Abstract
Background
MRI in patients bearing deep brain stimulation (DBS) electrodes may induce cerebral lesions due to electrode heating. To avoid neurological deficits related to MRI, post-operative MRI protocol was installed in our institution. However, our protocol comprised a higher specific absorption rate (SAR) and different positioning of lead excess than the later released electrode manufacturer's guidelines. The objective was to evaluate the safety using this protocol.
Methods
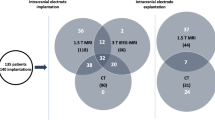
Between January 2000 and May 2008, post-operative MRI was performed in all patients. In selected patients, additional MRI scans were performed with the implanted generator. MRI was acquired at 1.5 T with a RF transmit/receive head coil comprising a T2-weighted fast spin echo (FSE) and a T1-weighted inversion recovery FSE sequence. Local cranial SAR values measured up to 0.9 W/kg compared to the manufacturer's recommendation of 0.1 W/kg. Initial scans (1–7 days after surgery) were performed with externalized leads, long-term scans (>30 days after surgery) with a connected generator. New neurological deficits were assessed before and after MRI. Additional MRIs were compared to the initial postoperative MRI with emphasis on new lesions.
Results
In 211 patients, 243 MRIs were performed, including 212 initial post-operative MRI. In 12% (n = 24), 31 additional MRI examinations for various clinical reasons were achieved. No patients demonstrated new neurological deficits during or after MRI acquisitions.
Conclusions
No complications were observed using this MRI protocol in DBS patients. Our results suggest that, within this setting, higher SAR values may be feasible for DBS patients than in the manufacturer's guidelines.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach S, Moshage W, Diem B, Bieberle T, Schibgilla V, Bachmann K (1997) Effects of magnetic resonance imaging on cardiac pacemakers and electrodes. Am Heart J 134:467–473
Arantes PR, Cardoso EF, Barreiros MA, Teixeira MJ, Goncalves MR, Barbosa ER, Sukwinder SS, Leite CC, Amaro E Jr (2006) Performing functional magnetic resonance imaging in patients with Parkinson's disease treated with deep brain stimulation. Mov Disord 21:1154–1162
Baker KB, Tkach J, Hall JD, Nyenhuis JA, Shellock FG, Rezai AR (2005) Reduction of magnetic resonance imaging-related heating in deep brain stimulation leads using a lead management device. Neurosurgery 57:392–397, discussion 392-397
Baker KB, Tkach JA, Phillips MD, Rezai AR (2006) Variability in RF-induced heating of a deep brain stimulation implant across MR systems. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:1236–1242
Bejjani BP, Dormont D, Pidoux B, Yelnik J, Damier P, Arnulf I, Bonnet AM, Marsault C, Agid Y, Philippon J, Cornu P (2000) Bilateral subthalamic stimulation for Parkinson's disease by using three-dimensional stereotactic magnetic resonance imaging and electrophysiological guidance. J Neurosurg 92:615–625
Bhidayasiri R, Bronstein JM, Sinha S, Krahl SE, Ahn S, Behnke EJ, Cohen MS, Frysinger R, Shellock FG (2005) Bilateral neurostimulation systems used for deep brain stimulation: in vitro study of MRI-related heating at 1.5 T and implications for clinical imaging of the brain. Magn Reson Imaging 23:549–555
Busse R (2004) Kreislauf. In: Schmidt RF LF, Thews G (eds) Physiologie des Menschen. Springer Medizin Verlag, Heidelberg, p 604
Carmichael DW, Pinto S, Limousin-Dowsey P, Thobois S, Allen PJ, Lemieux L, Yousry T, Thornton JS (2007) Functional MRI with active, fully implanted, deep brain stimulation systems: safety and experimental confounds. Neuroimage 37:508–517
Coubes P, Vasques X, Tancu C, Cif L, Biolsi B, Maldonado I, Bonafe A, Le Bars E (2008) Cerebral magnetic resonance imaging feasibility in patients with implanted neurostimulation system for deep brain stimulation. The Open Magnetic Resonance Journal 1−8
De Salles AA, Brekhus SD, De Souza EC, Behnke EJ, Farahani K, Anzai Y, Lufkin R (1995) Early postoperative appearance of radiofrequency lesions on magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgery 36:932–936, discussion 936−937
Deuschl G, Schade-Brittinger C, Krack P, Volkmann J, Schafer H, Botzel K, Daniels C, Deutschlander A, Dillmann U, Eisner W, Gruber D, Hamel W, Herzog J, Hilker R, Klebe S, Kloss M, Koy J, Krause M, Kupsch A, Lorenz D, Lorenzl S, Mehdorn HM, Moringlane JR, Oertel W, Pinsker MO, Reichmann H, Reuss A, Schneider GH, Schnitzler A, Steude U, Sturm V, Timmermann L, Tronnier V, Trottenberg T, Wojtecki L, Wolf E, Poewe W, Voges J (2006) A randomized trial of deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med 355:896–908
Finelli DA, Rezai AR, Ruggieri PM, Tkach JA, Nyenhuis JA, Hrdlicka G, Sharan A, Gonzalez-Martinez J, Stypulkowski PH, Shellock FG (2002) MR imaging-related heating of deep brain stimulation electrodes: in vitro study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1795–1802
Fraix V, Chabardes S, Krainik A, Seigneuret E, Grand S, Le Bas JF, Krack P, Benabid AL, Pollak P (2010) Effects of magnetic resonance imaging in patients with implanted deep brain stimulation systems. J Neurosurg (in press)
Georgi JC, Stippich C, Tronnier VM, Heiland S (2004) Active deep brain stimulation during MRI: a feasibility study. Magn Reson Med 51:380–388
Henderson JM, Tkach J, Phillips M, Baker K, Shellock FG, Rezai AR (2005) Permanent neurological deficit related to magnetic resonance imaging in a patient with implanted deep brain stimulation electrodes for Parkinson's disease: case report. Neurosurgery 57:E1063, discussion E1063
Jech R, Urgosik D, Tintera J, Nebuzelsky A, Krasensky J, Liscak R, Roth J, Ruzicka E (2001) Functional magnetic resonance imaging during deep brain stimulation: a pilot study in four patients with Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 16:1126–1132
Kupsch A, Benecke R, Muller J, Trottenberg T, Schneider GH, Poewe W, Eisner W, Wolters A, Muller JU, Deuschl G, Pinsker MO, Skogseid IM, Roeste GK, Vollmer-Haase J, Brentrup A, Krause M, Tronnier V, Schnitzler A, Voges J, Nikkhah G, Vesper J, Naumann M, Volkmann J (2006) Pallidal deep-brain stimulation in primary generalized or segmental dystonia. N Engl J Med 355:1978–1990
Larson PS, Richardson RM, Starr PA, Martin AJ (2008) Magnetic resonance imaging of implanted deep brain stimulators: experience in a large series. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 86:92–100
Limousin P, Martinez-Torres I (2008) Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease. Neurotherapeutics 5:309–319
Mallet L, Polosan M, Jaafari N, Baup N, Welter ML, Fontaine D, du Montcel ST, Yelnik J, Chereau I, Arbus C, Raoul S, Aouizerate B, Damier P, Chabardes S, Czernecki V, Ardouin C, Krebs MO, Bardinet E, Chaynes P, Burbaud P, Cornu P, Derost P, Bougerol T, Bataille B, Mattei V, Dormont D, Devaux B, Verin M, Houeto JL, Pollak P, Benabid AL, Agid Y, Krack P, Millet B, Pelissolo A (2008) Subthalamic nucleus stimulation in severe obsessive-compulsive disorder. N Engl J Med 359:2121–2134
Matsumi N, Matsumoto K, Mishima N, Moriyama E, Furuta T, Nishimoto A, Taguchi K (1994) Thermal damage threshold of brain tissue—histological study of heated normal monkey brains. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 34:209–215
Mayberg HS, Lozano AM, Voon V, McNeely HE, Seminowicz D, Hamani C, Schwalb JM, Kennedy SH (2005) Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron 45:651–660
Medtronic I (2006) MRI guidelines for medtronic deep brain stimulation systems. Medtronic, Minneapolis
Mohsin SA, Sheikh NM, Saeed U (2008) MRI-induced heating of deep brain stimulation leads. Phys Med Biol 53:5745–5756
Rezai AR, Finelli D, Nyenhuis JA, Hrdlicka G, Tkach J, Sharan A, Rugieri P, Stypulkowski PH, Shellock FG (2002) Neurostimulation systems for deep brain stimulation: in vitro evaluation of magnetic resonance imaging-related heating at 1.5 tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging 15:241–250
Rezai AR, Phillips M, Baker KB, Sharan AD, Nyenhuis J, Tkach J, Henderson J, Shellock FG (2004) Neurostimulation system used for deep brain stimulation (DBS): MR safety issues and implications of failing to follow safety recommendations. Invest Radiol 39:300–303
Schlaepfer TE, Cohen MX, Frick C, Kosel M, Brodesser D, Axmacher N, Joe AY, Kreft M, Lenartz D, Sturm V (2008) Deep brain stimulation to reward circuitry alleviates anhedonia in refractory major depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:368–377
Schlaepfer TE, Lieb K (2005) Deep brain stimulation for treatment of refractory depression. Lancet 366:1420–1422
Schuurman PR, Bosch DA, Bossuyt PM, Bonsel GJ, van Someren EJ, de Bie RM, Merkus MP, Speelman JD (2000) A comparison of continuous thalamic stimulation and thalamotomy for suppression of severe tremor. N Engl J Med 342:461–468
Shellock F (2001) Pocket guide to metallic implants and MR procedures: update 2001. Lippincott-Raven Healthcare, New York
Spiegel J, Fuss G, Backens M, Reith W, Magnus T, Becker G, Moringlane JR, Dillmann U (2003) Transient dystonia following magnetic resonance imaging in a patient with deep brain stimulation electrodes for the treatment of Parkinson disease. Case report. J Neurosurg 99:772–774
Starr PA, Christine CW, Theodosopoulos PV, Lindsey N, Byrd D, Mosley A, Marks WJ Jr (2002) Implantation of deep brain stimulators into the subthalamic nucleus: technical approach and magnetic resonance imaging-verified lead locations. J Neurosurg 97:370–387
Tagliati M, Jankovic J, Pagan F, Susatia F, Isaias IU, Okun MS (2009) Safety of MRI in patients with implanted deep brain stimulation devices. Neuroimage T53−T57
Tronnier VM, Staubert A, Hahnel S, Sarem-Aslani A (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging with implanted neurostimulators: an in vitro and in vivo study. Neurosurgery 44:118–125, discussion 125−116
Weaver FM, Follett K, Stern M, Hur K, Harris C, Marks WJ Jr, Rothlind J, Sagher O, Reda D, Moy CS, Pahwa R, Burchiel K, Hogarth P, Lai EC, Duda JE, Holloway K, Samii A, Horn S, Bronstein J, Stoner G, Heemskerk J, Huang GD (2009) Bilateral deep brain stimulation vs best medical therapy for patients with advanced Parkinson disease: a randomized controlled trial. Jama 301:63–73
Yamamoto T, Katayama Y, Fukaya C, Kurihara J, Oshima H, Kasai M (2000) Thalamotomy caused by cardioversion in a patient treated with deep brain stimulation. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 74:73–82
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weise, L.M., Schneider, G.H., Kupsch, A. et al. Postoperative MRI examinations in patients treated by deep brain stimulation using a non-standard protocol. Acta Neurochir 152, 2021–2027 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0738-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0738-y