Summary.
Background. The secondary injury process following spinal cord trauma has been shown to involve different mechanisms such as excessive release of excitatory amino-acids, and induction of free radical induced lipid peroxidation. In this experimental study, the time-level relationship of the nitric oxide and the neuroprotective effects of aminoguanidine were investigated in a rat spinal cord trauma model.
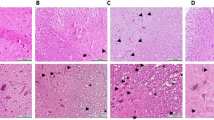
Methods. The experiments were performed on 63 Wistar albino rats divided into three groups; sham-operated control (Group 1), trauma created control (Group 2) and aminoguanidine group (Group 3). In groups 2 and 3, spinal cord trauma was produced at thoracic level by using weight the drop technique (at a severity of 50 gr-cm). After the trauma, the rats in Group 3, received an intraperitoneal injection of 100 mg/kg aminoquanidine twice a day for 3 days. The effects of the injury and the efficacy of aminoguanidine were determined based on biochemical parameters (lipid peroxidation and nitric oxide levels in tissue), and on light microscopy findings in cord tissue collected at different times post-injury. Biochemical parameters were performed one hour, three and five days after injury. Functional recovery was assessed at 3, and 5 days after cord trauma with the inclined-plane technique and Tarlov’s motor grading scale.
Findings. Although there was no statistically significant difference at the 1st hour, the values of the tissue nitric oxide in trauma created controls were 42% higher on the 3rd day and 40% higher on the 5th day when compared with those in sham controls. The levels of the tissue lipid peroxidation in trauma created controls were 88% higher at the 1st hour and 52.8% higher on the 5th day when compared with shame controls, but there was no meaningful difference on the 3rd day. In the trauma created control group, the mean motor function scores decreased to 1.16 ± 0.40 and to 1 ± 0 on the 3rd and 5th day, respectively. In this group the mean values of the inclined plane were 39.16 ± 2.04 on the 3rd day and 37.91 ± 1.02 on the 5th day. No statistically significant difference was observed in both tissue lipid peroxidation and nitric oxide levels for all time points between the aminoguanidine group and the sham-operated controls (p>0.01). The motor function scores were observed as 2.16 ± 0.40 on the 3rd day and as 3 ± 0 on the 5th day in aminoguanidine group. These values were significantly higher than the trauma created controls (p<0.01). Aminoguanidin treatment also improved the inclined plane performance of the rats; In this group, the mean values of the inclined plane scores were 44.58 ± 2.92 and 52.91 ± 1.88 on the 3rd and 5th days, respectively. These values were significantly higher than the trauma created controls (p<0.01).
Interpretation. This study shows that the nitric oxide level does not increase in the spinal cord tissue during the first hour after the spinal cord trauma. It increases significantly in the spinal cord tissue not only three days but also five days following the trauma. Aminoguanidine treatment, which is started just after the trauma, can prevent both the nitric oxide production and lipid peroxidation in spinal cord tissue and it can improve the functional status of the animals. In this respect, aminoguanidine may have a potential role in the treatment of acute spinal cord injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soy, O., Aslan, Ö., Uzun, H. et al. Time-level relationship for nitric oxide and the protective effects of aminoguanidine in experimental spinal cord injury. Acta Neurochir 146, 1329–1336 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-004-0343-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-004-0343-z