Abstract
Objective
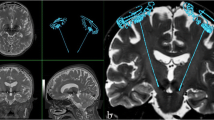
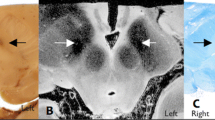
We compared the electrode positions of subthalamic nucleus (STN) deep brain stimulation (DBS) estimated at the immediate postoperative period with those estimated 6 months after surgery.
Methods
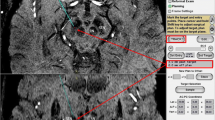
Brain CT scans were taken immediately and 6 months after bilateral STN DBS in 53 patients with Parkinson’s disease. The two images were fused using the mutual information technique. The discrepancies of electrode positions in three coordinates were measured in the fused images, and the relationship with the pneumocephalus was evaluated.
Results
The average discrepancy of x- and y-coordinates of electrode positions at the level of STN (3.5 mm below the anterior commissure–posterior commissure line) were 0.6 ± 0.5 mm (range, 0~2.1 mm) and 1.0 ± 0.8 mm (range, 0~5.2 mm), respectively. The average discrepancy of z-coordinates of the electrode tips of the fused images was 1.0 ± 0.8 mm (range, 0.1~4.0 mm). The volume of pneumocephalus (range, 0~76 ml) was correlated with the y-coordinate discrepancies (p < 0.005).
Conclusion
The electrode positions in the immediate postoperative CT might have significant discrepancies with those in the CT taken at a stable period after STN DBS especially when there is a large amount of pneumocephalus.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander E 3rd, Kooy HM, van Herk M, Schwartz M, Barnes PD, Tarbell N, Mulkern RV, Holupka EJ, Loeffler JS (1995) Magnetic resonance image-directed stereotactic neurosurgery: use of image fusion with computerized tomography to enhance spatial accuracy. J Neurosurg 83:271–276
Benabid AL, Chabardes S, Mitrofanis J, Pollak P (2009) Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol 8:67–81
Bittar RG, Burn SC, Bain PG, Owen SL, Joint C, Shlugman D, Aziz TZ (2005) Deep brain stimulation for movement disorders and pain. J Clin Neurosci 12:457–463
Breit S, LeBas JF, Koudsie A, Schulz J, Benazzouz A, Pollak P, Benabid AL (2006) Pretargeting for the implantation of stimulation electrodes into the subthalamic nucleus: a comparative study of magnetic resonance imaging and ventriculography. Neurosurgery 58:ONS83-95
Counelis GJ, Simuni T, Forman MS, Jaggi JL, Trojanowski JQ, Baltuch GH (2003) Bilateral subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for advanced PD: correlation of intraoperative MER and postoperative MRI with neuropathological findings. Mov Disord 18:1062–1065
Coyne T, Silburn P, Cook R, Silberstein P, Mellick G, Sinclair F, Fracchia G, Wasson D, Stanwell P (2006) Rapid subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation lead placement utilising CT/MRI fusion, microelectrode recording and test stimulation. Acta Neurochir Suppl 99:49–50
Guehl D, Edwards R, Cuny E, Burbaud P, Rougier A, Modolo J, Beuter A (2007) Statistical determination of the optimal subthalamic nucleus stimulation site in patients with Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg 106:101–110
Hamel W, Fietzek U, Morsnowski A, Schrader B, Herzog J, Weinert D, Pfister G, Muller D, Volkmann J, Deuschl G, Mehdorn HM (2003) Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson's disease: evaluation of active electrode contacts. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:1036–1046
Holtzheimer PE 3rd, Roberts DW, Darcey TM (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomography for target localization in functional stereotactic neurosurgery. Neurosurgery 45:290–297, discussion 297–298
Ken S, Di Gennaro G, Giulietti G, Sebastiano F, De Carli D, Garreffa G, Colonnese C, Passariello R, Lotterie JA, Maraviglia B (2007) Quantitative evaluation for brain CT/MRI coregistration based on maximization of mutual information in patients with focal epilepsy investigated with subdural electrodes. Magn Reson Imaging 25:883–888
Kim HJ, Paek SH, Kim JY, Lee JY, Lim YH, Kim DG, Jeon BS (2009) Two-year follow-up on the effect of unilateral subthalamic deep brain stimulation in highly asymmetric Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 24:329–335
Kim HJ, Paek SH, Kim JY, Lee JY, Lim YH, Kim MR, Kim DG, Jeon BS (2008) Chronic subthalamic deep brain stimulation improves pain in Parkinson disease. J Neurol 255:1889–1894
Limousin P, Krack P, Pollak P, Benazzouz A, Ardouin C, Hoffmann D, Benabid AL (1998) Electrical stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in advanced Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med 339:1105–1111
Limousin P, Pollak P, Benazzouz A, Hoffmann D, Le Bas JF, Broussolle E, Perret JE, Benabid AL (1995) Effect of parkinsonian signs and symptoms of bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation. Lancet 345:91–95
Maes F, Collignon A, Vandermeulen D, Marchal G, Suetens P (1997) Multimodality image registration by maximization of mutual information. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 16:187–198
McClelland S 3rd, Ford B, Senatus PB, Winfield LM, Du YE, Pullman SL, Yu Q, Frucht SJ, McKhann GM 2nd, Goodman RR (2005) Subthalamic stimulation for Parkinson disease: determination of electrode location necessary for clinical efficacy. Neurosurg Focus 19:E12
McClelland S 3rd, Senatus PB, Ford B, McKhann GM 2nd, Goodman RR (2007) Staged bilateral thalamic electrode implantation utilizing frameless stereotactic guidance. J Clin Neurosci 14:791–793
McClelland S 3rd, Vonsattel JP, Garcia RE, Amaya MD, Winfield LM, Pullman SL, Yu Q, Fahn S, Ford B, Goodman RR (2007) Relationship of clinical efficacy to postmortem-determined anatomic subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson syndrome. Clin Neuropathol 26:267–275
Miyagi Y, Shima F, Sasaki T (2007) Brain shift: an error factor during implantation of deep brain stimulation electrodes. J Neurosurg 107:989–997
Obuchi T, Katayama Y, Kobayashi K, Oshima H, Fukaya C, Yamamoto T (2008) Direction and predictive factors for the shift of brain structure during deep brain stimulation electrode implantation for advanced Parkinson's disease. Neuromodulation 11:302–310
Ott K, Tarlov E, Crowell R, Papadakis N (1976) Retained intracranial metallic foreign bodies. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 44:80–83
Peters TM, Clark J, Pike B, Drangova M, Olivier A (1987) Stereotactic surgical planning with magnetic resonance imaging, digital subtraction angiography and computed tomography. Appl Neurophysiol 50:33–38
Pinto S, Le Bas JF, Castana L, Krack P, Pollak P, Benabid AL (2007) Comparison of two techniques to postoperatively localize the electrode contacts used for subthalamic nucleus stimulation. Neurosurgery 60:285–292, discussion 292–284
Pollo C, Vingerhoets F, Pralong E, Ghika J, Maeder P, Meuli R, Thiran JP, Villemure JG (2007) Localization of electrodes in the subthalamic nucleus on magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg 106:36–44
Rampini PM, Locatelli M, Alimehmeti R, Tamma F, Caputo E, Priori A, Pesenti A, Rohr M, Egidi M (2003) Multiple sequential image-fusion and direct MRI localisation of the subthalamic nucleus for deep brain stimulation. J Neurosurg Sci 47:33–39
Saint-Cyr JA, Hoque T, Pereira LC, Dostrovsky JO, Hutchison WD, Mikulis DJ, Abosch A, Sime E, Lang AE, Lozano AM (2002) Localization of clinically effective stimulating electrodes in the human subthalamic nucleus on magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg 97:1152–1166
Sorensen N, Krauss J (1991) Movement of hemostatic clips from the ventricles through the aqueduct to the lumbar spinal canal. Case report J Neurosurg 74:143–146
Starr PA, Vitek JL, Bakay RA (1998) Ablative surgery and deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease. Neurosurgery 43:989–1013, discussion 1013–1015
Tisch S, Zrinzo L, Limousin P, Bhatia KP, Quinn N, Ashkan K, Hariz M (2007) Effect of electrode contact location on clinical efficacy of pallidal deep brain stimulation in primary generalised dystonia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:1314–1319
van den Munckhof P, Contarino MF, Bour LJ, Speelman JD, de Bie RM, Schuurman PR (2010) Postoperative curving and upward displacement of deep brain stimulation electrodes caused by brain shift. Neurosurgery 67:49–53, discussion 53–44
Vergani F, Landi A, Antonini A, Parolin M, Cilia R, Grimaldi M, Ferrarese C, Gaini SM, Sganzerla EP (2007) Anatomical identification of active contacts in subthalamic deep brain stimulation. Surg Neurol 67:140–146, discussion 146–147
Voges J, Volkmann J, Allert N, Lehrke R, Koulousakis A, Freund HJ, Sturm V (2002) Bilateral high-frequency stimulation in the subthalamic nucleus for the treatment of Parkinson disease: correlation of therapeutic effect with anatomical electrode position. J Neurosurg 96:269–279
Winkler D, Tittgemeyer M, Schwarz J, Preul C, Strecker K, Meixensberger J (2005) The first evaluation of brain shift during functional neurosurgery by deformation field analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:1161–1163
Yelnik J, Damier P, Demeret S, Gervais D, Bardinet E, Bejjani BP, Francois C, Houeto JL, Arnule I, Dormont D, Galanaud D, Pidoux B, Cornu P, Agid Y (2003) Localization of stimulating electrodes in patients with Parkinson disease by using a three-dimensional atlas-magnetic resonance imaging coregistration method. J Neurosurg 99:89–99
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by a grant from Korea Healthcare Technology R&D project, Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (A08-0663-A21724-08N1-000020B and A092052).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y.H., Kim, H.J., Kim, C. et al. Comparison of electrode location between immediate postoperative day and 6 months after bilateral subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation. Acta Neurochir 152, 2037–2045 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0771-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0771-x