777
Marbacher S, Tastan I, Neuschmelting V, Erhardt S, Coluccia D, Sherif C, Remonda L, Fandino J (2012) Long-Term Patency of Complex Bilobular, Bisaccular, and Broad-Neck Aneurysms in the Rabbit Microsurgical Venous Pouch Bifurcation Model. Neurol research 34:538–546
Matouk C, Mandell D, Günel M, Bulsara K, Malhotra A, Hebert R, Johnson M, Mikulis D, Minja F (2013) Vessel Wall Magnetic Resonance Imaging Identifies the Site-of-rupture in Patients with Multiple Intracranial Aneurysms: Proof-of-principle. Neurosurg 2012
Naggara O, White P, Guilbert F, Roy D, Weill A, Raymond J (2010) Endovascular treatment of intracranial unruptured aneurysms: systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature on safety and efficacy. Radiology 256:887–897
Park J, Lee C, Sim K, Huh J, Park J (2009) Imaging of the Walls of Saccular Cerebral Aneurysms With Double Inversion Recovery Black-Blood Sequence. J Magn Reson Imaging 30:1179–1183
Qiao Y, Steinman D, Qin Q, Etesami M, Schar M, Astor B, Wasserman B (2011) Intracranial Arterial Wall Imaging Using Three-Dimensional High Isotropic Resolution Black Blood MRI at 3.0 Tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging 34:22–30
Sherif C, Fandino J, Erhardt S, Di Ieva A, Killer M, Kleinpeter G, Marbacher S (2011) Microsurgical Arterial-bifurcation Aneurysms in the Rabbit Model: Technical Aspects. J Vis Exp 51
Sherif C, Marbacher S, Erhardt S, Fandino J (2011) Improved microsurgical creation of venous-pouch arterial-bifurcation aneurysms in rabbits. AJNR 32:165–169
Sherif C, Marbacher S, Fandino J (2009) High-resolution three-dimensional 3 T magnetic resonance angiography for the evaluation of experimental aneurysms in the rabbit. Neurol research 31:869–872
Sherif C, Plenk H (2011) Quantitative angiographic and histopathologic evaluation of experimental aneurysms. AJNR 32:E33–E34
Stehbens W (1975) Ultrastructure of aneurysms. Arch Neurol 32:798–807
Stehbens W (1985) The ultrastructure of experimental aneurysms in rabbits. Pathology 17:87–95
Stehbens W (2000) Histologic and Morphologic Comparison of Experimental Aneurysms with Human Intracranial Aneurysms. AJNR 21:1769–1773
Stehbens WE (1981) Chronic changes in experimental saccular and fusiform aneurysms in rabbits. Arch Pathol Lab Med 105:603–607
Steinman D, Antiga L, Wasserman B (2010) Overestimation of Cerebral Aneurysm Wall Thickness by Black Blood MRI? J Magn Reson Imaging 31:766
Swartz R, Bhuta S, Farb R, Agid R, Willinsky R, terBrugge K, Butany J, Wasserman B, Johnstone D, Silver F, Mikulis D (2009) Intracranial arterial wall imaging using high-resolution 3-tesla contrast-enhanced MRI. Neurology 72:627–634
Tulamo R, Frösen J, Junnikkakala S, Pateau A, Kangasniemi M, Niemelä M, Jääskeläinen J, Jokitalo E, Karatas A, Hernesniemi J, Meri S (2006) Complement activation associates with saccular cerebral aneurysm wall degeneration and rupture. Neurosurg 59:1069–1077
van der Kolk A, Zwanenburg J, Brundel M, Biessels G, Visser F, Luijten P, Hendrikse J (2011) Intracranial Vessel Wall Imaging at 7.0-T MRI. Stroke 42:2478–2484
Vlak M, Algra A, Brandenburg R, Rinkel G (2011) Prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms, with emphasis on sex, age, comorbidity, country, and time period: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 10:626–636
Watton P, Selimovic A, Raberger N, Huang P, Holzapfel G, Ventikos Y (2011) Modelling evolution and the evolving mechanical environment of saccular cerebral aneurysms. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 10:109–132
Wermer M, van der Schaaf I, Algra A, Rinkel G (2007) Risk of rupture of unruptured intracranial aneurysms in relation to patient and aneurysm characteristics: an updated meta-analysis. Stroke 38:1404–1410
Whittaker P, Schwab M, Canham P (1988) The molecular organization of collagen in saccular aneurysms assessed by polarized light microscopy. Connect Tissue Res 17:43–54
Wiebers D, Whisnant J, Forbes G (1998) For the International Study of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm Investigators. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms —risk of rupture and risks of surgical intervention. N Engl J Med 339:1725–1733
Acknowledgment
This study was funded by the Medical Scientific Fund of the Mayor of the City of Vienna. Sherif C. and Mach G. are shareholders of NVtec. Ltd., Vienna, Austria. The other authors have no industrial affiliations or financial interests.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sherif, C., Kleinpeter, G., Mach, G. et al. Evaluation of cerebral aneurysm wall thickness in experimental aneurysms: Comparison of 3T-MR imaging with direct microscopic measurements. Acta Neurochir 156, 27–34 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1919-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1919-2