Abstract
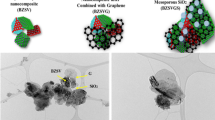
The fabrication of a heteroatom-doped nanocomposite based on cobalt oxide modified sulfur, phosphorus co-doped carbon nitride (Co3O4/SP-CN) with increased active sites is reported. The synthesized nanocomposite offers surprisingly high electrocatalytic oxidation efficacy toward human albumin (HA) despite its agglomeration. This improved efficacy of Co3O4/SP-CN nanocomposite could be attributed to its increased adsorption sites and surface defects, fast charge transportation capability, and conductivity. Additionally, morphological and compositional analysis of the fabricated Co3O4/SP-CN material has been performed through scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photon spectroscopy (XPS), and Raman spectroscopy. The fabricated electrode shows remarkable amperometric response against the HA with a limit of detection of 8.39 nM and linear range of 20–4000 nM at applied potential of 0.25 V versus Ag/AgCl in 0.1 M PBS (pH 8.2). The designed Co3O4/SP-CN electrode has been successfully applied to monitor HA in urine samples of diabetic patient with recovery percentage from 94.1 and 92.1% and with relative standard deviation (RSD) values of 5.8 and 7.8%. According to the best of our knowledge, this is the first report to use a Co3O4/SP-CN–based graphitic pencil (GP) electrode for monitoring of HA for early diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sagoo MK, Gnudi L (2020) Diabetic nephropathy: an overview. Diabetic Nephropathy:3–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9841-8_1
Asad HN, Al-Hakeim HK, Moustafa SR, Maes M (2022) Causal-pathway phenotype of chronic fatigue syndrome due to hemodialysis in patients with end-stage renal disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 22(2):191–206. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527321666220401140747
González-Juanatey JR et al (2022) A cost-effectiveness analysis of patiromer for the treatment of hyperkalemia in chronic kidney disease patients with and without heart failure in Spain. J Med Econ 25(1):640–649. https://doi.org/10.1080/13696998.2022.2074193
Papadopoulou-Marketou N et al (2017) Biomarkers of diabetic nephropathy: a 2017 update. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 54(5):326–342. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408363.2017.1377682
Cortvrindt C et al (2022) Urinary epidermal growth factor: a promising “next generation” biomarker in kidney disease. Am J Nephrol 53(5):372–387. https://doi.org/10.1159/000524586
Zoanni B et al (2021) Novel insights about albumin in cardiovascular diseases: Focus on heart failure. Mass Spectrom Rev 42(4):1113–1128. https://doi.org/10.1002/mas.21743
Eng E, Quaggin S (2022) Putting it all together: practical approach to the patient with diabetic kidney disease, in diabetes and kidney disease. Springer, pp 637–659. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86020-2_29
Rahmani A et al (2022) Clinical efficacy of Persian medicine diet combined with western medicine-based diet on proteinuria in pediatric nephrotic syndrome: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2022:2279209. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2279209
Zhang Y et al (2022) Deep learning-assisted smartphone-based molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence detection sensing platform: portable device and visual monitoring furosemide. Biosens Bioelectron 209:114262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114262
António M et al (2020) A simple aptamer-based colorimetric assay for rapid detection of C-reactive protein using gold nanoparticles. Talanta 214:120868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120868
Komatsu T et al (2014) Multi-spectroscopic analysis of seed quality and 13C-stable-iotopologue monitoring in initial growth metabolism of Jatropha curcas L. Metabolites 4(4):1018–1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4041018
Brinkman JW et al (2004) Which method for quantifying urinary albumin excretion gives what outcome? A comparison of immunonephelometry with HPLC. Kidney Int 66:S69–S75. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.09219.x
Woo J et al (1978) Radioimmunoassay for urinary albumin. Clin Chem 24(9):1464–1467. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/24.9.1464
Hartmann S (2014) Relevance of antibodies targeting the beta1-adrenergic receptor for renal function. Universität Würzburg. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.12997
Yeasmin S et al (2022) Current trends and challenges in point-of-care urinalysis of biomarkers in trace amounts. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 157:116786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2022.116786
Cieplak M et al (2015) Selective electrochemical sensing of human serum albumin by semi-covalent molecular imprinting. Biosens Bioelectron 74:960–966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.07.061
Silah H et al (2021) Modified indium tin oxide electrodes: electrochemical applications in pharmaceutical, biological, environmental and food analysis. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 141:116289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2021.116289
Guo Y, Li J (2020) MoS2 quantum dots: synthesis, properties and biological applications. Mater Sci Eng C 109:110511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110511
Hu C et al (2019) Extraction of the toluene exposure biomarkers hippuric acid and methylhippuric acid using a magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer, and their quantitation by LC-MS/MS. Microchimica Acta 186(3):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3239-6
Kays JC et al (2020) Shell-free copper indium sulfide quantum dots induce toxicity in vitro and in vivo. Nano Lett 20(3):1980–1991. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b05259
Liotta LF et al (2013) Co 3 O 4 nanocrystals and Co 3 O 4–MO x binary oxides for CO, CH 4 and VOC oxidation at low temperatures: a review. Cat Sci Technol 3(12):3085–3102. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00193H
Tonelli D, Scavetta E, Gualandi I (2019) Electrochemical deposition of nanomaterials for electrochemical sensing. Sensors 19(5):1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051186
Gao Y et al (2021) Doping strategy, properties and application of heteroatom-doped ordered mesoporous carbon. RSC Adv 11(10):5361–5383. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA08993A
Hong J et al (2012) Mesoporous carbon nitride with in situ sulfur doping for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from water under visible light. J Mater Chem 22(30):15006–15012. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM32053C
Zhu M et al (2019) Cobalt oxide supported on phosphorus-doped g-C3N4 as an efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Appl Energy Mater 2(7):4718–4729. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.9b00273
Shakeel F et al (2022) Melamine-derived N-rich C-entrapped Au nanoparticles for sensitive and selective monitoring of dopamine in blood samples. RSC Adv 12(40):26390–26399. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA02754B
Djadock CSA et al (2023) Distorted octahedral cobalt (ii)–acylpyrazolone complex with a tunable lattice-strain structure–an efficient electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Catal Sci Technol 13(7):2184–2200. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CY02068H
Barrio J, Volokh M, Shalom M (2020) Polymeric carbon nitrides and related metal-free materials for energy and environmental applications. J Mater Chem A 8(22):11075–11116. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA01973A
Jiang L et al (2017) Doping of graphitic carbon nitride for photocatalysis: a review. Appl Catal Environ 217:388–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.06.003
Hayat K et al (2020) CuO hollow cubic caves wrapped with biogenic N-rich graphitic C for simultaneous monitoring of uric acid and xanthine. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(42):47320–47329. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c15243
Khan F et al (2019) Carbon-dot wrapped ZnO nanoparticle-based photoelectrochemical sensor for selective monitoring of H 2 O 2 released from cancer cells. Microchimica Acta 186:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3227-x
Shenashen MA et al (2016) Mesoscopic fabric sheet racks and blocks as catalysts with efficiently exposed surfaces for methanol and ethanol electrooxidation. Adv Mater Interfaces 3(24):1600743. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201600743
Shoukat N et al (2023) Fabrication of CuO–NiO wrapped cellulose acetate/polyaniline electrospun nanofibers for sensitive monitoring of bisphenol-A. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 11(11):4299–4307. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c04482
Fazal MW et al (2023) Zn and Co loaded porous C decorated electrospun nanofibers as efficient oxygen evolution reaction for water splitting. ACS Appl Energy Mater 6(5):2739–2746. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.2c03439
Abbas Y et al (2020) Heteroatom-doped carbon nanoparticle–ionic liquid composites as electrochemical sensors for uric acid. ACS Appl Nano Mater 3(11):11383–11390. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.0c02466
Shakeel F et al (2023) Bioinspired NC coated BM-ZIF for electrochemical monitoring of adrenaline from blood and pharmaceutical samples. Electroanalysis 35(4):e202200128. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202200128
Wang K et al (2019) Co/Co3O4 nanoparticles coupled with hollow nanoporous carbon polyhedrons for the enhanced electrochemical sensing of acetaminophen. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7(22):18582–18592. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b04813
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through large group Research Project under grant number (RGP2/281/44).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The ethical approval has been taken with details Publi/01/22 (IRB/IRC, Ibn e Sina Research Institute, Multan Medical and Dental College, Multan, Pakistan).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zulfiqar, A., Zafar, F., Yaqub, B. et al. Cobalt oxide modified sulfur and phosphorus Co-doped g-C3N4 for screening of urinary human albumin. Microchim Acta 190, 355 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05936-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05936-3