Abstract
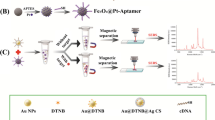
An ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) aptamer sensor (aptasensor) using a noble metal nanoparticle-magnetic nanospheres composite was developed for L-theanine detection. It makes use of Fe3O4@Au MNPs and Au@Ag NPs embedded with the Raman reporter 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (4MBA). Au@4MBA@Ag NPs modified by aptamer and Fe3O4@Au MNPs modified by cDNA created the aptasensor with the strongest Raman signal of 4MBA through the specific binding of the aptamer. With the preferred binding of L-theanine aptamer to L-theanine, Au@4MBA@Ag NPs were released from Fe3O4@Au MNPs, causing a linear decrease in SERS intensity to achieve the SERS detection of the L-theanine. The SERS peak of 4MBA at 1078 cm−1 was used for quantitative determination. SERS intensity showed a good log-linear relationship within the range 10−10 to 10−6 M of L-theanine. The aptasensor has a high selectivity for L-theanine compared with other twelve tested analytes. Hence, this aptasensor is a promising analytical tool for L-theanine detection. The developed method was applied to the analysis of real samples, demonstrating excellent performance. The comparison with the standard liquid chromatography mass spectrometry method showed an error within 20%.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Juneja LR, Chu DC, Okubo T, Nagato Y, Yokogoshi H (1999) L-theanine—a unique amino acid of green tea and its relaxation effect in humans. Trends Food Sci Technol 10:199–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0924-2244(99)00044-8
Kimura K, Ozeki M, Juneja LR, Ohira H (2007) L-Theanine reduces psychological and physiological stress responses. Biol Psychol 74:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2006.06.006
Bryan J (2008) Psychological effects of dietary components of tea: caffeine and L-theanine. Nutr Rev 66:82–90. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2007.00011.x
Turkozu D, Sanlier N (2017) L-theanine, unique amino acid of tea, and its metabolism, health effects, and safety. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 57:1681–1687. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2015.1016141
Hidese S, Ogawa S, Ota M, Ishida I, Yasukawa Z, Ozeki M, Kunugi H (2019) Effects of L-theanine administration on stress-related symptoms and cognitive functions in healthy adults: a randomized controlled trial. Nutrients 11(10):2362. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102362
Gong Y, Huang J-a, Shao Y, Liu Z, Pen J, Li J (2012) Measurement of theanine using reverse-phase ion-pair liquid chromatography with photodiode array detection. Food Chem 131:309–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.07.115
Desai MJ, Armstrong DW (2004) Analysis of derivatized and underivatized theanine enantiomers by high-performance liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure ionization-mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 18:251–256. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.1319
Yan J, Cai Y, Wang Y, Lin X, Li H (2014) Simultaneous determination of amino acids in tea leaves by micellar electrokinetic chromatography with laser-induced fluorescence detection. Food Chem 143:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.07.095
Sharma B, Frontiera RR, Henry A-I, Ringe E, Van Duyne RP (2012) SERS: materials, applications, and the future. Mater Today 15:16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1369-7021(12)70017-2
Guselnikova O, Lim H, Kim HJ, Kim SH, Gorbunova A, Eguchi M, Postnikov P, Nakanishi T, Asahi T, Na J, Yamauchi Y (2022) New trends in nanoarchitectured SERS substrates: nanospaces, 2D materials, and organic heterostructures. Small 18:2107182. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202107182
Mousavi SM, Hashemi SA, Rahmanian V, Kalashgrani MY, Gholami A, Omidifar N, Chiang W-H (2022) Highly sensitive flexible SERS-based sensing platform for detection of COVID-19. Biosensors 12(7):466. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070466
Zhang W, Tang S, Jin Y, Yang C, He L, Wang J, Chen Y (2020) Multiplex SERS-based lateral flow immunosensor for the detection of major mycotoxins in maize utilizing dual Raman labels and triple test lines. J Hazard Mater 393:122348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122348
Jiang L, Hassan MM, Ali S, Li H, Sheng R, Chen Q (2021) Evolving trends in SERS-based techniques for food quality and safety: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 112:225–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.04.006
Muhammad M, Huang Q (2021) A review of aptamer-based SERS biosensors: design strategies and applications. Talanta 227:122188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122188
Liu X, Guo J, Li Y, Wang B, Yang S, Chen W, Wu X, Guo J, Ma X (2021) SERS substrate fabrication for biochemical sensing: towards point-of-care diagnostics. J Mater Chem B 9:8378–8388. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1tb01299a
Aleknavičienė I, Pabrėža E, Talaikis M, Jankunec M, Račiukaitis G (2022) Low-cost SERS substrate featuring laser-ablated amorphous nanostructure. Appl Surf Sci 571:151248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151248
Zheng H, Ni D, Yu Z, Liang P (2017) Preparation of SERS-active substrates based on graphene oxide/silver nanocomposites for rapid zdetection of l-theanine. Food Chem 217:511–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.09.010
Song Y, Xu T, Xu LP, Zhang X (2018) Superwettable nanodendritic gold substrates for direct miRNA SERS detection. Nanoscale 10:20990–20994. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr07348a
Kim S, Ansah IB, Park JS, Dang H, Choi N, Lee W-C, Lee SH, Jung HS, Kim D-H, Yoo SM, Choo J, Kim S-H, Park S-G (2022) Early and direct detection of bacterial signaling molecules through one-pot Au electrodeposition onto paper-based 3D SERS substrates. Sensors Actuators B: Chem 358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2022.131504
Kim YS, Raston NH, Gu MB (2016) Aptamer-based nanobiosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 76:2–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.06.040
Wu L, Wang Y, Xu X, Liu Y, Lin B, Zhang M, Zhang J, Wan S, Yang C, Tan W (2021) Aptamer-based detection of circulating targets for precision medicine. Chem Rev 121:12035–12105. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01140
Yu H, Alkhamis O, Canoura J, Liu Y, Xiao Y (2021) Advances and challenges in small-molecule DNA aptamer isolation, characterization, and sensor development. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 60:16800–16823. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202008663
Zhou W, Huang PJ, Ding J, Liu J (2014) Aptamer-based biosensors for biomedical diagnostics. Analyst 139:2627–2640. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4an00132j
Song S, Wang L, Li J, Fan C, Zhao J (2008) Aptamer-based biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 27:108–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2007.12.004
Li D, Liu L, Huang Q, Tong T, Zhou Y, Li Z, Bai Q, Liang H, Chen L (2021) Recent advances on aptamer-based biosensors for detection of pathogenic bacteria. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 37:45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-03002-9
Wang Y, Yan B, Chen L (2013) SERS tags: novel optical nanoprobes for bioanalysis. Chem Rev 113:1391–1428. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr300120g
Fabris L (2016) SERS tags: the next promising tool for personalized cancer detection? ChemNanoMat 2:249–258. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnma.201500221
Lenzi E, Jimenez de Aberasturi D, Liz-Marzan LM (2019) Surface-enhanced raman scattering tags for three-dimensional bioimaging and biomarker detection. ACS Sens 4:1126–1137. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b00321
Zhang H, Ma X, Liu Y, Duan N, Wu S, Wang Z, Xu B (2015) Gold nanoparticles enhanced SERS aptasensor for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens Bioelectron 74:872–877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.07.033
Hanif S, Liu HL, Ahmed SA, Yang JM, Zhou Y, Pang J, Ji LN, Xia XH, Wang K (2017) Nanopipette-based SERS aptasensor for subcellular localization of cancer biomarker in single cells. Anal Chem 89:9911–9917. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b02147
Duan N, Qi S, Guo Y, Xu W, Wu S, Wang Z (2020) Fe3O4@Au@Ag nanoparticles as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrates for sensitive detection of clenbuterol hydrochloride in pork with the use of aptamer binding. Lwt 134:110017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110017
Chen R, Li S, Sun Y, Huo B, Xia Y, Qin Y, Li S, Shi B, He D, Liang J, Gao Z (2021) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy aptasensor for simultaneous determination of ochratoxin A and zearalenone using Au@Ag core-shell nanoparticles and gold nanorods. Mikrochim Acta 188:281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04919-6
Miao P, Tang Y, Wang L (2017) DNA modified Fe(3)O(4)@Au magnetic nanoparticles as selective probes for simultaneous detection of heavy metal ions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:3940–3947. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b14247
Song D, Yang R, Fang S, Liu Y, Long F, Zhu A (2018) SERS based aptasensor for ochratoxin A by combining Fe(3)O(4)@Au magnetic nanoparticles and Au-DTNB@Ag nanoprobes with multiple signal enhancement. Mikrochim Acta 185:491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3020-2
Xu W, Zhao A, Zuo F, Khan R, Hussain HMJ, Chang J (2020) Au@Ag core-shell nanoparticles for microRNA-21 determination based on duplex-specific nuclease signal amplification and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Mikrochim Acta 187:384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04330-7
F G (1972) Particle size and sol stability in metal colloids. Kolloid-Z Z Polymere 250:736–741. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01498565
Deng H, Li X, Peng Q, Wang X, Chen J, Li Y (2005) Monodisperse magnetic single-crystal ferrite microspheres. Angew Chem 117:2842–2845. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.200462551
Jana NR, Gearheart L, M CJ (2001) Evidence for seed-mediated nucleation in the chemical reduction of gold salts to gold nanoparticles. Chem Mater 13:2313–2322. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm000662n
Wang K, Sun DW, Pu H, Wei Q (2019) Shell thickness-dependent Au@Ag nanoparticles aggregates for high-performance SERS applications. Talanta 195:506–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.11.057
He H, Sun DW, Pu H, Huang L (2020) Bridging Fe(3)O(4)@Au nanoflowers and Au@Ag nanospheres with aptamer for ultrasensitive SERS detection of aflatoxin B1. Food Chem 324:126832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126832
Funding
The project was supported by the National Key R&D Plan (No. 2022YFF0606702), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 22174133, 12274386, 51832005, 62075203, and 1210042018), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LGF21F050002), the Preeminence Youth Science Funds of Zhejiang Province (No.LR19F050001), and the Key R&D Plan of Zhejiang Province (Nos. 2022C01127 and 2021C05005). Also, the work was greatly supported by NMPA Key Laboratory for POCT Technology Transforming and Quality Control.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This research did not involve human or animal samples.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Zhang, D., Wang, P. et al. Development of a SERS aptasensor for the determination of L-theanine using a noble metal nanoparticle-magnetic nanospheres composite. Microchim Acta 191, 158 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06245-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06245-z