Summary.
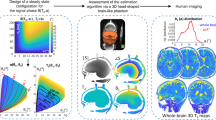
Background. Longitudinal relaxation time (T1) map generation from human brain slices renders possible the in vivo follow-up of the changes in T1 values during the course of several pathologies such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain injury etc. T1 values can be converted to water contents, thus brain oedema reducing therapy can be non-invasively evaluated. The purpose of the study was to work out a fast and simple MRI method to obtain T1 and water maps of the human brain.
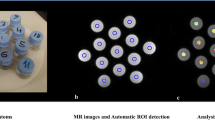
Method. The T1 values of Gadolinium solutions with different concentrations were determined by means of MRI methods at a clinical MR scanner operating at 1 Tesla. In order to validate these measurements, T1 values of the same Gadolinium solutions were also quantified with a relaxometer operating at the same field strength. T1 and water maps from the brains of healthy volunteers were obtained with an inversion prepared spoiled gradient echo sequence (turbo-FLASH).
Findings. The T1 values of Gadolinium solutions measured with the relaxometer showed a strong correlation (r > 0.999) with those determined with MRI sequences on the whole body scanner. The fastest MRI method to produce T1 and consequent water maps from human brain was the inversion prepared turbo-FLASH sequence.
Conclusions. The implemented turbo-FLASH method can produce T1 and water map of a single virtual brain slice within 2 minutes. However, brain tissue containing haemorrhage should be excluded from the measurement due to the large influence of excessive haemoglobin concentration on longitudinal relaxation. The proposed method is available on most of the MR scanners, thus T1 and water mapping of human brain can be routinely performed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kövér, F., Schwarcz, A., Pál, J. et al. Fast method for longitudinal relaxation time and water content mapping of the human brain on a clinical MR scanner. Acta Neurochir 146, 1341–1346 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-004-0370-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-004-0370-9