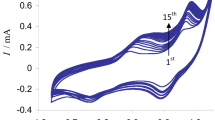
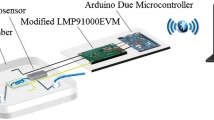
Abstract
Microliter volume pH determination is of great importance in the biomedical and industrial applications. The current available pH meter and measurement techniques are hard to reach the high demand of microliter volume pH determination in a repeatable, stable, and sensitivity manner. This work aims to fill the gap of microliter volume pH measurements while maintaining good sensing performance. The electrodeposited iridium oxide and cobalt hydroxide along with gold electrode served as working, counter, and reference electrode, respectively, for 10–12 μL volume pH measurements with Nernst constant of 55.9 ± 4.4 mV/pH. The electrodeposited thin film was further characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), Raman spectrometry, etc. to confirm its morphology and composition. The constructed pH sensor was used for human serum sample measurements to confirm the suitability of future applications. The results show that it has only 0.80% variation compared to a commercial pH meter with a limit of detection (LOD, or resolution) of ± 0.01 pH. It holds a great potential to be used in the future for microliter volume in situ pH measurements.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data are available upon requests to the corresponding author.
References
Lee KJ, Capon PK, Ebendorff-Heidepriem H, Keenan E, Brownfoot F, Schartner EP (2023) Influence of the photopolymerization matrix on the indicator response of optical fiber pH sensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 376:132999
Belotti Y, Jokhun D, Ponnambalam J, Valerio V, Lim C (2021) Machine learning based approach to pH imaging and classification of single cancer cells. APL Bioeng 5:016105
Jo A, Green A, Medina JE, Iyer S, Ohman AW, McCarthy ET, Reinhardt F, Gerton T, Demehin D, Mishra R, Kolin DL, Zheng H, Crum CP, Weinberg RA, Rueda BR, Castro CM, Dinulescu DM, Lee H (2023) Profiling extracellular vesicles in circulation enables the early detection of ovarian cancer. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.19.524549
Ges IA, Ivanov BL, Schaffer DK, Lima EA, Werdich AA, Baudenbacher FJ (2005) Thin-film IrOx pH microelectrode for microfluidic-based microsystems. Biosens Bioelectron 21:248–256
Moradi V, Akbari M, Wild P (2019) A fluorescence-based pH sensor with microfluidic mixing and fiber optic detection for wide range pH measurements. Sensors Actuators A Phys 297:111507
Kinoshita K, Madou M (1984) Electrochemical measurements on Pt, Ir, and Ti oxides as pH probes. J Electroche Soc 131:1089
Madou M, Kinoshita K (1984) Electrochemical measurements on metal oxide electrodes—I. Zirconium dioxide. Electrochim Acta 29:411–417
Yao S, Wang M, Madou M (2001) A pH electrode based on melt-oxidized iridium oxide. J Electrochem Soc 148:H29
Lu Y, Wang T, Cai Z, Cao Y, Yang H, Duan YY (2009) Anodically electrodeposited iridium oxide films microelectrodes for neural microstimulation and recording. Sensors Actuators B Chem 137:334–339
Lima AC, Jesus AA, Tenan MA, de Souza Silva AF, Oliveira AF (2005) Evaluation of a high sensitivity PbO2 pH-sensor. Talanta 66:225–228
Cheng Y, Xiong P, Yun CS, Strouse G, Zheng J, Yang R, Wang Z (2008) Mechanism and optimization of pH sensing using SnO2 nanobelt field effect transistors. Nano Lett 8:4179–4184
Fog A, Buck RP (1984) Electronic semiconducting oxides as pH sensors. Sensors Actuators 5:137–146
Katsube T, Lauks I, Zemel J (1981) pH-sensitive sputtered iridium oxide films. Sensors Actuators 2:399–410
Hitchman ML, Ramanathan S (1991) Potentiometric determination of proton activities in solutions containing hydrofluoric acid using thermally oxidized iridium electrodes. Analyst 116:1131–1133
Hendrikse J, Olthuis W, Bergveld P (1998) A method of reducing oxygen induced drift in iridium oxide pH sensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 53:97–103
Kim TY, Yang S (2014) Fabrication method and characterization of electrodeposited and heat-treated iridium oxide films for pH sensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem 196:31–38
Mani GK, Morohoshi M, Yasoda Y, Yokoyama S, Kimura H, Tsuchiya K (2017) ZnO-based microfluidic pH sensor: a versatile approach for quick recognition of circulating tumor cells in blood. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:5193–5203
Wang M, Yao S, Madou M (2002) A long-term stable iridium oxide pH electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 81:313–315
Mailley S, Hyland M, Mailley P, McLaughlin J, McAdams E (2002) Electrochemical and structural characterizations of electrodeposited iridium oxide thin-film electrodes applied to neurostimulating electrical signal. Mater Sci Eng C 21:167–175
Yoshino T, Baba N, Arai K (1987) Electrochromic IrOx thin films formed in sulfatoiridate (III, IV) complex solution by periodic reverse current electrolysis (PRIROF). Jpn J Appl Phys 26:1547
Yamanaka K (1989) Anodically electrodeposited iridium oxide films (AEIROF) from alkaline solutions for electrochromic display devices. Jpn J Appl Phys 28:632
Marzouk SA (2003) Improved electrodeposited iridium oxide pH sensor fabricated on etched titanium substrates. Anal Chem 75:1258–1266
Adeel M, Canzonieri V, Daniele S, Rizzolio F, Rahman MM (2021) Organobase assisted synthesis of Co (OH) 2 nanosheets enriched with oxygen vacancies for nonenzymatic glucose sensing at physiological pH. J Ind Eng Chem 103:165–174
Marzouk SA, Ufer S, Buck RP, Johnson TA, Dunlap LA, Cascio WE (1998) Electrodeposited iridium oxide pH electrode for measurement of extracellular myocardial acidosis during acute ischemia. Anal Chem 70:5054–5061
Chandra D, Sato T, Takeuchi R, Li D, Togashi T, Kurihara M, Saito K, Yui T, Yagi M (2017) Polymer surfactant-assisted tunable nanostructures of amorphous IrOx thin films for efficient electrocatalytic water oxidation. Catal Today 290:51–58
Khalil M, Wang S, Yu J, Lee RL, Liu N (2016) Electrodeposition of iridium oxide nanoparticles for pH sensing electrodes. J Electrochem Soc 163:B485
McNally E, Zhitomirsky I, Wilkinson D (2005) Cathodic electrodeposition of cobalt oxide films using polyelectrolytes. Mater Chem Phys 91:391–398
Serventi A, El Khakani M, Saint-Jacques R, Rickerby D (2001) Highly textured nanostructure of pulsed laser deposited IrO2 thin films as investigated by transmission electron microscopy. J Mater Res 16:2336–2342
Yang J, Liu H, Martens WN, Frost RL (2010) Synthesis and characterization of cobalt hydroxide, cobalt oxyhydroxide, and cobalt oxide nanodiscs. J Phys Chem C 114:111–119
Hüfner S, Wertheim G (1975) Core-line asymmetries in the x-ray-photoemission spectra of metals. Phys Rev B 11:678
Kim K, Sell C, Winograd N, Breiter M (1974) In: Breiter MW (ed) Electrochemical Society Softbound Proceedings Series
Wagner C, Riggs W, Davis L, Moulder J, Muilenberg G (1979) Handbook of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, vol 38. Perkin-Elmer Corp, Eden Prairie, MN
Fuggle JC, Mårtensson N (1980) Core-level binding energies in metals. J Electron Spectrosc Relat Phenom 21:275–281
Smith E, Dent G (2019) Modern Raman spectroscopy: a practical approach. John Wiley & Sons
Dong Q, Song D, Huang Y, Xu Z, Chapman JH, Willis WS, Li B, Lei Y (2018) High-temperature annealing enabled iridium oxide nanofibers for both non-enzymatic glucose and solid-state pH sensing. Electrochim Acta 281:117–126
Pavlovic Z, Ranjan C, van Gastel M, Schlögl R (2017) The active site for the water oxidising anodic iridium oxide probed through in situ Raman spectroscopy. Chem Commun 53:12414–12417
Gao Y, Li H, Yang G (2016) Amorphous Co (OH) 2 nanosheet electrocatalyst and the physical mechanism for its high activity and long-term cycle stability. J Appl Phys 119:034902
Zhang F, Yuan C, Lu X, Zhang L, Che Q, Zhang X (2012) Facile growth of mesoporous Co3O4 nanowire arrays on Ni foam for high performance electrochemical capacitors. J Power Sources 203:250–256
Burke LD, Mulcahy JK, Whelan DP (1984) Preparation of an oxidized iridium electrode and the variation of its potential with pH. J Electroanal Chem Interfacial Electrochem 163:117–128
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the help and discussion regarding the XPS analysis with Dr. Graham Dawson in the Department of Chemistry at Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University.
Funding
This research was supported by Research & Development Fund (Project Number: RDF-21-1-005) under Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QD designed the initial scheme of the experiments and fabricated the microelectrodes in clean room. WX designed the selectivity tests and human serum pH tests. WX carried out the SEM, XRD, Raman spectrometry, and analyzed the data of TEM, SAED, and metal mapping as well as pH sensing measurements. WX wrote the draft of the manuscript, and QD revised it. QD was responsible for the funding acquisition and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The work related to the microfluidic-based electrodeposition, microfabrication processes, and its solid-state pH sensor has been filed with a patent (Patent applicant: Qiuchen Dong, Weiyu Xiao) supported by the Research Development Fund (Project Number: RDF-21-1-005) of Xi’an Jiaotong Liverpool University in the People’s Republic of China with the application number of 202310526544.0, which is pending for approval.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 4.25 mb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, W., Dong, Q. Iridium oxide and cobalt hydroxide microfluidic-based potentiometric pH sensor. Microchim Acta 190, 457 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06035-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06035-z