Abstract
Background
Several investigators have described the efficacy and safety of unilateral deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the subthalamic nucleus (STN) for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Some patients who underwent unilateral STN DBS required additional surgery on the contralateral side because the unilateral treatment was insufficient. The goal of this study was to assess the efficacy and safety of staged bilateral STN DBS compared to the simultaneous bilateral procedure.
Methods
Ten patients with medically intractable PD underwent staged bilateral STN DBS, and 12 patients underwent a simultaneous bilateral procedure. Clinical assessments were performed preoperatively and 6 months after the last surgery using the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS), motor and activity of daily living (ADL) subscores, and Hoehn and Yahr stages.
Findings
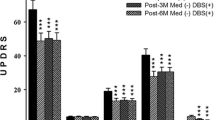
Both the staged and simultaneous groups experienced significant improvement in the UPDRS motor and ADL scores, and the Hoehn and Yahr stages. There were no statistical differences between the two groups in the percent improvement in UPDRS scores. The rate of adverse events in the staged group (20%) was less than that of the simultaneous group (42%), although the difference was not statistically significant.
Conclusions
Both the staged bilateral STN DBS and the simultaneous bilateral procedure are effective and safe treatment options, but the staged bilateral procedure may be regarded as the preferred choice for the treatment of some patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alegret M, Valldeoriola F, Marti M, Pilleri M, Junque C, Rumia J, Tolosa E (2004) Comparative cognitive effects of bilateral subthalamic stimulation and subcutaneous continuous infusion of apomorphine in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 19:1463–1469. doi:10.1002/mds.20237
Bejjani BP, Dormont D, Pidoux B, Yelnik J, Damier P, Arnulf I, Bonnet AM, Marsault C, Agid Y, Philippon J, Cornu P (2000) Bilateral subthalamic stimulation for Parkinson’s disease by using three-dimensional stereotactic magnetic resonance imaging and electrophysiological guidance. J Neurosurg 92:615–625
Derost PP, Ouchchane L, Morand D, Ulla M, Llorca PM, Barget M, Debilly B, Lemaire JJ, Durif F (2007) Is DBS-STN appropriate to treat severe Parkinson disease in an elderly population? Neurology 68:1345–1355. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000260059.77107.c2
Dujardin K, Defebvre L, Krystkowiak P, Blond S, Destee A (2001) Influence of chronic bilateral stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus on cognitive function in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 248:603–611. doi:10.1007/s004150170139
Ford B, Winfield L, Pullman SL, Frucht SJ, Du Y, Greene P, Cheringal JH, Yu Q, Cote LJ, Fahn S, McKhann GM 2nd, Goodman RR (2004) Subthalamic nucleus stimulation in advanced Parkinson’s disease: blinded assessments at one year follow up. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:1255–1259. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2003.027557
Germano IM, Gracies JM, Weisz DJ, Tse W, Koller WC, Olanow CW (2004) Unilateral stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson disease: a double-blind 12-month evaluation study. J Neurosurg 101:36–42
Houeto JL, Damier P, Bejjani PB, Staedler C, Bonnet AM, Arnulf I, Pidoux B, Dormont D, Cornu P, Agid Y (2000) Subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson disease: a multidisciplinary approach. Arch Neurol 57:461–465. doi:10.1001/archneur.57.4.461
Kumar R, Lozano AM, Kim YJ, Hutchison WD, Sime E, Halket E, Lang AE (1998) Double-blind evaluation of subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 51:850–855
Limousin P, Krack P, Pollak P, Benazzouz A, Ardouin C, Hoffmann D, Benabid AL (1998) Electrical stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in advanced Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 339:1105–1111. doi:10.1056/NEJM199810153391603
Linazasoro G, Van Blercom N, Lasa A (2003) Unilateral subthalamic deep brain stimulation in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 18:713–716. doi:10.1002/mds.10407
Molinuevo JL, Valldeoriola F, Tolosa E, Rumia J, Valls-Sole J, Roldan H, Ferrer E (2000) Levodopa withdrawal after bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation in advanced Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 57:983–988. doi:10.1001/archneur.57.7.983
Pahwa R, Wilkinson S, Smith D, Lyons K, Miyawaki E, Koller WC (1997) High-frequency stimulation of the globus pallidus for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 49:249–253. doi:10.1159/000112996
Romito LM, Scerrati M, Contarino MF, Iacoangeli M, Bentivoglio AR, Albanese A (2003) Bilateral high frequency subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: long-term neurological follow-up. J Neurosurg Sci 47:119–128
Saint-Cyr JA, Trepanier LL (2000) Neuropsychologic assessment of patients for movement disorder surgery. Mov Disord 15:771–783. doi:10.1002/1531-8257(200009)15:5<771::AID-MDS1003>3.0.CO;2-Y
Saint-Cyr JA, Trepanier LL, Kumar R, Lozano AM, Lang AE (2000) Neuropsychological consequences of chronic bilateral stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 123(Pt 10):2091–2108. doi:10.1093/brain/123.10.2091
Samii A, Kelly VE, Slimp JC, Shumway-Cook A, Goodkin R (2007) Staged unilateral versus bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulator implantation in Parkinson disease. Mov Disord 22:1476–1481. doi:10.1002/mds.21554
Simuni T, Jaggi JL, Mulholland H, Hurtig HI, Colcher A, Siderowf AD, Ravina B, Skolnick BE, Goldstein R, Stern MB, Baltuch GH (2002) Bilateral stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in patients with Parkinson disease: a study of efficacy and safety. J Neurosurg 96:666–672
Slowinski JL, Putzke JD, Uitti RJ, Lucas JA, Turk MF, Kall BA, Wharen RE (2007) Unilateral deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg 106:626–632. doi:10.3171/jns.2007.106.4.626
Tabbal SD, Revilla FJ, Mink JW, Schneider-Gibson P, Wernle AR, de Erausquin GA, Perlmutter JS, Rich KM, Dowling JL (2007) Safety and efficacy of subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation performed with limited intraoperative mapping for treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosurgery 61:119–127. doi:10.1227/01.neu.0000289725.97211.51
Thobois S, Mertens P, Guenot M, Hermier M, Mollion H, Bouvard M, Chazot G, Broussolle E, Sindou M (2002) Subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: clinical evaluation of 18 patients. J Neurol 249:529–534. doi:10.1007/s004150200059
Tir M, Devos D, Blond S, Touzet G, Reyns N, Duhamel A, Cottencin O, Dujardin K, Cassim F, Destee A, Defebvre L, Krystkowiak P (2007) Exhaustive, one-year follow-up of subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation in a large, single-center cohort of parkinsonian patients. Neurosurgery 61:297–304. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000285347.50028.B9
Trepanier LL, Kumar R, Lozano AM, Lang AE, Saint-Cyr JA (2000) Neuropsychological outcome of GPi pallidotomy and GPi or STN deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Cogn 42:324–347. doi:10.1006/brcg.1999.1108
Umemura A, Jaggi JL, Hurtig HI, Siderowf AD, Colcher A, Stern MB, Baltuch GH (2003) Deep brain stimulation for movement disorders: morbidity and mortality in 109 patients. J Neurosurg 98:779–784
Vingerhoets FJ, Villemure JG, Temperli P, Pollo C, Pralong E, Ghika J (2002) Subthalamic DBS replaces levodopa in Parkinson’s disease: two-year follow-up. Neurology 58:396–401
Volkmann J, Allert N, Voges J, Weiss PH, Freund HJ, Sturm V (2001) Safety and efficacy of pallidal or subthalamic nucleus stimulation in advanced PD. Neurology 56:548–551
Welter ML, Houeto JL, Tezenas du Montcel S, Mesnage V, Bonnet AM, Pillon B, Arnulf I, Pidoux B, Dormont D, Cornu P, Agid Y (2002) Clinical predictive factors of subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 125:575–583. doi:10.1093/brain/awf050
Wider C, Pollo C, Bloch J, Burkhard PR, Vingerhoets FJ (2008) Long-term outcome of 50 consecutive Parkinson’s disease patients treated with subthalamic deep brain stimulation. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 14:114–119. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2007.06.012
Woods SP, Fields JA, Troster AI (2002) Neuropsychological sequelae of subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: a critical review. Neuropsychol Rev 12:111–126. doi:10.1023/A:1016806711705
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Arihito Tsurumi for performing the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
No financial support was received for this research.
The findings presented herein have not been previously published.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanei, T., Kajita, Y., Kaneoke, Y. et al. Staged bilateral deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurochir 151, 589–594 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0293-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0293-6