Summary
Background. After subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) diagnostic evaluation of the underlying cause is warranted since the rebleeding rate is high. The objective of the study was to answer the question, whether 3-Dimensional computed tomographic angiography (3D-CTA) is able to accurately determine the surgical indications in patients with intracranial aneurysms.
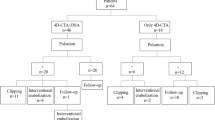
Methods. After performing 3D-CTA the size of the aneurysm, direction of the aneurysmal dome, neck position and variants of the circle of Willis were analysed. Surgery was performed solely on CTA data in those cases, where the aneurysm was clearly visible. If the findings were negative or inconclusive, intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography (DSA) was also done.
Findings. Between January 2001 and December 2002 100 patients (68 F, 32 M) were examined and 123 aneurysms (86 ruptured and 37 unruptured) were diagnosed. All patients received CTA preoperatively and in 27 patients selective DSA was additionally performed. Postoperatively in 34 patients the operative result was checked by DSA.
A good correlation between CTA and the intra-operative findings was present in 92 of 100 patients. One aneurysm was not seen on CTA, but was on DSA. In four cases we could confirm DSA findings in CTA after re-evaluation of the data. In three cases neither CTA nor DSA clearly showed an aneurysm, but it was confirmed during surgery.
A good correlation between CTA and DSA was found in 60 of 61 patients (98%). The correlation between CTA and intra-operative findings was good as expected in 92 patients, in 5 patients an aneurysm was detected on re-evaluation. Only one aneurysm could not be demonstrated by CTA but in DSA.
Conclusion. CTA is less invasive, less time consuming, cheaper and easier to demonstrate the essential information regarding the aneurysm than DSA. We therefore recommend that following a careful analysis most aneurysms – 92% – can be operated solely on CTA data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberico RA, Patel M, Casey S, Jacobs B, Maguire W, Decker R (1995) Evaluation of the circle of Willis with three-dimensional CT angiography in patients with suspected intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16: 1571–1578; discussion 1579–1580
Anderson GB, Findlay JM, Steinke DE, Ashforth R (1997) Experience with computed tomographic angiography for the detection of intracranial aneurysms in the setting of acute subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 41: 522–527; discussion 527–528
Anderson GB, Steinke DE, Petruk KC, Ashforth R, Findlay JM (1999) Computed tomographic angiography versus digital subtraction angiography for the diagnosis and early treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 45: 1315–1320; discussion 1320–1312
Boet R, Poon WS, Lam JM, Yu SC (2003) The surgical treatment of intracranial aneurysms based on computer tomographic angiography alone – streamlining the acute management of symptomatic aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145: 101–105; discussion 105
Chappell ET, Moure FC, Good MC (2003) Comparison of computed tomographic angiography with digital subtraction angiography in the diagnosis of cerebral aneurysms: a meta-analysis. Neurosurgery 52: 624–631; discussion 630–621
NW Dorsch N Young RJ Kingston et al. (1995) ArticleTitleEarly experience with spiral CT in the diagnosis of intracranial aneurysm. Neurosurgery 36 230–238 Occurrence Handle7708163
Ft Earnest G Forbes BA Sandok DG Piepgras RJ Faust DM Ilstrup LJ Arndt (1984) ArticleTitleComplications of cerebral angiography: prospective assessment of risk. AJR Am J Roentgenol 142 247–253 Occurrence Handle6198889
CM Fisher JP Kistler JM Davis (1980) ArticleTitleRelation of cerebral vasospasm to subarachnoid hemorrhage visualized by computerized tomographic scanning. Neurosurgery 6 1–9 Occurrence Handle7354892
A Gholkar JE Gillespie CW Hart D Mott I Isherwood (1988) ArticleTitleDynamic low-dose three-dimensional computed tomography: a preliminary study. Br J Radiol 61 1095–1099 Occurrence Handle3219491
JM Gonzalez-Darder JV Pesudo-Martinez RA Feliu-Tatay (2001) ArticleTitleMicrosurgical management of cerebral aneurysms based in CT angiography with three-dimensional reconstruction (3D-CTA) and without preoperative cerebral angiography. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 143 673–679 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s007010170045
Harbaugh RE, Schlusselberg DS, Jeffery R, Hayden S, Cromwell LD, Pluta D, English RA (1995) Three-dimensional computed tomographic angiography in the preoperative evaluation of cerebrovascular lesions. Neurosurgery 36: 320–326; discussion 326–327
H Hashimoto J Iida Y Hironaka M Okada T Sakaki (2000) ArticleTitleUse of spiral computerized tomography angiography in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage in whom subtraction angiography did not reveal cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg 92 278–283 Occurrence Handle10659015
DS Heffez M Mikhael K Jensen (1995) ArticleTitleOperative confirmation of three-dimensional computed tomographic and magnetic resonance imaging of cerebrovascular pathology. J Image Guid Surg 1 179–190 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1522-712X(1995)1:3<179::AID-IGS8>3.0.CO;2-7 Occurrence Handle9079444
Heiserman JE, Dean BL, Hodak JA, Flom RA, Bird CR, Drayer BP, Fram EK (1994) Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15: 1401–1407; discussion 1408–1411
Hoh BL, Cheung AC, Rabinov JD, Pryor JC, Carter BS, Ogilvy CS (2004) Results of a prospective protocol of computed tomographic angiography in place of catheter angiography as the only diagnostic and pretreatment planning study for cerebral aneurysms by a combined neurovascular team. Neurosurgery 54: 1329–1340; discussion 1340–1322
JK Hope JL Wilson FJ Thomson (1996) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional CT angiography in the detection and characterization of intracranial berry aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17 439–445 Occurrence Handle8881236
Hsiang JN, Liang EY, Lam JM, Zhu XL, Poon WS (1996) The role of computed tomographic angiography in the diagnosis of intracranial aneurysms and emergent aneurysm clipping. Neurosurgery 38: 481–487; discussion 487
WE Hunt RM Hess (1968) ArticleTitleSurgical risk as related to time of intervention in the repair of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 28 14–20 Occurrence Handle5635959
T Inagawa K Kamiya H Ogasawara T Yano (1987) ArticleTitleRebleeding of ruptured intracranial aneurysms in the acute stage. Surg Neurol 28 93–99 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0090-3019(87)90079-6 Occurrence Handle3603360
Karttunen AI, Jartti PH, Ukkola VA, Sajanti J, Haapea M (2003) Value of the quantity and distribution of subarachnoid haemorrhage on CT in the localization of a ruptured cerebral aneurysm. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145: 655–661; discussion 661
Katada K (2000) Role of multislice CT in neuroradiology – importance of isotropic volumetric data. Presented at the 3rd Asian Congress of Neurological Surgeons, Nagoya, Japan, Nov 5–9
Y Kato K Katada M Hayakawa M Nakane Y Ogura K Sano T Kanno (2001) ArticleTitleCan 3D-CTA surpass DSA in diagnosis of cerebral aneurysm? Acta Neurochir (Wien) 143 245–250 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s007010170104
Y Kato S Nair S Sanjaykumar K Katada K Hayakawa T Kanno (2002) ArticleTitleMulti-Slice 3D-CTA – An improvement over single slice helical CTA for cerebral aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 144 715–722 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00701-002-0932-7
GH Koenig WH Marshall SuffixJr GJ Poole RA Kramer (1979) ArticleTitleRupture of intracranial aneurysms during cerebral angiography: report of ten cases and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 5 314–324 Occurrence Handle503291
Y Korogi M Takahashi K Katada Y Ogura K Hasuo M Ochi H Utsunomiya T Abe S Imakita (1999) ArticleTitleIntracranial aneurysms: detection with three-dimensional CT angiography with volume rendering – comparison with conventional angiographic and surgical findings. Radiology 211 497–506 Occurrence Handle10228534
PH Lai CF Yang HB Pan C Chen JT Ho SS Hsu (1999) ArticleTitleDetection and assessment of circle of Willis aneurysms in acute subarachnoid hemorrhage with three-dimensional computed tomographic angiography: correlation with digital subtraction angiography findings. J Formos Med Assoc 98 672–677 Occurrence Handle10575836
EY Liang M Chan JH Hsiang SB Walkden WS Poon WW Lam C Metreweli (1995) ArticleTitleDetection and assessment of intracranial aneurysms: value of CT angiography with shaded-surface display. AJR Am J Roentgenol 165 1497–1502 Occurrence Handle7484596
M Matsumoto Y Endo M Sato S Sato J Sakuma Y Konno K Suzuki T Sasaki N Kodama T Katakura F Shishido (2002) ArticleTitleAcute aneurysm surgery using three-dimensional CT angiogrphy without conventional catheter angiography. Fukushima J Med Sci 48 63–73 Occurrence Handle12680610
M Matsumoto M Sato M Nakano Y Endo Y Watanabe T Sasaki K Suzuki N Kodama (2001) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional computerized tomography angiography-guided surgery of acutely ruptured cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg 94 718–727 Occurrence Handle11354402
M Matsumoto N Satoh T Kobayashi et al. (1996) ArticleTitle(Jpn) [Helical CT for emergency patients with cerebrovascular disease-diagnosis of cerebral aneurysms with subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) by three-dimensional CT angiography (3D-CTA)]. Kobayashi TSurg Cerebral Stroke 24 177–185
Y Murai R Tagaki Y Ikeda Y Yamamoto A Teramoto (1999) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional computerized tomography angiography in patients with hyperacute intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 91 424–431 Occurrence Handle10470817
Y Nakajima T Yoshimine H Yoshida K Sakashita M Okamoto M Kishikawa K Yagi J Yokota T Hayakawa (1998) ArticleTitleComputerized tomography angiography of ruptured cerebral aneurysms: factors affecting time to maximum contrast concentration. J Neurosurg 88 663–669 Occurrence Handle9525712
T Ogawa T Okudera K Noguchi N Sasaki A Inugami K Uemura N Yasui (1996) ArticleTitleCerebral aneurysms: evaluation with three-dimensional CT angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17 447–454 Occurrence Handle8881237
T Seruga G Bunc GE Klein (2001) ArticleTitleHelical high-resolution volume-rendered 3-dimensional computer tomography angiography in the detection of intracranial aneurysms. J Neuroimaging 11 280–286 Occurrence Handle11462295
M Strayle-Batra M Skalej AK Wakhloo U Ernemann R Klier K Voigt (1998) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional spiral CT angiography in the detection of cerebral aneurysm. Acta Radiol 39 233–238 Occurrence Handle9571935
Tampieri D, Leblanc R, Oleszek J, Pokrupa R, Melancon D (1995) Three-dimensional computed tomographic angiography of cerebral aneurysms. Neurosurgery 36: 749–754; discussion 754–745
S Tanabe M Ohtaki T Uede K Hashi S Suzuki H Takahashi (1995) ArticleTitle[Diagnosis of ruptured and unruptured cerebral aneurysms with three-dimensional CT angiography (3D-CTA)]. No Shinkei Geka 23 787–795 Occurrence Handle7566425
BK Velthuis GJ Rinkel LM Ramos TD Witkamp JW Berkelbach van der Sprenkel WP Vandertop MS van Leeuwen (1998) ArticleTitleSubarachnoid hemorrhage: aneurysm detection and preoperative evaluation with CT angiography. Radiology 208 423–430 Occurrence Handle9680571
BK Velthuis MS Van Leeuwen TD Witkamp LM Ramos JW Berkelbach van Der Sprenkel GJ Rinkel (1999) ArticleTitleComputerized tomography angiography in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: from aneurysm detection to treatment without conventional angiography. J Neurosurg 91 761–767 Occurrence Handle10541232
P Vieco W Shuman G Alsofrom C Gross (1995) ArticleTitleDetection of circle of WIllis aneurysms in patients with acute subarachnoid hemorrhage: a comparison of CT angiography and digital subtraction angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 165 425–430 Occurrence Handle7618571
JP Villablanca P Hooshi N Martin R Jahan G Duckwiler S Lim J Frazee YP Gobin J Sayre J Bentson F Vinuela (2002) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional helical computerized tomography angiography in the diagnosis, characterization, and management of middle cerebral artery aneurysms: comparison with conventional angiography and intraoperative findings. J Neurosurg 97 1322–1332 Occurrence Handle12507130
Y Watanabe Y Endo M Nakano et al. (1997) ArticleTitle(Jpn) [Three-dimensional computed tomographic angiography for patients with ruptured cerebral aneurysms]. Progress in CI 19 337–344
JR Waugh N Sacharias (1992) ArticleTitleArteriographic complications in the DSA era. Radiology 182 243–246 Occurrence Handle1727290
PM White EM Teasdale JM Wardlaw V Easton (2001) ArticleTitleIntracranial aneurysms: CT angiography and MR angiography for detection prospective blinded comparison in a large patient cohort. Radiology 219 739–749 Occurrence Handle11376263
PM White JM Wardlaw V Easton (2000) ArticleTitleCan noninvasive imaging accurately depict intracranial aneurysms? A systematic review. Radiology 217 361–370 Occurrence Handle11058629
M Wintermark A Uske M Chalaron L Regli P Maeder R Meuli P Schnyder S Binaghi (2003) ArticleTitleMultislice computerized tomography angiography in the evaluation of intracranial aneurysms: a comparison with intraarterial digital subtraction angiography. J Neurosurg 98 828–836 Occurrence Handle12691409
KS Wong EY Liang WW Lam YN Huang R Kay (1995) ArticleTitleSpiral computed tomography angiography in the assessment of middle cerebral artery occlusive disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 59 537–539 Occurrence Handle8530943
N Young NW Dorsch RJ Kingston G Markson J McMahon (2001) ArticleTitleIntracranial aneurysms: evaluation in 200 patients with spiral CT angiography. Eur Radiol 11 123–130 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s003300000523 Occurrence Handle11194903
Young N, Dorsch NW, Kingston RJ, Soo MY, Robinson A (1998) Spiral CT scanning in the detection and evaluation of aneurysms of the Circle of Willis. Surg Neurol 50: 50–60; discussion 60–51
A Zouaoui M Sahel B Marro S Clemenceau N Dargent A Bitar T Faillot L Capelle C Marsault (1997) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional computed tomographic angiography in detection of cerebral aneurysms in acute subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 41 125–130 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199707000-00026 Occurrence Handle9218304
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pechlivanis, I., Schmieder, K., Scholz, M. et al. 3-Dimensional computed tomographic angiography for use of surgery planning in patients with intracranial aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147, 1045–1053 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0577-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0577-4