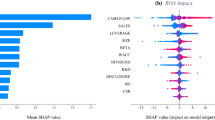
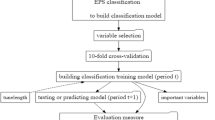
Abstract
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) has gained a great deal of interest in recent years due to the need for information that can help many stakeholders (e.g., governments, investors, professional organizations, researchers, etc.) understand companies’ contributions to the environment and society. CSR disclosure (CSRD) is now the key source of such information when analyzing, for example, an institution’s future performance. In the current body of CSRD literature, the majority of quantitative CSRD studies have relied on traditional statistical approaches for the correlation analysis of CSRD influencing factors. In this paper, we intend to quantitatively analyze firms’ characteristics related to CSRD in Saudi Arabia, understand CSRD and its influencing factors, and predict CSRD patterns. This study lays the groundwork to help companies make informed decisions. It also helps many other stakeholders better understand CSRD’s impacts. To achieve this, we propose a deep learning framework based on long short-term memory (LSTM) for identifying and predicting CSRD patterns. Moreover, a correlation-based technique is also used to visualize the relationships between variables and identify the significant features. The dataset used in this study was collected from annual reports, CSR reports, and firms’ websites between 2015 and 2018. It contains a variety of variables to explain the CSR behaviour of 117 companies. The proposed framework is evaluated with several approaches, including logistic regression (LR), K-nearest neighbours (KNN), support vector machines (SVM), random forests (RF), and decision trees (DT). Compared to other machine learning models, experiment results show that LSTM achieved acceptable results with the highest accuracy of \(88_\%\).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gray R, Dey C, Owen D, Evans R, Zadek S (1997) Struggling with the praxis of social accounting: stakeholders, accountability, audits and procedures. Audit Account J Account 10(3):325–364
Lindgren C, Huq AM, Carling K (2021) Who are the intended users of CSR reports? insights from a data-driven approach. Sustainability 13(3):1070
Gray R, Owen D, Maunders K (1987) Corporate social reporting: accounting and accountability. Prentice-Hall International
Patten DM (1991) Exposure, legitimacy, and social disclosure. J Account Public Policy 10(4):297–308
Wong EM, Ormiston ME, Tetlock PE (2011) The effects of top management team integrative complexity and decentralized decision making on corporate social performance. Acad Manag J 54(6):1207–1228
Jizi MI, Salama A, Dixon R, Stratling R (2014) Corporate governance and corporate social responsibility disclosure: evidence from the us banking sector. J Bus Ethics 125(4):601–615
Omair Alotaibi K, Hussainey K (2016) Determinants of CSR disclosure quantity and quality: evidence from non-financial listed firms in Saudi Arabia. Int J Discl Gov 13(4):364–393
Boshnak HA (2021) Determinants of corporate social and environmental voluntary disclosure in Saudi listed firms. J Financ Report Account 20:667–692
Al-Janadi Y, Rahman RA, Omar NH (2013) Corporate governance mechanisms and voluntary disclosure in Saudi Arabia. Res J Financ Account 4(4)
Habbash M (2016) Corporate governance and corporate social responsibility disclosure: evidence from Saudi Arabia. Soc Responsib J 12(4):740–754
Cowen SS, Ferreri LB, Parker LD (1987) The impact of corporate characteristics on social responsibility disclosure: a typology and frequency-based analysis. Account Organ Soc 12(2):111–122
Gray R, Kouhy R, Lavers S (1995) Corporate social and environmental reporting: a review of the literature and a longitudinal study of UK disclosure. Account Audit Accountab J 8(2):47–77
Guthrie J, Farneti F (2008) GRI sustainability reporting by Australian public sector organizations. Public Money Manag 28(6):361–366
Zeghal D, Ahmed SA (1990) Comparison of social responsibility information disclosure media used by canadian firms. Account Audit Accountab J 3(1)
Almars AM (2022) Attention-based bi-LSTM model for Arabic depression classification. CMC Comput Mater continua 71(2):3091–3106
Teoh T-T, Heng Q, Chia J, Shie J, Liaw S, Yang M, Nguwi Y-Y (2019) Machine learning-based corporate social responsibility prediction, In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems (CIS) and IEEE Conference on Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics (RAM), IEEE, pp. 501–505
Clarkson PM, Ponn J, Richardson GD, Rudzicz F, Tsang A, Wang J (2020) A textual analysis of us corporate social responsibility reports. Abacus 56(1):3–34
Hackston D, Milne MJ (1996) Some determinants of social and environmental disclosures in New Zealand companies. Account Audit Accountab J 9(1):77–108
Almars AM, Almaliki M, Noor TH, Alwateer MM, Atlam E (2022) Hann: hybrid attention neural network for detecting Covid-19 related rumors. IEEE Access 10:12334–12344
Al-Abdin A, Roy T, Nicholson JD (2018) Researching corporate social responsibility in the middle east: the current state and future directions. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 25(1):47–65
Jamali D, Karam C (2018) Corporate social responsibility in developing countries as an emerging field of study. Int J Manag Rev 20(1):32–61
Ortas E, Gallego-Álvarez I, Álvarez I (2019) National institutions, stakeholder engagement, and firms’ environmental, social, and governance performance. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 26(3):598–611
Sharma E (2019) A review of corporate social responsibility in developed and developing nations. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 26(4):712–720
Balakrishnan R, Qiu XY, Srinivasan P (2010) On the predictive ability of narrative disclosures in annual reports. Eur J Oper Res 202(3):789–801
Purda L, Skillicorn D (2015) Accounting variables, deception, and a bag of words: assessing the tools of fraud detection. Contemp Account Res 32(3):1193–1223
Hummel K, Mittelbach-Hörmanseder S, Cho CH, Matten D (2017) Implicit versus explicit corporate social responsibility disclosure: A textual analysis, SSRN Electron J 3090976
Loughran T, McDonald B (2011) When is a liability not a liability? textual analysis, dictionaries, and 10-ks. J Financ 66(1):35–65
Almars A, Li X, Zhao X (2019) Modelling user attitudes using hierarchical sentiment-topic model. Data Knowl Eng 119:139–149
Raghupathi V, Ren J, Raghupathi W (2020) Identifying corporate sustainability issues by analyzing shareholder resolutions: a machine-learning text analytics approach. Sustainability 12(11):4753
Nazari JA, Hrazdil K, Mahmoudian F (2017) Assessing social and environmental performance through narrative complexity in CSR reports. J Contemp Account Econ 13(2):166–178
Cho CH, Roberts RW, Patten DM (2010) The language of us corporate environmental disclosure. Acc Organ Soc 35(4):431–443
Muslu V, Mutlu S, Radhakrishnan S, Tsang A (2019) Corporate social responsibility report narratives and analyst forecast accuracy. J Bus Ethics 154(4):1119–1142
Tadawul (2017) New industry classification [Press release]. https://www.tadawul.com.sa/wps/portal/tadawul/knowledge-center/about/newindustry-classification?locale
Alharbi KMS (2021) The impact of the 2030 vision and firm characteristics on corporate social responsibility disclosure in Saudi Arabia, Ph.D. thesis, Victoria University
Almars AM, Ibrahim IA, Zhao X, Al-Maskari S (2018) Evaluation methods of hierarchical models, In: International Conference on Advanced Data Mining and Applications, Springer, pp. 455–464
Farghaly Abdelaliem SM, Alharbi KM, Baghdadi NA, Malki A (2023) Exploring the impact of private companies’ participation in health-related programs through corporate sustainable reporting. Sustainability 15(7):5906
Alazzani A, Aljanadi Y, Shreim O (2018) The impact of existence of royal family directors on corporate social responsibility reporting: a servant leadership perspective. Soc Responsib J 15(1):120–136
Issa A (2017) The factors influencing corporate social responsibility disclosure in the kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 11(10):1–19
Ding X, Qu Y, Shahzad M (2019) The impact of environmental administrative penalties on the disclosure of environmental information. Sustainability 11(20):5820
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organisation or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Almars, A.M., Alharbi, K.M. Corporate social responsibility disclosure prediction using LSTM neural network. Computing 106, 607–625 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-023-01239-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-023-01239-w