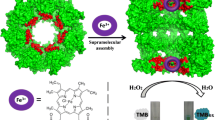
Abstract
A single-holed cobalt − nitrogen − carbon (Co − N − C) hollow structure nanozyme has been fabricated by in situ growth of zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF − 67) on the polystyrene (PS) sphere and following treatment by high-temperature carbonization. The Co − N − C nanostructure mimics the activity of oxidase and can activate O2 into reactive oxygen species (ROS), giving a remarkable enhancement on the chemiluminescence (CL) signal of luminol − O2 reaction. The Co − N − C oxidase mimic has further been exploited in the biosensing field by the determination of the activity of β − galactosidase (β − gal). The CL method for β − gal activity has a linear range of 0.5 mU·L−1 to 5.0 U·L−1, a detection limit of 0.167 mU·L−1, and the precision of 3.1% (5.0 U·L−1, n = 11). This method has been employed to assess inhibitor screening of β − gal and determine activity of β − gal in spiked human serum samples.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Wu JJX, Wang XY, Wang Q, Lou ZP, Li SR, Zhu YY, Qin L, Wei H (2019) Nanomaterials with enzyme−like characteristics (nanozymes): next−generation artificial enzymes (II). Chem Soc Rev 48:1004–1076. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cs00457a
Ouyang Y, O’Hagan MP, Willner I (2022) Functional catalytic nanoparticles (nanozymes) for sensing. Biosens Bioelectron 218:114768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114768
Liu QW, Zhang A, Wang RH, Zhang Q, Cui DX (2021) A review on metal and metal oxide−based nanozymes: properties, mechanisms, and applications. Nano-Micro Lett 13:154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820−021−00674−8
Li SQ, Liu XD, Chai HX, Huang YM (2018) Recent advances in the construction and analytical applications of metal−organic frameworks-based nanozymes. TRAC-Trend Anal Chem 105:391–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.06.001
Sun Y, Xu BL, Pan XT, Wang HY, Wu QY, Li SS, Jiang BY, Liu HY (2023) Carbon−based nanozymes: design, catalytic mechanism, and bioapplication. Coord Chem Rev 475:214896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214896
Wang ZR, Zhang RF, Yan XY, Fan KL (2020) Structure and activity of nanozymes: inspirations for de novo design of nanozymes. Mater Today 41:81–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2020.08.020
Shen LH, Ye DX, Zhao HB, Zhang JJ (2021) Perspectives for single−atom nanozymes: advanced synthesis, functional mechanisms, and biomedical applications. Anal Chem 93:1221–1231. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04084
Zhang CH, Chen CX, Zhao D, Kang G, Liu FN, Yang F, Lu YZ, Sun J (2022) Multienzyme cascades based on highly efficient metal−nitrogen−carbon nanozymes for construction of versatile bioassays. Anal Chem 94:3485–3493. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04018
Wang Y, Huang R, Han JW (2022) Metal−nitrogen−carbon−based nanozymes: advances and perspectives. J Phys D Appl Phys 5:323001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361−6463/ac6464
Tang TM, Wang ZL, Guan JQ (2023) Electronic structure regulation of single−site M−N−C electrocatalysts for carbon dioxide reduction. Acta Phys Chim Sin 39:2208033. https://doi.org/10.3866/PKU.WHXB202208033
Yan BS, Wang FT, He SJ, Liu WD, Zhang CH, Chen CX, Lu YZ (2022) Peroxidase−like activity of Ru−N−C nanozymes in colorimetric assay of acetylcholinesterase activity. Anal Chim Acta 1191:339362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.339362
Chen J, Hu S, Cai YL, Liu X, Wu YQi, Dai YH, Wang ZJ, (2022) Co–N/C–900 metal–organic framework–derived nanozyme as a H2O2–free oxidase mimic for the colorimetric sensing of L–cysteine. Analyst 147:915–922. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1an02179f
Sun LP, Yan Y, Chen S, Zhou ZJ, Tao W, Li C, Feng Y, Wang F (2022) Co–N–C single-atom nanozymes with oxidase-like activity for highly sensitive detection of biothiols. Anal Bioanal Chem 414:1857–1865. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03816-4
Song XK, Guo LL, Liao XM, Liu J, Sun JH, Li XP (2017) Hollow carbon nanopolyhedra for enhanced electrocatalysis via confined hierarchical porosity. Small 13:1700238. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201700238
Zhu Y, Zhang ZY, Lei Z, Tan YY, Wu W, Mu SC, Cheng NC (2020) Defect−enriched hollow porous Co−N−doped carbon for oxygen reduction reaction and Zn−Air batteries. Carbon 167:188–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.06.006
Hu WH, Zheng MB, Xu BY, Wei Y, Zhu W, Li Q, Pang H (2021) Design of hollow carbon−based materials derived from metal−organic frameworks for electrocatalysis and electrochemical energy storage. J Mater Chem A 9:3880. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ta10666f
Yang QH, Yang CC, Lin CH, Jiang HL (2019) Metal−organic−framework−derived hollow N−doped porous carbon with ultrahigh concentrations of single Zn atoms for efficient carbon dioxide conversion. Angew Chem 131:3549–3553. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201813494
Li M, Yang MQ, Zhu WH (2021) Advances in fluorescent sensors for β−galactosidase. Mater Chem Front 5:763–774. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0qm00683a
Lozano−Torres B, Blandez JF, Sancenon F, Martinez−Manez R, (2021) Chromo−fluorogenic probes for β−galactosidase detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 413:2361–2388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216−020−03111−8
Sun CQ, Zhang X, Tang MH, Liu L, Shi Y, Gao CH, Liao B, Zheng HZ (2019) New optical method for the determination of β−galactosidase and α−fetoprotein based on oxidase−like activity of fluorescein. Talanta 194:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.08.075
Liu ZP, Tian Y, Han Y, Bai E, Li YA, Xu ZW, Liu SS (2019) A “turn off−on” fluorescent nanoprobe consisting of CuInS2 quantum dots for determination of the activity of beta−glucosidase and for inhibitor screening. Microchim Acta 186:806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604−019−3918−3
Chen GY, Zhang H, Yang FQ (2021) A simple and portable method for beta−glucosidase activity assay and its inhibitor screening based on a personal glucose meter. Anal Chim Acta 1142:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.10.047
Deepa S, Venkatesan R, Jayalakshmi S, Priya M, Kim SC (2023) Recent advances in catalyst-enhanced luminol chemiluminescence system and its environmental and chemical applications. J Environ Chem Eng 11:109853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.109853
FonsecaBerzal C, Arenas DRM, Bohórquez ARR, Escario JA, Kouznetsov VV, Barrio AG (2013) Selective activity of 2,4−diaryl−1,2,3,4−tetrahydroquinolines on Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes and amastigotes expressing β−galactosidase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23:4851–4856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.06.079
Huang YY, Feng H, Liu W, Zhang SS, Tang C, Chen JR, Qian ZS (2017) Cation−driven luminescent self−assembled dots of copper nanoclusters with aggregation−induced emission for β−galactosidase activity monitoring. J Mater Chem B 5:5120–5127. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tb00901a
Wang BH, Wu TY, Chen GR, Liu XY, He QX, Li DS, Guan BY, Liu YL (2021) General synthesis of hierarchically macro/mesoporous Fe, Ni−doped CoSe/N−doped carbon nanoshells for enhanced electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Inorg Chem 60:6782–6789. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c00620
Guan BY, Yu L, Lou XW (2017) Formation of single−holed cobalt/N−doped carbon hollow particles with enhanced electrocatalytic activity toward oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline media. Adv Sci 4:1700247. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201700247
Chen XD, Shen K, Chen JY, Huang BB, Ding DN, Zhang L, Li YW (2017) Rational design of hollow N/Co−doped carbon spheres from bimetal−ZIFs for high−efficiency electrocatalysis. Chem Eng J 330:736–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.08.024
Tan JK, Xu CJ, Zhang XD, Huang YM (2022) MOFs-derived defect carbon encapsulated magnetic metallic Co nanoparticles capable of efficiently activating PMS to rapidly degrade dyes. Sep Purif Technol 289:120812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120812
Yuan S, Zhang JW, Hu LY, Li JN, Li SW, Gao YN, Zhang QH, Gu L, Yang WX, Feng X, Wang B (2021) Decarboxylation−induced defects in MOF−derived single cobalt atom@carbon electrocatalysts for efficient oxygen reduction. Angew Chem Int Ed 60:21685–21690. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202107053
Shi WB, Zhang XD, He SH, Huang YM (2011) CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles as a peroxidase mimic mediated chemiluminescence for hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Chem Commun 47:10785–10787. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cc14300j
Ji KX, Xia SY, Sang XQ, Zeid AM, Hussain A, Li JP, Xu GB (2023) Enhanced luminol chemiluminescence with oxidase−like properties of FeOOH nanorods for the sensitive detection of uric acid. Anal Chem 95:3267–3273. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c04247
Li HD, Wang JW, Du JX (2021) A novel luminol chemiluminescence system induced by black phosphorus quantum dots for cobalt (II) detection. Talanta 223:121712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121712
Xu XT, Ma YY, Ding SJ, Li YH (2021) Glucose oxidase@zinc–doped zeolitic imidazolate framework–67 as an effective cascade catalyst for one–step chemiluminescence sensing of glucose. Microchim Acta 188:427. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05096-2
Zhou Y, Du JX, Wang Z (2019) Fluorescein and its derivatives: new coreactants for luminol chemiluminescence reaction and its application for sensitive detection of cobalt ion. Talanta 191:422–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.09.007
Sun XQ, Lei J, Jin Y, Li BX (2020) Long−lasting and intense chemiluminescence of luminol triggered by oxidized g−C3N4 nanosheets. Anal Chem 92:11860–11868. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02221
Zhao CX, Cui HB, Duan J, Zhang SH, Lv JG (2018) Self−catalyzing chemiluminescence of luminol−diazonium ion and its application for catalyst−free hydrogen peroxide detection and rat arthritis imaging. Anal Chem 90:2201–2209. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04544
Ren L, Li HD, Du JX (2020) Black phosphorus quantum dots are useful oxidase mimics for colorimetric determination of biothiols. Microchim Acta 187:229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4222-y
Zhang LJ, Shi MN, Zhou WJ, Guan WJ, Lu C (2021) Disordered assembly of donors and acceptors on layered double hydroxides for high−efficiency chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer. Anal Chem 93:7724–7731. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c01136
Yang D, Liu JJ, Hu WL, Xiao Y, Chen HH, Long YJ, Zheng HZ (2023) Nano-ferroelectric oxidase mimics for colorimetric detection of glutathione. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 393:134170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.13417
Funding
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21675107) and the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi province (No. 2021JZ − 22, 2024JC − YBMS − 124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, D., Ge, M., Qian, F. et al. Single-holed cobalt − nitrogen − carbon hollow structure with oxidase-mimicking activity for the chemiluminescence determination of β − galactosidase activity. Microchim Acta 191, 200 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06285-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06285-5