Summary
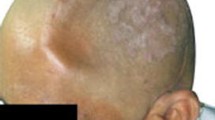
The paper presents clinical evaluation of the polypropylene-polyester knit used as a cranioplasty material.
Material. Between year 1980 and 2002 275 cranioplastic procedures using the polypropylene-polyester plates Codubix were carried out in the Department of Neurosurgery of the Medical University of Łódź. There were 146 patients who primarily sustained head injuries and 129 non-traumatic patients with craniectomies carried out for various other reasons. In the majority of cases, i.e. in 158 patients, cranioplasty was performed later than 6 months after the primary surgery. The largest implant measured 430 cm2.
Results. Excellent and good outcome was achieved in 92% of the patients whereas the rate of local infection was 8%.
Conclusions. Codubix knitted polypropylene-polyester implant proved to be useful and a safe cranioplastic material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
KH Abbott (1953) ArticleTitleUse of frozen cranial bone flaps for autogenous and homologous grafts. J Neurosurg 10 380–388 Occurrence Handle13070062
ME Cabenela MB Coventry CS MacCarty et al. (1970) ArticleTitleThe fate of patients with methyl methacrylate cranioplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 52B 340–353
Delashaw JB Jr, Persing JA (1996) Repair of cranial defects. In: Youmans JR (ed). Neurological surgery. 4th edn, vol. 3. Philadelphia, W. B. Saunders
SR Durham JG McComb ML Levy (2003) ArticleTitleCorrection of large >25 cm(2)) cranial defects with “reinforced” hydroxyapatite cement: technique and complications. Neurosurgery 52 IssueID4 842–845 Occurrence Handle10.1227/01.NEU.0000054220.01290.8E Occurrence Handle12657179
BL Eppley L Hollier S Stal (2003) ArticleTitleHydroxyapatite cranioplasty: 2. Clinical experience with a new quick-setting material. J Craniofac Surg 14 IssueID2 209–214 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00001665-200303000-00014 Occurrence Handle12621292
T Flannery RS McConnell (2001) ArticleTitleCranioplasty: why throw the bone flap out? Br J Neurosurg 15 IssueID6 518–520 Occurrence Handle10.1080/02688690120097732 Occurrence Handle11814006
WM Hammon LG Kempe (1971) ArticleTitleMethyl methacrylate cranioplasty: Thirteen years’experience with 417 patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 25 69–77 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01808863
Z Kotwica M Zawirski S Andrzejak W Papierz (1991) ArticleTitleChmielowski cranioplasty of an extremely large cranial defect caused by transitional meningioma with a knitted polypropylene-polyester Prothesis “codubix”. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 112 147–150 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01405144
GN Kreider (1920) ArticleTitleRepair of cranial defect by new method. JAMA 64 1024
Laidlaw J (2000) Cranioplasty. In: Kaye AH, Black P (eds) Operative neurosurgery vol. 1. Harcourt Publishers Limited
Liu JK, Gottfried ON, Cole CD, Dougherty WR, Couldwell WT (2004) Porous polyethylene implant for cranioplasty and skull base reconstruction. Neurosurg Focus 15: 16(3)
BL Meel (2004) ArticleTitleFatal systemic allergic reaction following acrylic cranioplasty: a case report. J Clin Forensic Med 11 IssueID4 205–207 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.jcfm.2004.04.004 Occurrence Handle15363754
DM Poetker KB Pytynia GA Meyer PA Wackym (2004) ArticleTitleComplication rate of transtemporal hydroxyapatite cement cranioplasties: a case series review of 76 cranioplasties. Otol Neurotol 25 IssueID4 604–609 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00129492-200407000-00031 Occurrence Handle15241242
A Sanan JS Haines (1997) ArticleTitleRepairing holes in the head: a history of cranioplasty. Neurosurgery 40 IssueID3 588–603 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199703000-00033 Occurrence Handle9055300
W Saringer I Nobauer-Huhmann E Knosp (2002) ArticleTitleCranioplasty with individual carbon fibre reinforced polymere (CFRP) medical grade implants based on CAD/CAM technique. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 144 IssueID11 1193–1203 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00701-002-0995-5
G Wurm B Tomancok K Holl J Trenkler (2004) ArticleTitleProspective study on cranioplasty with individual carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) implants produced by means of stereolithography. Surg Neurol 62 IssueID6 510–521 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.surneu.2004.01.025 Occurrence Handle15576119
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andrzejak, S., Fortuniak, J., Wróbel-Wiśniewska, G. et al. Clinical evaluation of the polypropylene-polyester knit used as a cranioplasty material. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147, 973–976 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0581-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0581-8