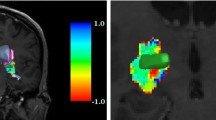
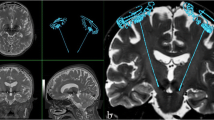
Abstract
Purpose
MRI has been utilized to localize the electrode after deep brain stimulation, but its accuracy has been questioned due to image distortion. Under the hypothesis that MRI is not adequate for evaluation of electrode position after deep brain stimulation, this study is aimed at validating the accuracy of MRI in electrode localization in comparison with CT scan.
Methods
Sixty one patients who had undergone STN DBS were enrolled for the analysis. Using mutual information technique, CT and MRI taken at 6 months after the operation were fused. The x and y coordinates of the centers of electrodes shown of CT and MRI were compared in the fused images to calculate average difference at five different levels. The difference of the tips of the electrodes, designated as the z coordinate, was also calculated.
Results
The average of the distance between the centers of the electrodes in the five levels estimated in the fused image of brain CT and MRI taken at least 6 months after STN DBS was 1.33 mm (0.1–5.8 mm). The average discrepancy of x coordinates for all five levels between MRI and CT was 0.56 ± 0.54 mm (0–5.7 mm), the discrepancy of y coordinates was 1.06 ± 0.59 mm (0–3.5 mm), and for the z coordinate, it was 0.98 ± 0.52 mm (0–3.1 mm) (all p values < 0.001). Notably, the average discrepancy of x coordinates at 3.5 mm below AC–PC level, i.e., at the STN level between MRI and CT, was 0.59 ± 0.42 mm (0–2.4 mm); the discrepancy of y coordinates was 0.81 ± 0.47 mm (0–2.9 mm) (p values < 0.001).
Conclusions
The results suggest that there was significant discrepancy between the centers of electrodes estimated by CT and MRI after STN DBS surgery.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bittar RG, Burn SC, Bain PG, Owen SL, Joint C, Shlugman D, Aziz TZ (2005) Deep brain stimulation for movement disorders and pain. J Clin Neurosci 12:457–463
Breit S, LeBas JF, Koudsie A, Schulz J, Benazzouz A, Pollak P, Benabid AL (2006) Pretargeting for the implantation of stimulation electrodes into the subthalamic nucleus: a comparative study of magnetic resonance imaging and ventriculography. Neurosurgery 58:ONS83–ONS95
Brooks ML, O’Connor MJ, Sperling MR, Mayer DP (1992) Magnetic resonance imaging in localization of EEG depth electrodes for seizure monitoring. Epilepsia 33:888–891
Counelis GJ, Simuni T, Forman MS, Jaggi JL, Trojanowski JQ, Baltuch GH (2003) Bilateral subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for advanced PD: correlation of intraoperative MER and postoperative MRI with neuropathological findings. Mov Disord 18:1062–1065
Coyne T, Silburn P, Cook R, Silberstein P, Mellick G, Sinclair F, Fracchia G, Wasson D, Stanwell P (2006) Rapid subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation lead placement utilising CT/MRI fusion, microelectrode recording and test stimulation. Acta Neurochir Suppl 99:49–50
Dormont D, Cornu P, Pidoux B, Bonnet AM, Biondi A, Oppenheim C, Hasboun D, Damier P, Cuchet E, Philippon J, Agid Y, Marsault C (1997) Chronic thalamic stimulation with three-dimensional MR stereotactic guidance. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:1093–1107
Hamel W, Fietzek U, Morsnowski A, Schrader B, Herzog J, Weinert D, Pfister G, Muller D, Volkmann J, Deuschl G, Mehdorn HM (2003) Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease: evaluation of active electrode contacts. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:1036–1046
Holtzheimer PE 3rd, Roberts DW, Darcey TM (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomography for target localization in functional stereotactic neurosurgery. Neurosurgery 45:290–297, discussion 297–298
Kondziolka D, Dempsey PK, Lunsford LD, Kestle JR, Dolan EJ, Kanal E, Tasker RR (1992) A comparison between magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography for stereotactic coordinate determination. Neurosurgery 30:402–406, discussion 406–407
Lee JY, Han JH, Kim HJ, Jeon BS, Kim DG, Paek SH (2008) STN DBS of advanced Parkinson’s disease experienced in a specialized monitoring unit with a prospective protocol. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 44:26–35
Lee JY, Jeon BS, Paek SH, Lim YH, Kim MR, Kim C (2010) Reprogramming guided by the fused images of MRI and CT in subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson disease. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 112:47–53
Limousin P, Krack P, Pollak P, Benazzouz A, Ardouin C, Hoffmann D, Benabid AL (1998) Electrical stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in advanced Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 339:1105–1111
Limousin P, Pollak P, Benazzouz A, Hoffmann D, Le Bas JF, Broussolle E, Perret JE, Benabid AL (1995) Effect of parkinsonian signs and symptoms of bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation. Lancet 345:91–95
Maes F, Collignon A, Vandermeulen D, Marchal G, Suetens P (1997) Multimodality image registration by maximization of mutual information. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 16:187–198
Martinez-Santiesteban FM, Swanson SD, Noll DC, Anderson DJ (2007) Magnetic field perturbation of neural recording and stimulating microelectrodes. Phys Med Biol 52:2073–2088
McClelland S 3rd, Ford B, Senatus PB, Winfield LM, Du YE, Pullman SL, Yu Q, Frucht SJ, McKhann GM 2nd, Goodman RR (2005) Subthalamic stimulation for Parkinson disease: determination of electrode location necessary for clinical efficacy. Neurosurg Focus 19:E12
McClelland S 3rd, Senatus PB, Ford B, McKhann GM 2nd, Goodman RR (2007) Staged bilateral thalamic electrode implantation utilizing frameless stereotactic guidance. J Clin Neurosci 14:791–793
Paek SH, Han JH, Lee JY, Kim C, Jeon BS, Kim DG (2008) Electrode position determined by fused images of preoperative and postoperative magnetic resonance imaging and surgical outcome after subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation. Neurosurgery 63:925–936, discussion 936–927
Pinto S, Le Bas JF, Castana L, Krack P, Pollak P, Benabid AL (2007) Comparison of two techniques to postoperatively localize the electrode contacts used for subthalamic nucleus stimulation. Neurosurgery 60:285–292, discussion 292–284
Pollo C, Villemure JG, Vingerhoets F, Ghika J, Maeder P, Meuli R (2004) Magnetic resonance artifact induced by the electrode Activa 3389: an in vitro and in vivo study. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 146:161–164
Pollo C, Vingerhoets F, Pralong E, Ghika J, Maeder P, Meuli R, Thiran JP, Villemure JG (2007) Localization of electrodes in the subthalamic nucleus on magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg 106:36–44
Rampini PM, Locatelli M, Alimehmeti R, Tamma F, Caputo E, Priori A, Pesenti A, Rohr M, Egidi M (2003) Multiple sequential image-fusion and direct MRI localisation of the subthalamic nucleus for deep brain stimulation. J Neurosurg Sci 47:33–39
Rezai AR, Lozano AM, Crawley AP, Joy ML, Davis KD, Kwan CL, Dostrovsky JO, Tasker RR, Mikulis DJ (1999) Thalamic stimulation and functional magnetic resonance imaging: localization of cortical and subcortical activation with implanted electrodes. Technical note. J Neurosurg 90:583–590
Rezai AR, Phillips M, Baker KB, Sharan AD, Nyenhuis J, Tkach J, Henderson J, Shellock FG (2004) Neurostimulation system used for deep brain stimulation (DBS): MR safety issues and implications of failing to follow safety recommendations. Invest Radiol 39:300–303
Saint-Cyr JA, Hoque T, Pereira LC, Dostrovsky JO, Hutchison WD, Mikulis DJ, Abosch A, Sime E, Lang AE, Lozano AM (2002) Localization of clinically effective stimulating electrodes in the human subthalamic nucleus on magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg 97:1152–1166
Simon SL, Douglas P, Baltuch GH, Jaggi JL (2005) Error analysis of MRI and leksell stereotactic frame target localization in deep brain stimulation surgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 83:1–5
Spiegel J, Fuss G, Backens M, Reith W, Magnus T, Becker G, Moringlane JR, Dillmann U (2003) Transient dystonia following magnetic resonance imaging in a patient with deep brain stimulation electrodes for the treatment of Parkinson disease. Case report. J Neurosurg 99:772–774
Starr PA, Vitek JL, Bakay RA (1998) Ablative surgery and deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. Neurosurgery 43:989–1013, discussion 1013–1015
Sumanaweera TS, Adler JR Jr, Napel S, Glover GH (1994) Characterization of spatial distortion in magnetic resonance imaging and its implications for stereotactic surgery. Neurosurgery 35:696–703, discussion 703–694
Tagliati M, Jankovic J, Pagan F, Susatia F, Isaias IU, Okun MS, Grp NPFDW (2009) Safety of MRI in patients with implanted deep brain stimulation devices. Neuroimage 47:T53–T57
Tisch S, Zrinzo L, Limousin P, Bhatia KP, Quinn N, Ashkan K, Hariz M (2007) Effect of electrode contact location on clinical efficacy of pallidal deep brain stimulation in primary generalised dystonia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:1314–1319
Tronnier VM, Staubert A, Hahnel S, Sarem-Aslani A (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging with implanted neurostimulators: an in vitro and in vivo study. Neurosurgery 44:118–125
Uitti RJ, Tsuboi Y, Pooley RA, Putzke JD, Turk MF, Wszolek ZK, Witte RJ, Wharen RE Jr (2002) Magnetic resonance imaging and deep brain stimulation. Neurosurgery 51:1423–1428, discussion 1428–1431
Vergani F, Landi A, Antonini A, Parolin M, Cilia R, Grimaldi M, Ferrarese C, Gaini SM, Sganzerla EP (2007) Anatomical identification of active contacts in subthalamic deep brain stimulation. Surg Neurol 67:140–146, discussion 146–147
Voges J, Volkmann J, Allert N, Lehrke R, Koulousakis A, Freund HJ, Sturm V (2002) Bilateral high-frequency stimulation in the subthalamic nucleus for the treatment of Parkinson disease: correlation of therapeutic effect with anatomical electrode position. J Neurosurg 96:269–279
Winkler D, Tittgemeyer M, Schwarz J, Preul C, Strecker K, Meixensberger J (2005) The first evaluation of brain shift during functional neurosurgery by deformation field analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:1161–1163
Yelnik J, Damier P, Demeret S, Gervais D, Bardinet E, Bejjani BP, Francois C, Houeto JL, Arnule I, Dormont D, Galanaud D, Pidoux B, Cornu P, Agid Y (2003) Localization of stimulating electrodes in patients with Parkinson disease by using a three-dimensional atlas-magnetic resonance imaging coregistration method. J Neurosurg 99:89–99
Zhang J, Wilson CL, Levesque MF, Behnke EJ, Lufkin RB (1993) Temperature changes in nickel-chromium intracranial depth electrodes during MR scanning. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 14:497–500
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Healthcare technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare & Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (A092052).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.Y., Kim, J.W., Lee, JY. et al. Is MRI a reliable tool to locate the electrode after deep brain stimulation surgery? Comparison study of CT and MRI for the localization of electrodes after DBS. Acta Neurochir 152, 2029–2036 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0779-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0779-2