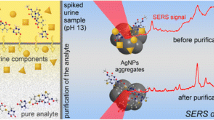
Abstract
A high-throughput surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-sensing platform is presented for FNT detection in human urine without any sample preparation. The sensing platform is based on plasmonics-active silver-coated sharply branched gold nanostars (SGNS). The effect of silver thickness was investigated experimentally and theoretically, and the results indicated that SERS enhancement was maximum at an optimum silver thickness of 45 nm on the sharply spiked SGNS. The proposed high-throughput SERS platform exhibited ultrahigh sensitivity and excellent enhancement uniformity for a model analyte, i.e., crystal violet. Moreover, the SERS-sensing platform demonstrated good sensitivity of FNT spiked in human urine samples with two differential linear response ranges of 2 to 0.2 µg/mL and 0.1 µg/mL to 100 pg/mL, respectively, with a detection limit as low as 10.02 pg/mL. The spiked human urine samples show satisfactory recovery values from 92.5 to 102% with relative standard deviations (RSD) of less than 10%. In summary, the high-throughput performance of the proposed microplate-based SERS platform demonstrated great potential for rapid low-cost SERS-based sensing applications.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peng PW, Sandler AN (1999) A review of the use of fentanyl analgesia in the management of acute pain in adults. J Am Soc Anesthesiologists 90(2):576–599
Stanley TH (2014) The fentanyl story. J Pain 15(12):1215–1226
Suzuki J, El-Haddad S (2017) A review: fentanyl and non-pharmaceutical fentanyls. Drug Alcohol Depend 171:107–116
N.C.f.I.P.a.C. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Overdose deaths in 2021 increased half as much as in 2020 – but are still up 15% 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/pressroom/nchs_press_releases/2022/202205.htm. (Accessed May 11, 2022.
Gilbert N, Antonides LH, Schofield CJ, Costello A, Kilkelly B, Cain AR, Dalziel PRV, Horner K, Mewis RE, Sutcliffe OB (2020) Hitting the jackpot – development of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) and other rapid screening methods for the analysis of 18 fentanyl-derived synthetic opioids. Drug Test Anal 12(6):798–811
Poklis J, Poklis A, Wolf C, Mainland M, Hair L, Devers K, Chrostowski L, Arbefeville E, Merves M, Pearson J (2015) Postmortem tissue distribution of acetyl fentanyl, fentanyl and their respective nor-metabolites analyzed by ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci Int 257:435–441
Abbott DL, Limoges JF, Virkler KJ, Tracy SJ, Sarris GG (2022) ELISA screens for fentanyl in urine are susceptible to false-positives in high concentration methamphetamine samples. J Anal Toxicol 46(4):457–459
Langer J, Jimenez de Aberasturi D, Aizpurua J, Alvarez-Puebla RA, Auguié B, Baumberg JJ, Bazan GC, Bell SEJ, Boisen A, Brolo AG, Choo J, Cialla-May D, Deckert V, Fabris L, Faulds K, García de Abajo FJ, Goodacre R, Graham D, Haes AJ, Haynes CL, Huck C, Itoh T, Käll M, Kneipp J, Kotov NA, Kuang H, Le Ru EC, Lee HK, Li J-F, Ling XY, Maier SA, Mayerhöfer T, Moskovits M, Murakoshi K, Nam J-M, Nie S, Ozaki Y, Pastoriza-Santos I, Perez-Juste J, Popp J, Pucci A, Reich S, Ren B, Schatz GC, Shegai T, Schlücker S, Tay L-L, Thomas KG, Tian Z-Q, Van Duyne RP, Vo-Dinh T, Wang Y, Willets KA, Xu C, Xu H, Xu Y, Yamamoto YS, Zhao B, Liz-Marzán LM (2020) Present and future of surface-enhanced raman scattering. ACS Nano 14(1):28–117
Markina NE, Goryacheva IY, Markin AV (2022) Surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy for the determination of medical and narcotic drugs in human biofluids. J Anal Chem 77(8):930–947
Markina NE, Markin AV, Cialla-May D (2023) Cyclodextrin-assisted SERS determination of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in urine and blood plasma. Talanta 254:124083
Markina NE, Ustinov SN, Zakharevich AM, Markin AV (2020) Copper nanoparticles for SERS-based determination of some cephalosporin antibiotics in spiked human urine. Anal Chim Acta 1138:9–17
Vo-Dinh T (1998) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy using metallic nanostructures1 The submitted manuscript has been authored by a contractor of the U.S Government under contract No. DE-AC05-96OR22464. Accordingly, the U.S. Government retains a nonexclusive, royalty-free license to publish or reproduce the published form of this contribution, or allow others to do so, for U.S. Government purposes.1. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 17(8):557–582
Yan F, Wabuyele MB, Griffin GD, Vass AA, Tuan V-D (2005) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of chemical and biological agent simulants. IEEE Sens J 5(4):665–670
Zhang M, Pan J, Xu X, Fu G, Zhang L, Sun P, Yan X, Liu F, Wang C, Liu X, Lu G (2022) Gold-trisoctahedra-coated capillary-based SERS platform for microsampling and sensitive detection of trace fentanyl. Anal Chem 94(11):4850–4858
Masterson AN, Hati S, Ren G, Liyanage T, Manicke NE, Goodpaster JV, Sardar R (2021) Enhancing nonfouling and sensitivity of surface-enhanced raman scattering substrates for potent drug analysis in blood plasma via fabrication of a flexible plasmonic patch. Anal Chem 93(4):2578–2588
Yu WW, White IM (2013) Inkjet-printed paper-based SERS dipsticks and swabs for trace chemical detection. Analyst 138(4):1020–1025
Turzhitsky V, Zhang L, Horowitz GL, Vitkin E, Khan U, Zakharov Y, Qiu L, Itzkan I, Perelman LT (2018) Picoanalysis of drugs in biofluids with quantitative label-free surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Small 14(47):1802392
Yu F, Su M, Tian L, Wang H, Liu H (2018) Organic solvent as internal standards for quantitative and high-throughput liquid interfacial SERS analysis in complex media. Anal Chem 90(8):5232–5238
Bell SEJ, Sirimuthu NMS (2008) Quantitative surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem Soc Rev 37(5):1012–1024
Andreou C, Hoonejani MR, Barmi MR, Moskovits M, Meinhart CD (2013) Rapid detection of drugs of abuse in saliva using surface enhanced raman spectroscopy and microfluidics. ACS Nano 7(8):7157–7164
Jaworska A, Fornasaro S, Sergo V, Bonifacio A (2016) Potential of surface enhanced raman spectroscopy (SERS) in therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM). A critical review. Biosensors 6(3):47
Atta S, Tsoulos TV, Fabris L (2016) Shaping gold nanostar electric fields for surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy enhancement via silica coating and selective etching. J Phys Chem C 120(37):20749–20758
Atta S, Vo-Dinh T (2022) Bimetallic gold nanostars having high aspect ratio spikes for sensitive surface-enhanced raman scattering sensing. ACS Appl Nano Mater 5(9):12562–12570
Daimon M, Masumura A (2007) Measurement of the refractive index of distilled water from the near-infrared region to the ultraviolet region. Appl Opt 46(18):3811–3820
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6(12):4370–4379
Ma J, Liu X, Wang R, Zhang J, Jiang P, Wang Y, Tu G (2020) Bimetallic core–shell nanostars with tunable surface plasmon resonance for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. ACS Appl Nano Mater 3(11):10885–10894
Borah R, Verbruggen SW (2020) Silver–gold bimetallic alloy versus core–shell nanoparticles: implications for plasmonic enhancement and photothermal applications. J Phys Chem C 124(22):12081–12094
Fales AM, Yuan H, Vo-Dinh T (2014) Development of hybrid silver-coated gold nanostars for nonaggregated surface-enhanced raman scattering. J Phys Chem C 118(7):3708–3715
Li J-J, Wu C, Zhao J, Weng G-J, Zhu J, Zhao J-W (2018) Synthesis and SERS activity of super-multibranched AuAg nanostructure via silver coating-induced aggregation of nanostars. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 204:380–387
Zhu J, Chen X-H, Li J-J, Zhao J-W (2019) The synthesis of Ag-coated tetrapod gold nanostars and the improvement of surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 211:154–165
Atta S, Beetz M, Fabris L (2019) Understanding the role of AgNO3 concentration and seed morphology in the achievement of tunable shape control in gold nanostars. Nanoscale 11(6):2946–2958
Theodorou IG, Jawad ZAR, Jiang Q, Aboagye EO, Porter AE, Ryan MP, Xie F (2017) Gold nanostar substrates for metal-enhanced fluorescence through the first and second near-infrared windows. Chem Mater 29(16):6916–6926
Meng W, Hu F, Zhang L-Y, Jiang X-H, Lu L-D, Wang X (2013) SERS and DFT study of crystal violet. J Mol Struct 1035:326–331
Pan X, Li L, Lin H, Tan J, Wang H, Liao M, Chen C, Shan B, Chen Y, Li M (2019) A graphene oxide-gold nanostar hybrid based-paper biosensor for label-free SERS detection of serum bilirubin for diagnosis of jaundice. Biosens Bioelectron 145:111713
Su X, Liu X, Xie Y, Chen M, Zhong H, Li M (2023) Quantitative label-free SERS detection of trace fentanyl in biofluids with a freestanding hydrophobic plasmonic paper biosensor. Anal Chem 95(7):3821–3829
Shende C, Farquharson A, Brouillette C, Smith W, Farquharson S (2019) Quantitative measurements of codeine and fentanyl on a surface-enhanced Raman-active pad test. Molecules 24(14):2578
Huang Z, Feng S, Guan Q, Lin T, Zhao J, Nguan CYC, Zeng H, Harriman D, Li H, Du C (2021) Correlation of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic fingerprints of kidney transplant recipient urine with kidney function parameters. Sci Rep 11(1):2463
Zhang Y, Halifax JC, Tangsombatvisit C, Yun C, Pang S, Hooshfar S, Wu AHB, Lynch KL (2022) Development and application of a high-resolution mass spectrometry method for the detection of fentanyl analogs in urine and serum. J Mass Spectrom Adv Clin Lab 26:1–6
Funding
This work is funded by the National Institutes of Health (R01GM135486) and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (INV-040790).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Atta, S., Canning, A.J. & Vo-Dinh, T. Rapid SERS assay for determination of the opioid fentanyl using silver-coated sharply branched gold nanostars. Microchim Acta 191, 110 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06172-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06172-5