Summary
Intracranial tuberculoma is typically located in the parenchyma. Lesions limited to the ventricular system are uncommon. It is difficult to make a differential diagnosis from other lesions if no systemic tuberculosis is present.
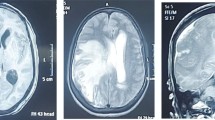
This study investigates a case of solitary intraventricular tuberculoma in a 19-year-old female patient with an initial clinical symptom of progressive headache. Cranial computed tomography revealed a strongly enhanced lesion in the lateral ventricle. Histopathology of the tumor demonstrated chronic inflammation, caseous necrosis, epithelioid cells and Langhans’ giant cell. The culture study grew M. Tuberculosis.
Solitary intraventricular tuberculoma in adults is extremely rare. Medical treatment is the preferred management method of this disease, and surgical intervention should be considered in certain situations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, PW., Lin, TK. & Chang, CN. Solitary intraventricular tuberculoma in adults. Acta Neurochir 146, 1151–1154 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-004-0291-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-004-0291-7