Abstract
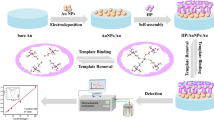
A magnetic fluorescent molecularly imprinted sensor was successfully prepared and implemented to determine catechol (CT). Fe3O4 nanoparticles were synthesized by the solvothermal technique and mesoporous Fe3O4@SiO2@mSiO2 imprinted carriers were prepared by coating nonporous and mesoporous SiO2 shells on the surface of the Fe3O4 subsequently. The magnetic surface molecularly imprinted fluorescent sensor was created after the magnetic mesoporous carriers were modified with γ-methacryloxyl propyl trimethoxy silane to introduce double bonds on the surface of the carries and the polymerization was carried out in the presence of CT and fluorescent monomers. The magnetic mesoporous carriers were modified with γ-methacryloxyl propyl trimethoxy silane and double bonds were introduced on the surface of the carriers. After CT binding with the molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs), the fluorescent intensity of the molecularly imprinted polymers (Ex = 400 nm, Em = 523 nm) increased significantly. The fluorescent intensity ratio (F/F0) of the sensor demonstrated a favorable linear correlation with the concentration of CT between 5 and 50 μM with a detection limit of 0.025 μM. Furthermore, the sensor was successfully applied to determine CT in actual samples with recoveries of 96.4–105% and relative standard deviations were lower than 3.5%. The results indicated that the research of our present work provided an efficient approach for swiftly and accurately determining organic pollutant in water.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from thecorresponding author upon request.
References
IndrajithNaik E, Sunil Kumar Naik TS, Pradeepa E, Singh S, Naik HSB (2022) Design and fabrication of an innovative electrochemical sensor based on Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles for the detection of toxic catechol. Mater Chem Phys 281:125860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.125860
Wang J, Yang J, Xu P, Liu H, Zhang L, Zhang S, Tian L (2020) Gold nanoparticles decorated biochar modified electrode for the high-performance simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and catechol. Sens Actuators B Chem 306:127590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127590
Lu Z, Wei K, Ma H, Duan R, Sun M, Zou P, Yin J, Wang X, Wang Y, Wu C, Su G, Wu M, Zhou X, Ye J, Rao H (2023) Bimetallic MOF synergy molecularly imprinted ratiometric electrochemical sensor based on MXene decorated with polythionine for ultra-sensitive sensing of catechol. Anal Chim Acta 1251:340983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2023.340983
Huang SZ, Tang Q, Wei KN, Yang RP, Tao Z, Huang Y, Xiao X (2022) A colorimetric supramolecular sensor array based on charge-transfer complexes for multiplex aniline and phenolic pollutants detection. Anal Chim Acta 1233:340504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2022.340504
Moldoveanu SC, Kiser M (2007) Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry versus liquid chromatography/fluorescence detection in the analysis of phenols in mainstream cigarette smoke. J Chromatogr A 1141:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.11.100
Ye Q, Yan F, Kong D, Zhang J, Zhou X, Xu J, Chen L (2017) Constructing a fluorescent probe for specific detection of catechol based on 4-carboxyphenylboronic acid-functionalized carbon dots. Sens Actuators B Chem 250:712–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.03.081
Wang YQ, Fang Z, Min H, Xu XY, Li Y (2022) Sensitive determination of ofloxacin by molecularly imprinted polymers containing ionic liquid functionalized carbon quantum dots and europium ion. ACS Appl Nano Mater 5:8467–8474. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.2c01583
Yang Y, Liu X, Meng S, Mao S, Tao W, Li Z (2023) Molecularly imprinted polymers-isolated AuNP-enhanced CdTe QD fluorescence sensor for selective and sensitive oxytetracycline detection in real water samples. J Hazard Mater 458:131941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131941
Kang F, Yang W, Guo M, Pedersen LB, Nielsen LP (2023) Highly selective microsensor for monitoring trace phosphine in the environment. Anal Chem 95:2460–2468. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c04652
Duo Y, Xiang Z, Gao G, Luo G, Tang BZ (2023) Biomedical application of aggregation-induced emission luminogen-based fluorescent sensors. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 167:117252. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.13218
Li H, Sheng W, Haruna SA, Hassan MM, Chen Q (2023) Recent advances in rare earth ion-doped upconversion nanomaterials: from design to their applications in food safety analysis. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 22:3732–3764. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.13218
Wei X, Zhang S, Wang T, Chen A, Guo J, Bai B, Yang S, Li Y, Wang X, Liu X (2022) Molecularly imprinted CsPbBr3 quantum dot-based fluorescent sensor for trace tetracycline detection in aqueous environments. J Mater Chem C 10:8432–8440. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2TC00558A
Aznar-Gadea E, Sanchez-Alarcon I, Soosaimanickam A, Rodriguez-Canto PJ, Perez-Pla F, Martínez-Pastor JP, Abargues R (2022) Molecularly imprinted nanocomposites of CsPbBr3 nanocrystals: an approach towards fast and selective gas sensing of explosive taggants. J Mater Chem C 10:1754–1766. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1TC05169E
Belbruno JJ (2019) Molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem Rev 119:94–119. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00171
Cao Y, Feng T, Xu J, Xue C (2019) Recent advances of molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensors in the detection of food safety hazard factors. Biosens Bioelectron 141:111447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111447
Zhou H, Liu R, Chen Q, Zheng X, Qiu J, Ding T, He L (2022) Surface molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for the determination of vancomycin and norvancomycin in milk by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 369:130886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130886
Song Z, Li J, Lu W, Li B, Yang G, Bi Y, Arabi M, Wang X, Ma J, Chen L (2022) Molecularly imprinted polymers based materials and their applications in chromatographic and electrophoretic separations. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 146:116504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2021.116504
Wang J, Feng J, Wei C (2023) Molecularly imprinted polyaniline immobilized on Fe3O4/ZnO composite for selective degradation of amoxycillin under visible light irradiation. Appl Surf Sci 609:155324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155324
Wang Y, Zhao W, Gao R, Hussain S, Hao Y, Tian J, Chen S, Feng Y, Zhao Y, Qu Y (2022) Preparation of lightweight daisy-like magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers via etching synergized template immobilization for enhanced rapid detection of trace 17β-estradiol. J Hazard Mater 424:127216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127216
Shao Y, Wang P, Zheng R, Zhao Z, An J, Hao C, Kang M (2023) Preparation of molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescence sensor for visual detection of tetrabromobisphenol A in water samples. Microchim Acta 190:161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05745-8
Huang Y, Sun X, Yang J, Cao Z, Wang R, Li L, Ding Y (2023) A molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor with dual functional monomers for selective determination of gatifloxacin. Microchim Acta 190:261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05839-3
Chen L, Wang X, Lu W, Wu X, Li J (2016) Molecular imprinting: perspectives and applications. Chem Soc Rev 45:2137–2211. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CS00061D
Cao Y, Huang Z, Luo L, Li J, Li P, Liu X (2021) Rapid and selective extraction of norfloxacin from milk using magnetic molecular imprinting polymers nanoparticles. Food Chem 353:129464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129464
Zhang G, Ali MM, Feng X, Zhou J, Hu L (2021) Mesoporous molecularly imprinted materials: from preparation to biorecognition and analysis. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 144:116426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2021.116426
Xie L, Guo J, Zhang Y, Hu Y, You Q, Shi S (2015) Novel molecular imprinted polymers over magnetic mesoporous silica microspheres for selective and efficient determination of protocatechuic acid in Syzygium aromaticum. Food Chem 178:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.01.069
Luo S, Sun X, Zhang L, Miao Y, Yan G (2024) Preparation of room-temperature phosphorescence-ratiometric fluorescence magnetic mesoporous imprinted microspheres and its application in detection of malachite green and tartrazine in multimatrix. Food Chem 430:137096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137096
Yang J, Chen S, Zhang B, Tu Q, Wang J, Yuan M (2022) Non-biological fluorescent chemosensors for pesticides detection. Talanta 240:123200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.123200
Zhang F, Chen F, Shen R, Chen YX, Zhao Z, Zhang B, Fang J (2023) Naphthalimide fluorescent skeleton for facile and accurate quantification of glutathione. Anal Chem 95:4301–4309. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c04098
Mendes Alvarenga L, dos Reis Feliciano C, Giordano Alvarenga B, Maximiler Campos De Paula H, Luiza Coelho Y, Henrique Mendes Da Silva L, Fernando Gorup L, Gonçalves Santos M, Sindra Virtuoso L (2023) Preparation of a composite sensor based on a fluorescent and magnetic molecular imprint polymer for metronidazole extraction–detection. J Mol Liq 390:123027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2023.123027
Zhu W, Zhou Y, Liu S, Luo M, Du J, Fan J, Xiong H, Peng H (2021) A novel magnetic fluorescent molecularly imprinted sensor for highly selective and sensitive detection of 4-nitrophenol in food samples through a dual-recognition mechanism. Food Chem 348:129126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129126
Nadali A, Leili M, Afkhami A, Bahrami A, Karami M (2021) Synthesize and application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers (mag-MIPs) to extract 1-Aminopyrene from the human urine sample. J Environ Chem Eng 9:106253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106253
Shao Y, Zhu Y, Zheng R, Wang P, Zhao Z, An J (2022) Highly sensitive and selective surface molecularly imprinted polymer electrochemical sensor prepared by Au and MXene modified glassy carbon electrode for efficient detection of tetrabromobisphenol A in water. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:3104–3116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00562-8
Gauci G, Magri DC (2022) Solvent-polarity reconfigurable fluorescent 4-piperazino-N-aryl-1,8-naphthalimide crown ether logic gates. RSC Adv 12:35270–35278. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra07568g
Liu Y, Tan L, Wang K, Wang J (2022) Molecularly imprinted probe based on CdTe QDs and magnetic nanoparticles for selective recognition of malachite green in seawater and its sensing mechanisms. Microchim Acta 190:8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05579-w
Zhao M, Wang J, Lian Z (2021) Fluorescence assay of oxytetracycline in seawater after selective capture using magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Mar Pollut Bull 163:111962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111962
Wang W, Xu Y, Liu X, Peng L, Huang T, Yan Y, Li C (2020) Efficient fabrication of ratiometric fluorescence imprinting sensors based on organic-inorganic composite materials and highly sensitive detection of oxytetracycline in milk. Microchem J 157:105053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105053
Li H, Jiang J, Wang Z, Wang X, Liu X, Yan Y, Li C (2017) A high performance and highly-controllable core-shell imprinted sensor based on the surface-enhanced Raman scattering for detection of R6G in water. J Colloid Interface Sci 501:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.04.010
Toudeshki RM, Dadfarnia S, Haji Shabani AM (2019) Surface molecularly imprinted polymer on magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes for selective recognition and preconcentration of metformin in biological fluids prior to its sensitive chemiluminescence determination: central composite design optimization. Anal Chim Acta 1089:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.08.070
Liu J, Che R, Chen H, Zhang F, Xia F, Wu Q, Wang M (2012) Microwave absorption enhancement of multifunctional composite microspheres with spinel Fe3O4 cores and anatase TiO2 shells. Small 8:1214–1221. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201102245
Choi H, Um K, Im M, Lee K (2015) A simple method for nanostructure engineering of mesoporous zinc silicate particles. Chem Mater 27:2343–2349. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm503768j
Limaee NY, Rouhani S, Olya ME, Najafi F (2020) Selective recognition of herbicides in water using a fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymer sensor. J Fluoresc 30:375–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-020-02508-z
Wang L, Wen L, Zhao L, Chao J, Tao F, Wang F, Li C (2022) Development of fluorescence sensor and test paper based on molecularly imprinted carbon quantum dots for spiked detection of domoic acid in shellfish and lake water. Anal Chim Acta 1197:339515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2022.339515
Xu Y, Huang T, Wang S, Meng M, Yan Y (2022) SiO2-coated molecularly imprinted sensor based on Si quantum dots for selective detection of catechol in river water. J Environ Chem Eng 10:106850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106850
Huang T, Xu Y, Meng M, Li C (2022) PVDF-based molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescent test paper with improved visualization effect for catechol monitoring. Microchem J 178:107369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2022.107369
Rao H, Liu X, Ding F, Wan Y, Zhao X, Liang R, Zou P, Wang Y, Wang X, Zhao Q (2018) Nitrogen-doped carbon nanosheet frameworks decorated with Fe and molecularly imprinted polymer for simultaneous detection of mebendazole and catechol. Chem Eng J 338:478–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.064
Wang H, Hu Q, Meng Y, Jin Z, Fang Z, Fu Q, Gao W, Xu L, Song Y, Lu F (2018) Efficient detection of hazardous catechol and hydroquinone with MOF-rGO modified carbon paste electrode. J Hazard Mater 353:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.02.029
Yang Q, Li J, Wang X, Peng H, Xiong H, Chen L (2019) Dual-emission color-controllable nanoparticle based molecular imprinting ratiometric fluorescence sensor for the visual detection of Brilliant Blue. Sens Actuators B Chem 284:428–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.12.134
Wang X, Yu J, Wu X, Fu J, Kang Q, Shen D, Li J, Chen L (2016) A molecular imprinting-based turn-on Ratiometric fluorescence sensor for highly selective and sensitive detection of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). Biosens Bioelectron 81:438–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.03.031
Funding
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (Program No. 21806097, 22005234), the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (2024JC-YBMS-109), the Shaanxi Provincial Education Department’s Scientific Research Program Funded (Program No. 18JK0104), and the Research Starting Foundation of Shaanxi University of Science and Technology (Program No. 2016BJ-80) are all to be thanked for their support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yanming Shao: conceptualization; investigation; methodology; data curation; writing—original draft; writing—review and editing. Zhizhen Zhao: investigation; methodology; formal analysis; data curation; validation; writing—original draft; writing—review and editing. Jun An: methodology; formal analysis. Caifeng Hao: investigation; data curation. Mengyi Kang: resources; validation. Xuan Rong: data curation. Huanhuan Zhao: validation. Huanran Feng: supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Y., Zhao, Z., An, J. et al. Preparation of surface molecular imprinting fluorescent sensor based on magnetic porous silica for sensitive and selective determination of catechol. Microchim Acta 191, 156 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06244-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06244-0