Abstract.
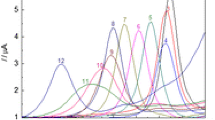
The electrochemical oxidation of catechol to ortho quinone at a glassy carbon electrode in the presence of cysteine is shown to lead to the deposition of a quinone-cysteine adduct at the electrode surface. Square wave voltammetry is shown to enable voltammetric resolution of unreacted orthoquinone and the accumulated adduct species such that quantification of both species is possible over a range of pH 2 – pH 6. The reaction is shown to be selective towards cysteine with little interference from cystine, homocysteine or glutathione. The foundations of a detection protocol are reported with the sensitivity shown to be capable of attenuation through the facile manipulation of the number of electro-initiated derivatisation scans. The application of six consecutive derivatisation scans is shown to provide a linear range of 2–20 μM cysteine that is well within the region required for physiological monitoring.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received December 4, 2000. Revision March 30, 2001.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
White, P., Lawrence, N., Tsai, Y. et al. Electrochemically Driven Derivatisation-Detection of Cysteine. Mikrochim Acta 137, 87–91 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s006040170033
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s006040170033