Abstract
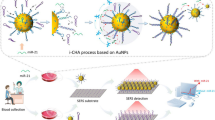
Based on Au nano-cone array (Au-NCA) and a three-segment hybridization strategy, a novel SERS biosensor is proposed for the ultrasensitive detection of the microRNA miR-21. The uniform, stable, and reproducible Au-NCA was prepared by the single-layer colloidal ball template method. Subsequently, the target was hybridized with sequence 2. The resulting target-sequence 2 complex was then hybridized with sequence 1 anchored on Au-NCA. Thus, a three-segment sequence complex was formed. SERS measurements can be performed without the need for complex purification and amplification steps. Due to the ability of miR-21 to perform specific complementary hybridization with two sequences, SERS biosensors have superior specificity for miR-21 without interference from other miRNAs. Under the optimal conditions, the SERS biosensor was applied and the limit of detection (LOD) was as low as 3.02 aM. This method has been successfully used to the detection of miR-21 in the serum of lymphoma patients and healthy volunteers. The results are consistent with the traditional test methods. Therefore, this novel SERS biosensor shows excellent clinical translational potential in the detection of lymphoma.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xiong X, Xie X, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Wang L (2022) Tumor-associated macrophages in lymphoma: from mechanisms to therapy. Int Immunopharmacol 112:109235
Vega F, Miranda RN, Medeiros LJ (2020) KSHV/HHV8-positive large B-cell lymphomas and associated diseases: a heterogeneous group of lymphoproliferative processes with significant clinicopathological overlap. Modern Pathol 33:18–28
Tsuji T, Satoh K, Nakano H, Nishide Y, Uemura Y, Tanaka S, Kogo M (2015) Predictors of the necessity for lymph node biopsy of cervical lymphadenopathy. J Cranio Maxill Surg 43:2200–2204
Sin KM, Ho SKD, Wong BYK, Gill H, Khong P-L, Lee EYP (2017) Beyond the lymph nodes: FDG-PET/CT in primary extranodal lymphoma. Clin Imag 42:25–33
Regazzo G, Marchesi F, Spagnuolo M, Díaz Méndez AB, Masi S, Mengarelli A, Rizzo MG (2021) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: time to focus on circulating blood nucleic acids? Blood Rev 47:100776
Ouyang J, Zhan X, Guo S, Cai S, Lei J, Zeng S, Yu L (2020) Progress and trends on the analysis of nucleic acid and its modification. J Pharmaceut Biomed 191:113589
Song C, Chen W, Kuang J, Yao Y, Tang S, Zhao Z, Guo X, Shen W, Lee HK (2021) Recent advances in the detection of multiple microRNAs. Trac-Trend Anal Chem 139:116269
Zhang D, Bian F, Cai L, Wang T, Kong T, Zhao Y (2019) Bioinspired photonic barcodes for multiplexed target cycling and hybridization chain reaction. Biosens Bioelectron 143:111629
Fuertes T, Ramiro AR, de Yebenes VG (2020) miRNA-based therapies in B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Trends Immunol 41:932–947
Estephan R, Kil SH, Rosen ST, Querfeld C (2018) PD-L1 expression is regulated by microRNAs-21 and -130 in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Blood 132:4108
Gohar SF, Kamal Eldin S, El-Bassal F, Shehata A, Azzam A, Tawfik E, Al Hassanin SA (2018) 1032P—the impact of serum microRNA-21 on outcome of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. Ann Oncol 29:viii367
Ma Y, Suolitiken D, Chen B, Xu X, Kang H, Zhiguang L (2020) Circulating microRNAs is a potential prognostic biomarker in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Blood 136:40–41
Rahouma M, Rashed RA, Asker HA, Abdel-Azim LR, Naguib E, Khaled H (2019) 1074PD - Prognostic value of microRNA-21/ Ki-67 in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: NCI experience. Ann Oncol 30:v437
Vitek P, Krsmanovic P, Mocikova H, Chramostova K, Pytlík R, Stopka T, Trněný M (2022) 3218 – Circulating microRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma: sensitive tool for detection of secondary CNS involvement, monitoring of therapy and prediction of CNS relapse in aggressive B-NHL lymphomas. Exp Hematol 111:S153–S154
Gines G, Menezes R, Xiao W, Rondelez Y, Taly V (2020) Emerging isothermal amplification technologies for microRNA biosensing: applications to liquid biopsies. Mol Aspects Med 72:100832
Li M, Liu Z, Liu Y, Luo H, Huang K-J, Tan X (2023) Capacitor-parallel-amplified decoupled photoelectrochemical/electrochromic dual-mode bioassay for sensitive detection of microRNA with high reliability. Biosens Bioelectron 232:115310
Zayani R, Rabti A, Ben Aoun S, Raouafi N (2021) Fluorescent and electrochemical bimodal bioplatform for femtomolar detection of microRNAs in blood sera. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 327:128950
Yue S, Fang J, Xu Z (2022) Advances in droplet microfluidics for SERS and Raman analysis. Biosens Bioelectron 198:113822
Zhang M-z, Zhou Z-m, Xu J, Wang W-l, Pu S-h, Hu W-y, Luo P, Tian Z-q, Gong Z-b, Liu G-k (2022) Qualitative analysis of trace quinolone antibiotics by SERS with fine structure dependent sensitivity. Spectrochim Acta A 278:121365
Zhu J, Agyekum AA, Kutsanedzie FYH, Li H, Chen Q, Ouyang Q, Jiang H (2018) Qualitative and quantitative analysis of chlorpyrifos residues in tea by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) combined with chemometric models. LWT 97:760–769
Khulbe KC, Matsuura T (2000) Characterization of synthetic membranes by Raman spectroscopy, electron spin resonance, and atomic force microscopy; a review. Polymer 41:1917–1935
Qu C, Li Y, Du S, Geng Y, Su M, Liu H (2022) Raman spectroscopy for rapid fingerprint analysis of meat quality and security: principles, progress and prospects. Food Res Int 161:111805
Mandal P, Tewari BS (2022) Progress in surface enhanced Raman scattering molecular sensing: a review. Surf Interfaces 28:101655
Chen M, Huang Y, Miao J, Fan Y, Lai K (2023) A highly sensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering sensor with MIL-100(Fe)/Au composites for detection of malachite green in fish pond water. Spectrochim Acta A 292:122432
Neng J, Wang J, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Chen P (2023) Trace analysis of food by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy combined with molecular imprinting technology: principle, application, challenges, and prospects. Food Chem 429:136883
Guo M, Li M, Fu H, Zhang Y, Chen T, Tang H, Zhang T, Li H (2023) Quantitative analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) combined with Random Forest. Spectrochim Acta A 287:122057
Cai J, Liu R, Jia S, Feng Z, Lin L, Zheng Z, Wu S, Wang Z (2021) SERS hotspots distribution of the highly ordered noble metal arrays on flexible substrates. Opt Mater 122:111779
Nie B, Luo Y, Shi J, Gao L, Duan G (2019) Bowl-like Pore array made of hollow Au/Ag alloy nanoparticles for SERS detection of melamine in solid milk powder. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 301:127087
Gu X, Tian S, Chen Y, Wang Y, Gu D, Guo E, Liu Y, Li J, Deng A (2021) A SERS-based competitive immunoassay using highly ordered gold cavity arrays as the substrate for simultaneous detection of β-adrenergic agonists. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 345:130230
Lu Y, Zhan C, Yu L, Yu Y, Jia H, Chen X, Zhang D, Gao R (2023) Multifunctional nanocone array as solid immunoassay plate and SERS substrate for the early diagnosis of prostate cancer on microfluidic chip. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 376:133046
Ge S, Chen G, Cao D, Lin H, Liu Z, Yu M, Wang S, Wang Z, Zhou M (2023) Au/SiNCA-based SERS analysis coupled with machine learning for the early-stage diagnosis of cisplatin-induced liver injury. Anal Chim Acta 1254:341113
Xu W, Bao H, Zhang H, Fu H, Zhao Q, Li Y, Cai W (2021) Ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection of gaseous sulfur-mustard simulant based on thin oxide-coated gold nanocone arrays. J Hazard Mater 420:126668
Cheson BD (2018) PET/CT in lymphoma: current overview and future directions. Semin Nucl Med 48:76–81
Laane E, Tani E, Björklund E, Elmberger G, Everaus H, Skoog L, Porwit-MacDonald A (2010) Flow cytometric immunophenotyping including Bcl-2 detection on fine needle aspirates in the diagnosis of reactive lymphadenopathy and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Cytom Part B-Clin Cy 64B:34–42
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Jiangsu Graduate Scientific Research Innovation Program (No. SJCX22_1813) and Chinese and Western Medicine Cooperation Project of Subei People’s Hospital (No. ZXXTGG2022BO3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 162 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, M., Gao, J., Chen, Z. et al. Au nano-cone array for SERS detection of associated miRNA in lymphoma patients. Microchim Acta 191, 40 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06095-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06095-1