Abstract
Background
Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma (JNA) is a rare benign tumor occurring almost exclusively in adolescent and young adult males. The tumor is characterized by slow progression, aggressive growth, high vascularization, and increased rate of persistence and recurrence. The aim of this study was to describe a case of giant JNA from our practice and discuss the controversies of surgical treatment of advanced JNA.
Material and methods
A series of 29 consecutive male patients with JNA Fisch grade III and IV was surgically treated in Burdenko Neurosurgical Institute from 2000 until 2008. In the vast majority of cases, endovascular embolization and surgical removal via orbitozygomatic approach were applied.
Results
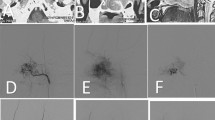
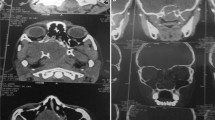
Gross total resection was achieved in 24 cases (83%). Complications were encountered in eight cases. No mortality was observed. In three patients, the diseases recurred. An illustrative case is described.
Conclusion
Surgical treatment is the basic tactics in management of extensive JNA including endovascular embolization and resection of the tumor. We recommend using orbitozygomatic approach or its modifications in JNA. Radiation therapy may be recommended for patients with small residual tumor.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews JC, Fisch U, Valavanis A, Aeppli U, Makek MS (1989) The surgical management of extensive nasopharyngeal angiofibromas with the infratemporal fossa approach. Laryngoscope 99:429–437
Bales C, Kotapka M, Loevner LA, Al-Rawi M, Weinstein G, Hurst R, Weber RS (2002) Craniofacial resection of advanced juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128:1071–1078
Banhiran W, Casiano RR (2005) Endoscopic sinus surgery for benign and malignant nasal and sinus neoplasm. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 13:50–54
Cansiz H, Güvenç MG, Şekercioğlu N (2006) Surgical approaches to juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 24:3–8
Carrau RL, Snyderman CH, Kassam AB, Jungreis CA (2004) Endoscopic and endoscopic-assisted surgery for juvenile angiofibroma. Laryngoscope 111(3):483–487
Cruz AAV, Atique JMC, Melo-Filho FV, Elias J (2004) Orbital involvement in juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: prevalence and treatment. Ophth Plast Reconstr Surg 4:296–300
Dare AO, Gibbons KJ, Proulx GM, Festermaker RA (2003) Resection followed by radiosurgery for advanced juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: report of two cases. Neurosurgery 52(5):1207–1211
Donald PJ, Enepikedes D, Boggan J (2004) Giant juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130:882–886
Douglas R, Wormald PJ (2006) Endoscopic surgery for juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: where are the limits? Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 14:1–5
El-Bahnawy OA, El-Dien AES, Amer T (2004) Endoscopic-assisted midfacial degloving approach for type III juvenile angiofibroma. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 68:21–28
El-Banhawy OA, Ragab A, El-Sharnoby MM (2006) Surgical resection of type III angiofibroma without preoperative embolization. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 70:1715–1723
Ferreira LM, Gomes EF, Azevedo JF, Souza RF, Araujo R, Rios AS (2006) Endoscopic surgery of nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Rev Bras Otorrinolaryngol 72(4):475–480
Lloyd G, Howard D, Phelps P, Cheesman A (1999) Juvenile angiofibroma: the lessons of 20 years of modern imaging. J Laryngol Otol 113:127–134
Mair EA, Battiata A, Castler JD (2003) Endoscopic laser-assisted excision of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibrioma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129:454–459
Marshall AH, Bradley PJ (2006) Management dilemmas in the treatment and follow-up of advanced juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. ORL 28:273–278
McCombe A, Lund VJ, Howard DJ (1990) Recurrence in juvenile angiofibroma. Rhinology 28(2):97–102
Moschos M, Demetra A, Kontogeorgos G (1998) Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma—a rare case of primary orbital development. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 78:506–508
Önerci TM, Yücel ÖT, Öğretmenoğlu O (2003) Endoscopic surgery in treatment of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Int J Pediatr Ororhinolaryngol 67:1219–1225
Pryor SG, Moore EJ, Kasperbauer JL (2005) Endoscopic versus traditional approaches for excision of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Laryngoscope 115:1201–1207
Radkowski D, McGill T, Healy GB, Ohlms L, Jones DT (1996) Angiofibroma: changes in staging and treatment. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 122:122–129
Roger G, Tran Ba Huy P, Froehlich P, Van Den Abbelle T, Klossek JM, Serrano E, Garabedian EN, Herman P (2002) Exclusively endoscopic removal of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Trends and limits. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128:928–936
Schick B, Urbschat S (2004) New aspects of pathogenesis of juvenile angiofibroma. Hosp Med 65:269–273
Yi ZX, Li ZC, Cheng JM, Zhang R, Lin C, Zhou AD, Fan ZM (2007) Huge nasopharyngeal angiofibroma with intracranial extension: change in the dura mater and choice of surgical management. J Laryngol Otol 121:1108–1112
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cherekaev, V.A., Golbin, D.A., Kapitanov, D.N. et al. Advanced craniofacial juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Description of surgical series, case report, and review of literature. Acta Neurochir 153, 499–508 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0922-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0922-0