Abstract
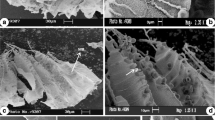
Mericarp morphology of 15 taxa of Salvia L. section Hymenosphace Benth. in Turkey were investigated by light microscopy (LM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to evaluate the utility of mericarp characters in systematic studies. Mericarps ranged from 2.50 to 5.38 mm in length and 2.04 to 4.70 mm in width. Mericarp shape was prolate-spheroid or near spherical with a length-to-width ratio of 1.02–1.48. Transverse sections of the mericarps were rounded or rounded-trigonous. Mericarp surfaces presented colliculate, reticulate, verrucate or foveate sculpturing patterns, mostly as a result of the sculpturing of the exocarp cell walls with the pattern determined by whether the periclinal walls were concave or convex and whether the anticlinal walls were raised or sunken. Colliculate surface sculpturing (periclinal walls convex) was the most common among the taxa examined. The variation in the nature of surface sculpturing, mericarp shape and size, exocarp cell shape, nature of transverse sections and abscission scar diameter proved useful diagnostic characters. Variation was sufficient to distinguish taxa at species level, including morphologically similar species. Data provided here are also relevant to phylogenetic questions at higher levels within Salvia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baylac S, Racine P (2003) Inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase by essential oils and other natural fragrant extracts. Int J Aromatherapy 13:138–142
Behçet L, Avlamaz D (2009) A new record for Turkey: Salvia aristata Aucher ex Benth. (Lamiaceae). Turk J Bot 33:61–63
Celep F, Doğan M (2010) Salvia ekimiana (Lamiaceae), a new species from Turkey. Ann Bot Fenn 47:63–66
Celep F, Doğan M, Duran A (2009a) A new record for the Flora of Turkey: Salvia viscosa Jacq. (Labiatae). Turk J Bot 33:57–60
Celep F, Doğan M, Bagherpour S, Kahraman A (2009b) A new variety of Salvia sericeotomentosa (Lamiaceae) from South Anatolia, Turkey. Novon 19:432–435
Chalchat JC, Michet A, Pasquier B (1998) Study of clones of Salvia officinalis L. yields and chemical composition of essential oil. Flavour Fragr J 13:68–70
Demirci B, Başer KHC, Yıldız B, Bahçecioğlu Z (2003) Composition of the essential oils of six endemic Salvia spp. from Turkey. Flavour Fragr J 18:116–121
Demissew S, Harley MM (1992) Trichome, seed surface and pollen characters in Stachys, Lamioideae (Labiatae) in Tropical Africa. In: Harley RM, Reynolds T (eds) Advances in Labiatae science. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, pp 149–166
Dönmez A (2001) A new Turkish species of Salvia L. (Lamiaceae). Bot J Linn Soc 137:413–416
Duletić-Lauševic S, Marin PD (1999) Pericarp structure and myxocarpy in selected genera of Nepetoideae (Lamiaceae). Nord J Bot 19:435–446
Guerin GR (2005) Nutlet morphology in Hemigenia R. BR. and Microcorys R. BR. (Lamiaceae). Pl Syst Evol 254:49–68
Hamzaoğlu E, Duran A, Pınar NM (2005) Salvia anatolica (Lamiaceae), a new species from East Anatolia, Turkey. Ann Bot Fenn 42:215–220
Hedge IC (1965) Studies in the Flora of Afghanistan III: an account of Salvia. Notes R Bot Gard Edinb 26(4):408
Hedge IC (1970) Observations on the mucilage of Salvia Fruits. Notes R Bot Gard Edinb 30:79–95
Hedge IC (1982) Salvia L. In: Davis PH (ed) Flora of Turkey and the East Aegean Islands, vol 7. Edinburgh University Press, Edinburgh, pp 400–461
Huber-Morath A (1982) Salvia nydeggeri Hub.-Mor. nova species Sectio Eusphace Benth. Bauhinia 7(3):181
Husain SZ, Marin PD, Šilic C, Qaiser M, Petković B (1990) A micromorphological study of some representative genera in the tribe Saturejeae (Lamiaceae). Bot J Linn Soc 103:59–80
Ilçim A, Celep F, Dogan M (2009) Salvia marashica (Lamiaceae), a new pinnatisect-leaved species from Turkey. Ann Bot Fenn 46:75–79
Kahraman A, Doğan M (2010) Comparative study of Salvia limbata C.A. and S. palaestina Bentham (sect. Aethiopis Bentham, Labiatae) from East Anatolia, Turkey. Acta Bot Croat 69:47–64
Kahraman A, Celep F, Doğan M (2009) A new record for the Flora of Turkey: Salvia macrosiphon Boiss. (Labiatae). Turk J Bot 33:53–55
Kahraman A, Celep F, Doğan M, Bagherpour S (2010) A taxonomic revision of Salvia euphratica sensu lato and its closely related species (sect. Hymenosphace, Lamiaceae) by using multivariety analysis. Turk J Bot (in press)
Kamatou GPP, Makunga NP, Ramogola WPN, Viljoen AM (2008) South African Salvia species: a review of biological activities and phytochemistry. J Ethnopharmacol 119:667–672
Marin PD, Petković BP, Duletić S (1994) Nutlet sculpturing of selected Teucrium species (Lamiaceae): a character of taxonomic significance. Pl Syst Evol 192:199–214
Marin PD, Duletić S, Petković B (1996) Nutlet ornamentation in selected Salvia L. species (Lamiaceae). Fl Medit 6:203–211
Moon HK, Hong SP (2006) Nutlet morphology and anatomy of the genus Lycopus (Lamiaceae. Mentheae). Pl Res J 119:633–644
Oran SA (1996) Ultrastructure of nutlet surface of the genus Salvia L. in Jordan and the neighbouring countries. Dirasat Nat Eng Sci 23:393–408
Ryding O (1992) Pericarp structure and phylogeny within Lamiaceae subfamily Nepetoideae tribe Ocimeae. Nord J Bot 12:273–298
Ryding O (1994) Pericarp structure and phylogeny of Lamiaceae subfamily Pogostemonoideae. Nord J Bot 14:59–63
Ryding O (1995) Pericarp structure and phylogeny of Lamiaceae–Verbenaceae complex. Pl Syst Evol 198:101–141
Salmaki Y, Zarre S, Jamzad Z (2008) Nutlet micromorphology and its systematic implication in Stachys L. (Lamiaceae) in Iran. Feddes Repert 119:607–621
Stearn WT (2004) Botanical Latin. London
Turner BL, Delprete PG (1996) Nutlet sculpturing in Scutellaria sect. Resinosa (Lamiaceae) and its taxonomic utility. Pl Syst Evol 199:109–120
Ulubelen A (2003) Cardioactive and antibacterial terpenoids from some Salvia species. Phytochemistry 64:395–399
Vural M, Adıgüzel N (1996) A new species from Central Anatolia: Salvia aytachii M. Vural et N. Adıgüzel (Labiatae). Turk J Bot 20:531–534
Walker JB, Sytsma KJ (2007) Staminal evolution in the genus Salvia (Lamiaceae): molecular phylogenetic evidence for multiple origins of the staminal lever. Ann Bot 100:375–391
Walker JB, Sytsma KJ, Treutlein J, Wink M (2004) Salvia (Lamiaceae) is not monophletic: implications for the systematics, radiation, and ecological specializations of Salvia and tribe Mentheae. Am J Bot 91(7):1115–1125
Wojciechowska B (1966) Morphology and anatomy of fruits and seeds in the family Labiatae with particular respect to medicinal species (Polish with English summary). Monogr Bot 21:82–133
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the curators of following herbaria ANK, AEF, BM, E, G, GAZI, HUB, ISTE, ISTF, K and W for allowing us to study their Salvia collections and the Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey (TUBİTAK-TBAG-104 T 450) for their financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kahraman, A., Celep, F., Doğan, M. et al. Mericarp morphology and its systematic implications for the genus Salvia L. section Hymenosphace Benth. (Lamiaceae) in Turkey. Plant Syst Evol 292, 33–39 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-010-0394-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-010-0394-y