Abstract
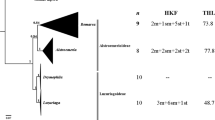
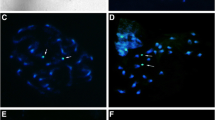
The somatic chromosome numbers of the eleven Australian seagrass species belonging to five genera in the Family Cymodoceaceae were determined. The chromosome numbers in Amphibolis and Thalassodendron are reported for the first time. Cymodocea and Halodule species have the following chromosome numbers: Cymodocea angustata Ostenf., 2n = 14, 28; C. rotundata Ehrenb. & Hempr. ex Asch., 2n = 14; C. serrulata (R. Br.) Asch. & Magnus, 2n = 14, 28; Halodule pinifolia (Miki) den Hartog, 2n = 32; H. uninervis (Forsk.) Asch., 2n = 32; H. tridentata (Steinh.) Endl. ex Unger, 2n = 14. Halodule has the highest chromosome numbers among the seagrasses and they are the largest in sizes with a distinct bimodal type in the family. Syringodium isoetifolium (Asch.) Dandy has 2n = 20. Both endemic Amphibolis antarctica (Labill.) Sonder ex Asch. and A. griffithii (J. Black) den Hartog have 2n = ca. 36 and have the smallest chromosomes in the family appearing as small dots. Thalassodendron pachyrhizum den Hartog has 2n = 28. Chromosome numbers appear to be identical or closely related among different species in the same genus but they vary in the five genera in the Cymodoceaceae suggesting that these five genera may have evolved independently in the past.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benenett MD (1998) Plant genome values: how much do we know? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:2011–2016
den Hartog C (1970) The Sea-grasses of the World. Verhandelingen der Koninklijke Nederlandsche Akademie van Wetenschappen. Afdeeling Natuurkunde, Tweed Reeks, 59:1–275
den Hartog C, Kuo J (2006) Taxonomy and biogeography of seagrasses. In: Larkum AWD, Orth RJ, Duarte CM (eds) Seagrasses: biology, ecology and conservation. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 1–23
den Hartog C, van Loenhoud PJ, Roelofs JGM, van de Sande JCPM (1979) Chromosome numbers of three seagrasses from the Netherlands Antilles. Aquat Bot 7:267–271
den Hartog C, Hennan J, Noten Th MPA, Van Wilk RJ (1987) Chromosome number numbers of the European seagrasses. Pl Syst Evol 156:55–59
Drew EA (1983) Sugars, cyclitols and seagrass phylogeny. Aquat Bot 15:387–408
Ito Y, Tanaka N (2011) Hybridisation in a tropical seagrass genus Halodule (Cymodoceae), inferred from plastid and nuclear DNA phylogenies. Telopea 13:219–231
Kirkman H, Cook IH (1987) Distribution and leaf growth of Thalassodendron pachyrhizum den Hartog in southern Western Australia. Aquat Bot 27:257–266
Kuo J (2003) Chromosome numbers of the Australian Zosteraceae. Pl Syst Evol 226:155–163
Kuo J (2011) Cymodoceace. In: Wilson A (ed) Flora of Australia, vol 39., Australian BiolResources Study, Canberra, pp 120–134
Kuo J, den Hartog C (2001) Seagrass taxonomy and identification key. In: Short FT, Coles RG (eds) Global seagrass research methods. Elsevier Sciences BV, Amsterdam, pp 31–58
Kuo J, den Hartog C (2006) Seagrass morphology, anatomy and ultrastructure. In: Larkum AWD, Orth RJ, Duarte CM (eds) Seagrasses: biology, ecology and conservation. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 57–81
Kuo J, McComb AJ (1989) Seagrass taxonomy, structure and development. In: Larkum AWD, McComb AJ, Shepherd SA (eds) Biology of seagrasses. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 6–73
Kuo J, McComb AJ (1998) Cymodoceaceae. In: Kubitzki K (ed) The families and genera of vascular plants. Flowering plants. Monocotyledons, Alismatanae and Commelinanae (except Gramineae), vol IV. Springer, Berlin, pp 133–140
Kuo J, James S, Kirkman H, den Hartog C (1990) Chromosome numbers and their systematic implication in Australian Posidonia. Pl Syst Evol 171:199–204
Les DH, Haynes RH (1995) Systematics of subclass Alismatide: a synthesis of approaches. In: Rudall PJ, Cribb PJ, Cuter DF, Humphries CJ (eds) Monocotyledons: systematics and evolution. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, pp 1–26
Les DH, Cleland MA, Waycott M (1997) Phylogenetic studies in Alismatidae, II: evolution of marine angiosperms (seagrasses) and hydrophily. Syst Bot 22:143–163
Lumbert SH, den Hartog C, Phillips RC, Olsen FS (1984) The occurrence of fossil seagrasses in the avon park formation (late middle eocene), Levy County, Florida, USA). Aquat Bot 20:121–129
McMillan C (1991) Isozyme patterning in marine spermatophytes. In: Triest L (ed) Isozymes in Water Plants. Op Bot Berg 4, pp 193200
McMillan C, Young PC, Cambridge ML, Masini RJ, Walker DI (1983) The status of an endemic Australian seagrass, Cymodocea angustata Ostenfeld. Aquat Bot 17:231–241
Stace CA (2000) Cytology and cytogenetics as a fundamental taxonomic resource for the 20th and 21st centuries. Taxon 49:451–477
Tomlinson PB (1982) Helobiae (Alismatidae). In: Metcalfe CR (ed) Anatomy of the monocotyledons, vol VII. Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 1–559
Uchiyama H (1993) Karyomorphology of seagrass and their allied genera. In: International Workshop on Seagrass Biology, Kominato, Japan. University of Tokyo, Japan, pp 51–56
Waycott M, Les DH (1996) An integrated approach to the evolutionary study of seagrasses. In: Kuo J, Phillips RC, Walker DI, Kirkman H (eds) Seagrass biology: Proceedings of an International Workshop, Rottnest Island, Australia, University of Western Australia, Perth, pp 71–78
Waycott M, Procaccini G, Les DH, Reusch TB (2006) Seagrass evolution, ecology and conservation: a genetic perspective. In: Larkum AWD, Orth RJ, Duarte CM (eds) Seagrasses: biology. Ecology and Conservation, Springer, pp 25–50
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuo, J. Chromosome numbers of the Australian Cymodoceaceae. Plant Syst Evol 299, 1443–1448 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-013-0806-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-013-0806-x