Abstract
Background
The objective of this study was to assess the possibility of predicting histological characteristics of meningiomas on the basis of preoperative MRI and the correlation of the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and collagen XVIII with histological parameters already established as predictive of the course of these tumors.
Methods
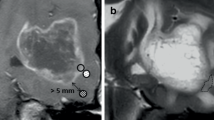
Expression of VEGF and collagen XVIII as well as other histological characteristics was examined in meningioma tissues from 20 patients. Preoperative MRI, including dynamic imaging of contrast enhancement, was analyzed. Times to maximum enhancement and maximum intensity increase were noted from dynamic imaging. The relative intensity of the tumor in fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR), T2-weighted and contrast enhanced T1-weighted images, as well as volumes of tumor and edema, was calculated. The edema-tumor volume ratio was defined as the edema index (EI).
Results
Both VEGF and collagen XVIII were expressed in all meningioma samples. Edema was present in 60 % of cases. The strongest correlation of VEGF expression was to EI. Among histological parameters, microvessel density (MVD) and cellularity correlated moderately with VEGF. Collagen XVIII expression correlated strongly with the maximal intensity increase after contrast agent administration (ρ = 0.71, P = 0.001) as well as with MVD and intensity of the meningioma on FLAIR images.
Conclusion
Meningiomas with faster and more intense enhancement in dynamic studies, indicative of good tumor blood supply and permeability of vasculature, are associated with high levels of collagen XVIII and VEGF expression. Occurrence of peritumoral edema in meningiomas is strongly correlated with expression of VEGF.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Juffer AH, Marin U, Niemitalo O, Koivukangas J (2008) Computer modeling of brain tumor growth. Mini Rev Med Chem 8:1494–1506
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285:1182–1186
Stupack DG, Cheresh DA (2004) Integrins and angiogenesis. Curr Top Dev Biol 64:207–238
Holash J, Wiegand SJ, Yancopoulos GD (1999) New model of tumor angiogenesis: dynamic balance between vessel regression and growth mediated by angiopoietins and VEGF. Oncogene 18:5356–5362
Provias J, Claffey K, delAguila L, Lau N, Feldkamp M, Guha A (1997) Meningiomas: role of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor in angiogenesis and peritumoral edema. Neurosurgery 40:1016–1026
Weindel K, Moringlane JR, Marme D, Weich HA (1994) Detection and quantification of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor in brain tumor tissue and cyst fluid: the key to angiogenesis? Neurosurgery 35:439–448
Yoshioka H, Hama S, Taniguchi E, Sugiyama K, Arita K, Kurisu K (1999) Peritumoral brain edema associated with meningioma: influence of vascular endothelial growth factor expression and vascular blood supply. Cancer 85:936–944
Utriainen A, Sormunen R, Kettunen M, Carvalhaes LS, Sajanti E, Eklund L, Kauppinen R, Kitten GT, Pihlajaniemi T (2004) Structurally altered basement membranes and hydrocephalus in a type XVIII collagen deficient mouse line. Hum Mol Genet 13:2089–2099
O’Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR, Folkman J (1997) Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell 88:277–285
Rehn M, Veikkola T, Kukk-Valdre E, Nakamura H, Ilmonen M, Lombardo C, Pihlajaniemi T, Alitalo K, Vuori K (2001) Interaction of endostatin with integrins implicated in angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:1024–1029
Wickstrom SA, Alitalo K, Keski-Oja J (2002) Endostatin associates with integrin alpha5beta1 and caveolin-1, and activates Src via a tyrosyl phosphatase-dependent pathway in human endothelial cells. Cancer Res 62:5580–5589
Wickstrom SA, Alitalo K, Keski-Oja J (2003) Endostatin associates with lipid rafts and induces reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton via down-regulation of RhoA activity. J Biol Chem 278:37895–37901
Eriksson K, Magnusson P, Dixelius J, Claesson-Welsh L, Cross MJ (2003) Angiostatin and endostatin inhibit endothelial cell migration in response to FGF and VEGF without interfering with specific intracellular signal transduction pathways. FEBS Lett 536:19–24
Kim YM, Hwang S, Kim YM, Pyun BJ, Kim TY, Lee ST, Gho YS, Kwon YG (2002) Endostatin blocks vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated signaling via direct interaction with KDR/Flk-1. J Biol Chem 277:27872–27879
Hurskainen M, Eklund L, Hagg PO, Fruttiger M, Sormunen R, Ilves M, Pihlajaniemi T (2005) Abnormal maturation of the retinal vasculature in type XVIII collagen/endostatin deficient mice and changes in retinal glial cells due to lack of collagen types XV and XVIII. FASEB J 19:1564–1566
Morimoto T, Aoyagi M, Tamaki M, Yoshino Y, Hori H, Duan L, Yano T, Shibata M, Ohno K, Hirakawa K, Yamaguchi N (2002) Increased levels of tissue endostatin in human malignant gliomas. Clin Cancer Res 8:2933–2938
Strik HM, Schluesener HJ, Seid K, Meyermann R, Deininger MH (2001) Localization of endostatin in rat and human gliomas. Cancer 91:1013–1019
Kirsch M, Weigel P, Pinzer T, Carroll RS, Black PM, Schackert HK, Schackert G (2005) Therapy of hematogenous melanoma brain metastases with endostatin. Clin Cancer Res 11:1259–1267
Pradilla G, Legnani FG, Petrangolini G, Francescato P, Chillemi F, Tyler BM, Gaini SM, Brem H, Olivi A, DiMeco F (2005) Local delivery of a synthetic endostatin fragment for the treatment of experimental gliomas. Neurosurgery 57:1032–1040
Fukai N, Eklund L, Marneros AG, Oh SP, Keene DR, Tamarkin L, Niemela M, Ilves M, Li E, Pihlajaniemi T, Olsen BR (2002) Lack of collagen XVIII/endostatin results in eye abnormalities. EMBO J 21:1535–1544
Sund M, Hamano Y, Sugimoto H, Sudhakar A, Soubasakos M, Yerramalla U, Benjamin LE, Lawler J, Kieran M, Shah A, Kalluri R (2005) Function of endogenous inhibitors of angiogenesis as endothelium-specific tumor suppressors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2934–2939
Mantle RE, Lach B, Delgado MR, Baeesa S, Belanger G (1999) Predicting the probability of meningioma recurrence based on the quantity of peritumoral brain edema on computerized tomography scanning. J Neurosurg 91:375–383
Yamasaki F, Yoshioka H, Hama S, Sugiyama K, Arita K, Kurisu K (2000) Recurrence of meningiomas. Cancer 89:1102–1110
Bitzer M, Klose U, Geist-Barth B, Nagele T, Schick F, Morgalla M, Claussen CD, Voigt K (2002) Alterations in diffusion and perfusion in the pathogenesis of peritumoral brain edema in meningiomas. Eur Radiol 12:2062–2076
Ide M, Jimbo M, Yamamoto M, Umebara Y, Hagiwara S, Kubo O (1996) MIB-1 staining index and peritumoral brain edema of meningiomas. Cancer 78:133–143
Tamiya T, Ono Y, Matsumoto K, Ohmoto T (2001) Peritumoral brain edema in intracranial meningiomas: effects of radiological and histological factors. Neurosurgery 49:1046–1051
Nakano T, Asano K, Miura H, Itoh S, Suzuki S (2002) Meningiomas with brain edema: radiological characteristics on MRI and review of the literature. Clin Imaging 26:243–249
Chen TC, Zee CS, Miller CA, Weiss MH, Tang G, Chin L, Levy ML, Apuzzo ML (1992) Magnetic resonance imaging and pathological correlates of meningiomas. Neurosurgery 31:1015–1021
Smith HP, Challa VR, Moody DM, Kelly DL Jr (1981) Biological features of meningiomas that determine the production of cerebral edema. Neurosurgery 8:428–433
Maiuri F, Iaconetta G, de Divitiis O, Cirillo S, Di Salle F, De Caro ML (1999) Intracranial meningiomas: correlations between MR imaging and histology. Eur J Radiol 31:69–75
Nagele T, Petersen D, Klose U, Grodd W, Opitz H, Gut E, Martos J, Voigt K (1993) Dynamic contrast enhancement of intracranial tumors with snapshot-FLASH MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 14:89–98
Oka Y, Kusunoki K, Nochide I, Igase K, Harada H, Sadamoto K, Nagasawa K (2002) Assessment of hemodynamics of meningioma with dynamic MR imaging. No To Shinkei 54:589–593
Yrjana SK, Tuominen H, Karttunen A, Lahdesluoma N, Heikkinen E, Koivukangas J (2006) Low-field MR imaging of meningiomas including dynamic contrast enhancement study: evaluation of surgical and histopathologic characteristics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:2128–2134
Laitakari J, Nayha V, Stenback F (2004) Size, shape, structure, and direction of angiogenesis in laryngeal tumour development. J Clin Pathol 57:394–401
Valtola R, Salven P, Heikkila P, Taipale J, Joensuu H, Rehn M, Pihlajaniemi T, Weich H, deWaal R, Alitalo K (1999) VEGFR-3 and its ligand VEGF-C are associated with angiogenesis in breast cancer. Am J Pathol 154:1381–1390
Yrjana SK, Katisko JP, Ojala RO, Tervonen O, Schiffbauer H, Koivukangas J (2002) Versatile intraoperative MRI in neurosurgery and radiology. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 144:271–278
Yrjana SK, Vaara T, Karttunen A, Katisko J, Koivukangas J (2004) Dynamic MR imaging of brain tumors in low field using undersampled projection reconstruction. Magn Reson Imaging 22:799–805
Gerstner ER, Duda DG, di Tomaso E, Ryg PA, Loeffler JS, Sorensen AG, Ivy P, Jain RK, Batchelor TT (2009) VEGF inhibitors in the treatment of cerebral edema in patients with brain cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6:229–236
Ding YS, Wang HD, Tang K, Hu ZG, Jin W, Yan W (2008) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human meningiomas and peritumoral brain areas. Ann Clin Lab Sci 38:344–351
Paek SH, Kim CY, Kim YY, Park IA, Kim MS, Kim DG, Jung HW (2002) Correlation of clinical and biological parameters with peritumoral edema in meningioma. J Neurooncol 60:235–245
Marneros AG, Olsen BR (2005) Physiological role of collagen XVIII and endostatin. FASEB J 19:716–728
Moulton KS, Olsen BR, Sonn S, Fukai N, Zurakowski D, Zeng X (2004) Loss of collagen XVIII enhances neovascularization and vascular permeability in atherosclerosis. Circulation 110:1330–1336
Lamszus K, Lengler U, Schmidt NO, Stavrou D, Ergun S, Westphal M (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor, hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, and placenta growth factor in human meningiomas and their relation to angiogenesis and malignancy. Neurosurgery 46:938–947
Fernando NT, Koch M, Rothrock C, Gollogly LK, D’Amore PA, Ryeom S, Yoon SS (2008) Tumor escape from endogenous, extracellular matrix-associated angiogenesis inhibitors by up-regulation of multiple proangiogenic factors. Clin Cancer Res 14:1529–1539
Lobato RD, Alday R, Gomez PA, Rivas JJ, Dominguez J, Cabrera A, Madero S, Ayerbe J (1996) Brain oedema in patients with intracranial meningioma. Correlation between clinical, radiological, and histological factors and the presence and intensity of oedema. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 138:485–493
Wilmes LJ, Pallavicini MG, Fleming LM, Gibbs J, Wang D, Li KL, Partridge SC, Henry RG, Shalinsky DR, Hu-Lowe D, Park JW, McShane TM, Lu Y, Brasch RC, Hylton NM (2007) AG-013736, a novel inhibitor of VEGF receptor tyrosine kinases, inhibits breast cancer growth and decreases vascular permeability as detected by dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 25:319–327
Koivukangas J, Katisko J, Yrjänä S, Tuominen J, Schiffbauer H, Ilkko E (2003) Successful neurosurgical 0.23T intraoperative MRI in a shared facility. Monduzzi Editore Medimond. Proceedings of the 12th European Congress of Neurosurgery (EANS), Lisbon , 439–444
Acknowledgments
We thank Pasi Ohtonen, MSc, for assistance with statistical analysis; Anna-Leena Heula, MD, for help in collecting the patient data.
Conflicts of Interest
None
Financial support and industry affiliations
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Comment
The authors correlated VEGF and collagen XVIII expression with preoperative MRI parameters in a small sample of meningiomas. They found that expression of collagen XVIII was best predicted preoperatively from the maximal intensity increase seen in dynamic T1-weighted imaging and also the signal intensity on FLAIR images. They also calculated an edema index on MRI that was found to correlate with expression of VEGF but not with collagen XVIII expression. Meningiomas that displayed high intensity on T2 and FLAIR MR images, and those with faster and more intense enhancement in dynamic studies, tended to have a higher VEGF and collagen XVIII expression. The current results are interesting since they give us some clues with regard to the formation of edema in meningiomas and potentially also the growth rates. Nonetheless, the results must be seen as preliminary findings because of the small number of patients. Particularly, there were only few patients included with a higher edema index and also with high density of vascular collagen XVIII expression.
H.J. Steiger
Dusseldorf, Germany
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salokorpi, N., Yrjänä, S., Tuominen, H. et al. Expression of VEGF and collagen XVIII in meningiomas: correlations with histopathological and MRI characteristics. Acta Neurochir 155, 989–996 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1699-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1699-8